by Scott Muniz | Aug 17, 2020 | Uncategorized
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Starting October 31 2020, Yammer Groups API endpoints will only support the usage of Azure Active Directory (AAD) tokens. Yammer Groups API endpoints will no longer support the usage of Yammer OAuth tokens. Microsoft recommends that customers and partners transition to using Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL) and AAD tokens with the Yammer API.
Last year, we announced Native Mode, which gets your network ready to experience Microsoft 365 integrations. Native Mode requires that all your users are created in AAD, all Groups are Microsoft