by Scott Muniz | Aug 20, 2020 | Uncategorized
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
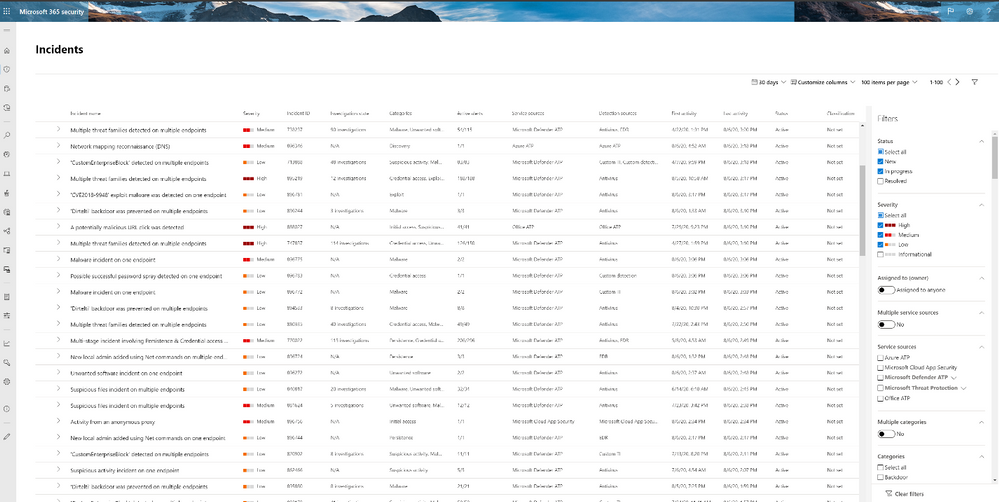
The new incident naming feature in Microsoft Threat Protection now lets you understand an incident’s scope at a glance!
When you are looking at the incident queue and need to determine which incident you should look at next, hints about the content of the incident play an important role in making this choice. Giving incidents automatic names is complex because it encompasses a variety of different suspicious activities.
Our researchers have developed a state-of-the-art algorithm that automatically describes incidents with comprehensive names, leveraging the MITRE ATT&CK® categories we have for each alert. Instead of having numerical incident names like Incident 1234, you now see incident names like Multi-stage incident involving Discovery & Collection reported by multiple sources.

Now, analysts can quickly understand the scope of the incident right from the Microsoft Threat Protection incident queue. Having the incidents name and supporting data (like the number of endpoints affected, users affected, detection sources, categories, and more) in one view, analysts can make faster decisions based on the nature of the incident. This improvement saves analysts time and effort better spent investigating and remediating high-priority threats.
Here are some examples of incident names developed with the new algorithm:
- ‘Dirtelti’ backdoor was prevented on multiple endpoints
- Office process dropped and executed a PE file on multiple endpoints
- Multi-stage incident involving Initial access & Execution on one endpoint reported by multiple sources
- Ransomware activity
- Multi-stage incident involving Discovery & Command and control on one endpoint
To learn more about incident in Microsoft Threat Protection go to the following links:
by Scott Muniz | Aug 20, 2020 | Uncategorized
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
With back to school coming in much of the world, we wanted to make sure that educators have the tools they need to be successful, whether they are working in a hybrid learning environment, remote learning, or in person. We’ve been listening to OneNote-loving educators and students around the world, and as always, we try and ensure that their needs are met with our tools.
1) More inclusive with OneNote Live Captions
As announced at the BETT conference earlier this year, OneNote will be adding a Live Captions feature which allows any student to connect OneNote to Microsoft Translator captions via a Join Code and receive the translation stream directly into the OneNote app. This allows captions from the educator speaking to flow directly into OneNote for reading, while still allowing the student to take notes. In addition, the student can pause the captions, highlight portions, and then have the entire transcription saved as a page into OneNote. This feature will benefit all learners but especially those who may be hard of hearing or speak a different native language than the educator. The private education-only preview rolls out in OneNote web next week to our Education Insider program.
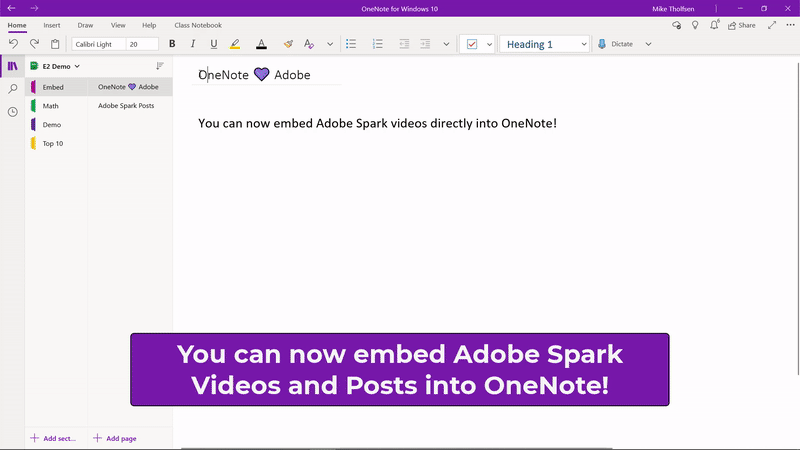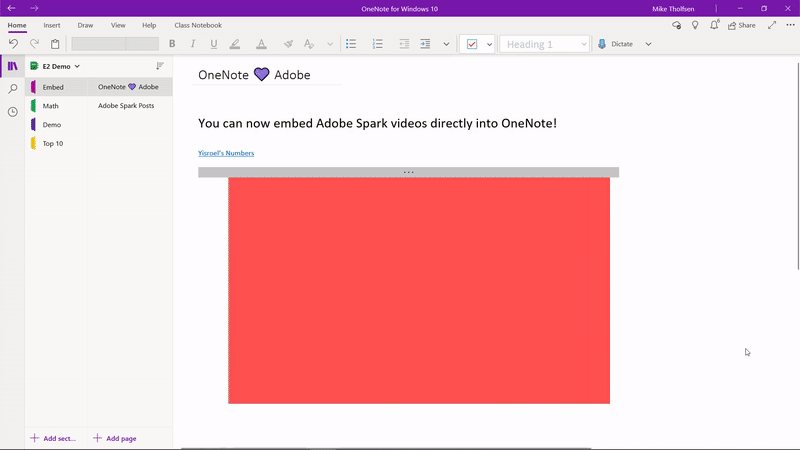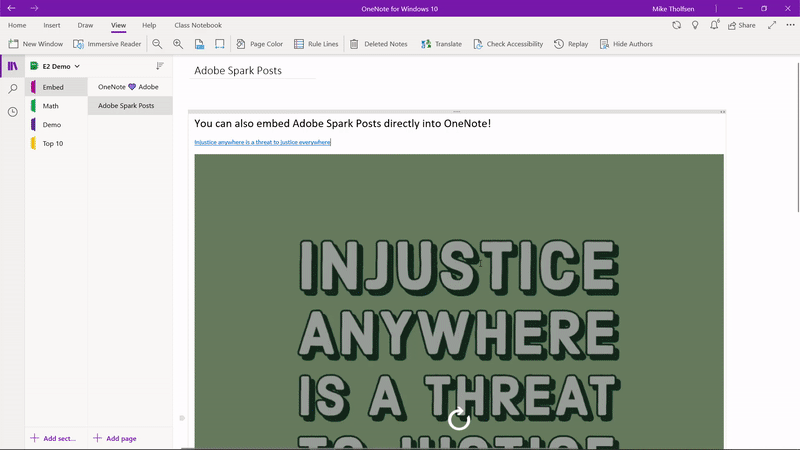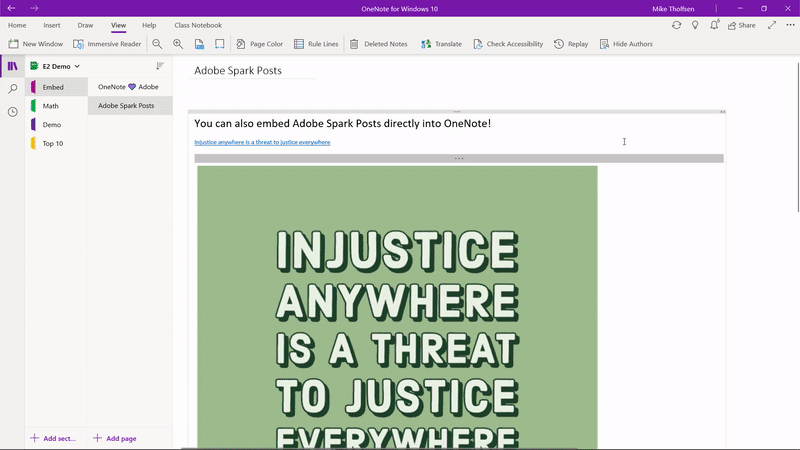
2) Embed Adobe Spark Videos and Posts into OneNote
Educators love Adobe Spark, and they also love OneNote! Adobe Spark lets students and educators transform their ideas into stunning visual stories. Today we are excited to announce support for embedding Adobe Spark Videos and Posts directly into OneNote. This will allow educators and students to interactively engage with the content. We look to add additional Adobe Spark product support to embed in OneNote in the future.
Note: Adobe Spark posts currently work on OneNote Windows 10, OneNote Online, OneNote iPad and Mac. OneNote 2016 support will come in the future

You can find the entire list of OneNote Embed partners here.
3) Class Notebook and Microsoft Teams Updates
So many educators today are using Microsoft Teams in their in-person or virtual classroom, so ensuring the OneNote Class and Staff Notebook is a core part of that experience is critical. Today we are excited to announce a set of improvements for OneNote inside of Teams.
Roster updates from School Data Sync automatically update the Class Notebook roster
In the past, when School Data Sync made roster updates from the students in the class, these updates would not happen until the educator went and clicked on the “Class Notebook” tab in the Class Team, which was a big complaint and time water. Now, these SDS updates automatically flow to the OneNote Class Notebook, and the educator saves a bit of time!
Set Channels to create sections in Collaboration Space or Content Library
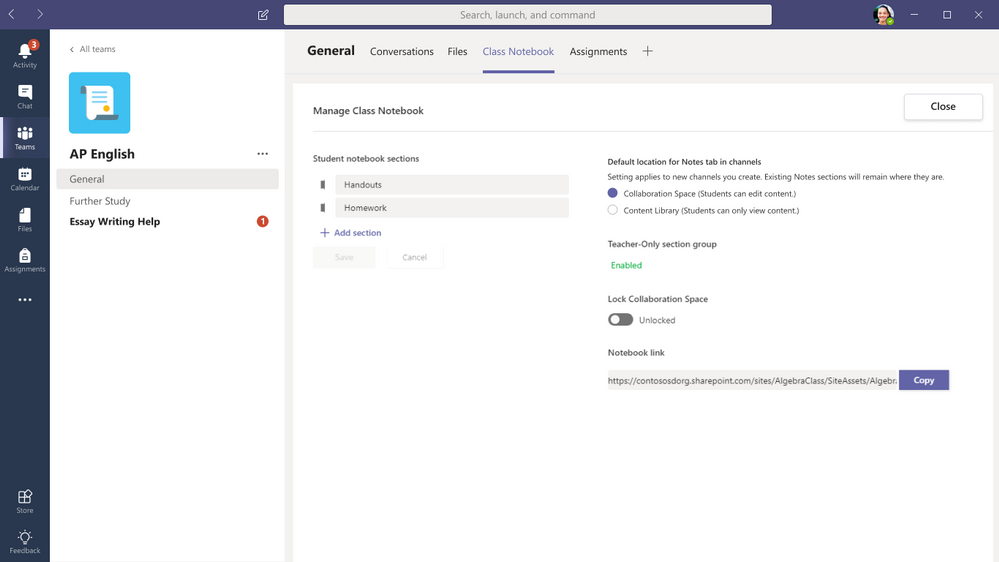
This feature was inspired directly from Dr. David Kellermann of UNSW in Australia. For the past few years, when creating a new channel, all Sections are created in the Collaboration Space, with no other option. Dr. Kellerman teaches his classes by using Teams channels as units, and always wanted to have any channel he created make a read-only Section in the Content Library of his Class Notebook. With this new update, the educator has the option to choose where new Sections go. THanks to Dr. Kellermann for the inspiration! This update will be found in a new option under “Manage Notebook” inside of Teams, and rolls out in late August.
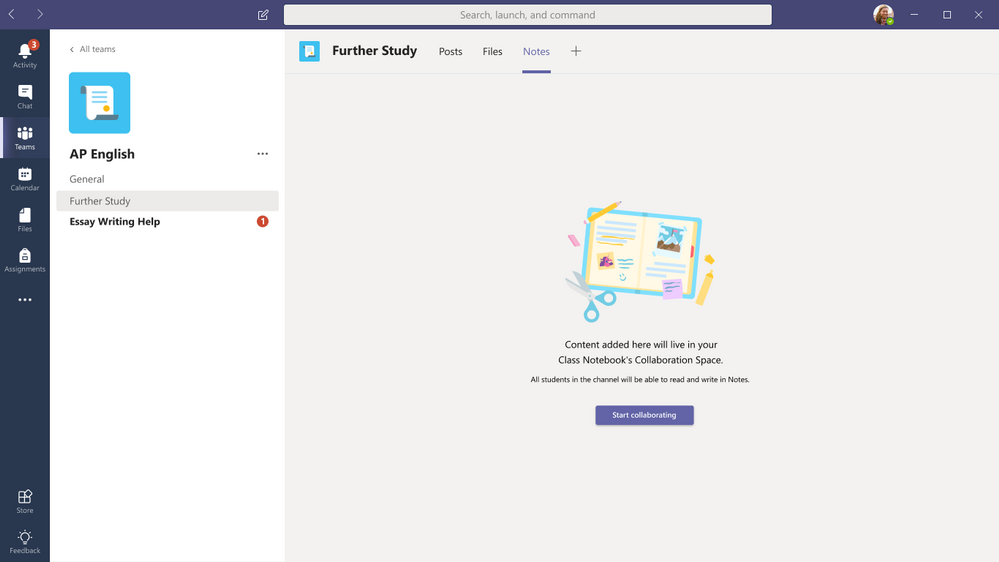
A better First Run Experience for then “Notes” section in a Channel
To make it easier and more obvious that the “Notes” section in a new Channel is part of the Class Notebook or Staff, we’ve added a first run page that explicitly explains the link between the
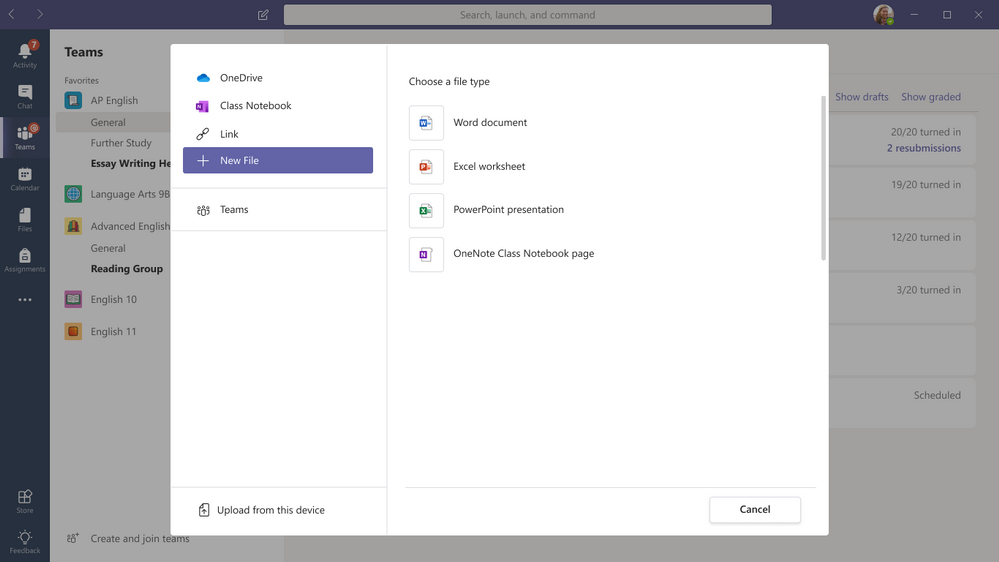
Create a new OneNote page in the “New File” dialog of Assignments
When educators are creating assignments, or students are attaching work, it’s handy to be able to create a New File on the fly. Currently, Teams Assignments supports creating a new Word, Excel or PowerPoint document. We will be adding the ability to also create a blank OneNote page, that can easily be filled out, through the New File dialog.
Page Distribution speed improvements
One of the top requests we’ve had is to speed up Page Distribution when using the OneNote Class Notebook toolbar. Our engineers have been hard at work over the summer, and we’ve made a large set of improvements that speed up page distribution on average by 65%! Mileage may vary, but overall educators and students should experience a significant performance improvements when distributing pages. Also be sure to follow out OneNote Best Practices when using the Class Notebook toolbar.
Students and Educators get a notification when a page is distributed
A great benefit of using the Class Notebook inside of Teams is the Class Notebook bot. We are making a new update that will allow any Educator using Page Distribution in the OneNote client, to ensure that all students get a notification in Teams after the page is distributed! This has been a top UserVoice request that we are glad to take care of. This notification will work for educators using the Class Notebook Toolbar in OneNote Windows 10, iPad, Web and Mac.
The “Teacher Only” Section Group is enabled by default now
A common request from educators is to just enable the “Teacher Only” section group by default. It takes extra clicks to go and do this after the Class or Staff Notebook is set up. So we’ve recently made a change do this will always be enabled by default, and save educators a few less clicks.
For those of you that like lists, here are the updates in list format, with the dates as well:
- Roster updates from School Data Sync automatically update the Class Notebook roster – live now
- Page Distribution speed improvements – live now
- The “Teacher Only” Section Group is enabled by default now – live now
- A better First Run Experience for then “Notes” section in a Channel – live now
- Embed Adobe Spark Videos and Posts into OneNote – live now
- OneNote Live Captions – private beta rollouts to our Education Insiders this week
- Set Channels to create sections in Collaboration Space or Content Library – end of August
- Create a new OneNote page in the “New File” dialog of Assignments – early September
- Students and Educators get a notification when a page is distributed – September
We hope you enjoy these new OneNote updates! Don’t hesitate to reach out with any questions or comments.
Mike Tholfsen
Principal Product Manager
Microsoft Education
@mtholfsen

by Scott Muniz | Aug 20, 2020 | Uncategorized
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Hi Everyone! Sujay here from the Program Management team for System Center Data Protection Manager (DPM) and Microsoft Azure Backup Server (MABS)
While talking to DPM and MABS customers I come across many questions around the tiered storage requirement for storage pool. With this blog post I will try to answer the most important question Why tiered storage? and some of the frequently asked questions (FAQs) about using the tiered storage.
This post is going to be a long one, but I promise to be worth your time. And if you are looking for tldr version; Use tiered storage for DPM storage pool, period. 
Before I jump into the questions, I recommend you to get yourself familiarize with the following terminologies I have referenced multiple times in my blog.
Note: I might use DPM at many places but everything in this blog is applicable for MABS as well. Make sure you are using MABS v3 with UR1.
Let’s get started.
Why the backup jobs take longer time on Modern Backup Storage over the period?
During the backup process one of the important steps is to take snapshot of the replica on the DPM server to create Recovery Point. This is done using block cloning feature of ReFS. Over a period of time, as daily/weekly backup jobs run and snapshots are taken, it causes increased fragmentation of the replica. Also, with each clone operation the size of the metadata is increases The block cloning operation is metadata intensive. During each block cloning operation, the files metadata and global ref count table would be read from the disk to the memory. This would result in high amount of I/O operations to underlying storage.
Let’s take an example of 400GB replica size (the replica contains the backup data stored on DPM server for specific data source). We observed that with the worst possible fragmentation, the metadata size can go up to 4% of the replica size, which would be 16GB in this case. This would result to read of 16GB of metadata during every cloning operation. If we assume ReFS cluster size of 4K, total I/O operations required for single cloning operation would be around 4 million. With the standard disk (HDD) of around 200 IOPS, this can take almost 20K seconds or around 5 hours to just clone the replica. This is the worst-case scenario – we are assuming all IOPS are random and worst possible fragmentation. This may not be always the case with your environment.
How does the tiered storage solve this problem?
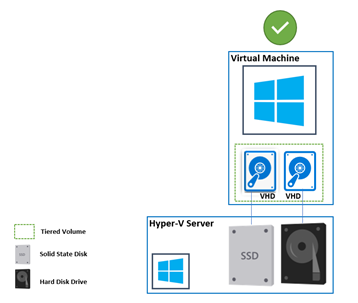
With DPM 2019, we enhanced MBS to take advantage of hybrid storage aka Tiered Storage feature in ReFS configured using Storage Spaces. ReFS divides volume into two logical storage known as tiers. These tiers can have their own drive and resilience types, allowing each tier to optimize for either performance or capacity. Once these tiers are configured, ReFS uses them to deliver fast storage for hot data and capacity-efficient storage for cold data. DPM uses this in a slightly different way to improve the overall backup performance.
DPM (with the help of ReFS), uses the performance tier (SSD) to store entire file system metadata which is required for block cloning operation. This improves the cloning performance to a great extent. If we take the same example as above and take the cheapest SSD available in the market, it offers 10K IOPS. The cloning time would cut down drastically to around 6 to 7 minutes. The tiered storage is the cost-efficient solution offered by ReFS to cater to high IOPS demanding application and DPM makes the most out of it by using just the small size of SSD.
What should be the size of SSD tier and Why?
As mentioned above in the worst possible fragmentation scenario the metadata size of the file system can grow up to 4% of the replica size. And since DPM requires SSD tier to store only ReFS metadata (which is required for cloning operation) the SSD size of 4% of total DPM storage is recommended.
Do I need to upgrade my server or external storage if it doesn’t support SSD?
The storage for DPM pool could be directly attached storage (Internal) or the external storage like SAN storage.
If you are using internal storage you need to connect SSD to the DPM server and if your server doesn’t have provision for SSD you can also use PCIe based SSDs.
If you are using external storage (like SAN device) and if your storage supports SSD you can add the SSD to external storage. If that’s not possible you can still use the SSD connected directly to the DPM server (including PCIe based SSD) in combination with HDDs from external storage to create tiered storage.

What if my DPM server is running on Virtual Machine? Can I use tiered storage on VM?
Yes. Configuring tiered storage using Windows Storage Spaces is supported on Virtual Machine.
The VM should have virtual SSD carved out of Physical SSD on the Hyper-V host. The Hyper-V host can have the physical SSDs connected locally or from external storage. While configuring the Windows Storage Space on Virtual Machine, you need to make sure that Media Type for the disk are configured correctly.
Use the following command to set the appropriate Media Type:
Set-PhysicalDisk -UniqueId <UniqueId String> -MediaType <HDD|SSD>
How can I configure the tiered storage?
Please refer to our documentation here which provides the step by step guidance to configure tiered storage. Additionally, I strongly recommend you to review the pre-requisites for Storage Spaces here.
What resiliency option can be configured for tiered volume in DPM?
DPM supports all the resiliency option supported by Windows Storage Spaces: Simple, Mirror and Parity. The Storage Space pre-requisites document explains the pros and cons of each option here.
For DPM, you can also use the combination of the resiliency option to optimize performance or capacity.
|
Performance tier
|
Capacity tier
|
|
Mirrored SSD
|
Mirrored HDD
|
|
Mirrored SSD
|
Parity HDD
|
Note: When you are configuring Storage Spaces, you should not configure any resiliency (RAID) at hardware layer. This is pre-requisite for the Storage Spaces.
What is the recommended sector size for tiered storage?
We strongly recommend keeping the sector size to 4096. And to avoid multiplexing / demultiplexing of IO operations, the sector size should be consistent across all the layers from ReFS to storage hardware.
Why is Windows Server 2019 recommended to install DPM 2019 or MABS v3?
As you know DPM is highly dependent on Resilient File System (ReFS). Windows Server 2019 brings various enhancements to ReFS which are not available with Windows Server 2016. Also, it is important that you always install the latest Cumulative Update for Windows Server 2019 which brings additional fixes to ReFS. For example, recently the January 23, 2020—KB4534321 update had performance improvement for ReFS block cloning operation.
Is there any alternative to improve the backup job performance?
Although we highly recommend you to migrate to tiered storage, there is another way which can help you to improve the backup performance. If the backup jobs are taking longer time only for specific data sources, to reduce the fragmentation, you can move the data source to another volume where you have enough free space. This will allow to store the replica in more contiguous space which should result in reduced fragmentation. Remember having enough free space on the volume is important to get contiguous space. While this should improve the performance but over the period as the fragmentation increases you might see degraded performance.
With DPM 2019 UR2, you can use optimized migration to migrate only active replica to new volume while retaining the older recovery points on the existing volume. Read more about how to migrate data source to new volume here.
How do I know the current fragmentation status of the replica?
We have added –CheckReplicaFragmentation parameter to Copy-DPMDatasourceReplica PowerShell cmdlet. This allows you to check the fragmentation status of the replica for the Data Source.
Note: To use this cmdlet you need to have at least UR1 for DPM 2019 or UR9 for DPM 2016.
I hope this was helpful information and now you know why using tiered storage for DPM storage will improve the backup job performance. So, start using tiered storage and let us know how your experience is. While I have tried to cover most frequently asked questions in this blog, I am sure there will be still more questions. Please post your questions in the comments and I will try to answer them as best as I can.
-Sujay and rest of the DPM team at Microsoft
by Scott Muniz | Aug 20, 2020 | Uncategorized
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.

In this weekly discussion of latest news and topics around Microsoft 365, hosts – Vesa Juvonen (Microsoft), Waldek Mastykarz (Rencore), are joined by Yannick Reekmans – MVP, Microsoft 365 Solution Architect and developer at Qubix.
Topics raised during this session:
- Customers’ shifting priorities, Microsoft’s shifting product capabilities, and Partner monetization opportunities.
- Discussion on purpose-built apps vs delivering experiences
- Teams vs SharePoint extensibility
- Value-add vs branded UI and strategies for Customer migration to cloud and for staying up-to-date on latest technologies.
- Fundamental approach – lead with Teams and add SharePoint for news and Intranet.
In this episode, 19 recently released articles from Microsoft and the PnP Community are highlighted.
This episode was recorded on Monday, August 17, 2020.
Did we miss your article? Please use #PnPWeekly hashtag in the Twitter for letting us know the content which you have created.
As always, if you need help on an issue, want to share a discovery, or just want to say: “Job well done”, please reach out to Vesa, to Waldek or to your PnP Community.
Sharing is caring!
by Scott Muniz | Aug 20, 2020 | Uncategorized
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Microsoft Teams usage has increased greatly during the current pandemic. All types of organizations are using the communications tool to stay connected with its employees and customers alike. The increase of use has also resulted in an increase of demand of system administrator’s time to manage Microsoft Teams. Everything from adding users and groups to managing policies of said users and groups can be managed via PowerShell. This post will highlight the foundations to get started and provide links to continue your automation through script writing journey.
Let’s begin …
Step 1: Getting started
- Launch PowerShell and run the following command
Install-Module -Name MicrosoftTeams
- With the Microsoft Teams cmdlet installed, use the following to login into your Microsoft Teams tenant
Connect-MicrosoftTeams
Note: This will also work if multi-factor authentication is enabled and you will be asked for your Office 365 credentials to sign in
- Use the following command to see a list of available Microsoft Teams cmdlets
Get-TeamHelp
Step 2: Choose your MS Teams cmdlet adventure
There is a plethora of cmdlets available as listed by the previous step. Here is a list of the cmdlets you will use most often:
Step 3: Managing Microsoft Teams policies
Policies within Microsoft Teams govern over a user’s or team’s abilities within teams and channels. Policies can enforce on behalf of a single user or an entire organization. The automation that PowerShell provides allow the Microsoft Teams administrator the ability to assign custom policies to multiple users as required.
In this example, the following script assigns the Human Resources Management Policy to all users in the Human Resources group. The script begins by getting the GroupObjectId of the group. Once acquired, it then finds the members of that group and assigns the policy to all users in the group.
$group = Get-AzureADGroup -SearchString "Human Resources group"
$members = Get-AzureADGroupMember -ObjectId $group.ObjectId -All $true | Where-Object {$_.ObjectType -eq "User"}$members | ForEach-Object { Grant-CsTeamsChannelsPolicy -PolicyName "Human Resources Management Policy" -Identity $_.UserPrincipalName}
As always, please share your comments below on bettering the above script or any questions you may have.






Recent Comments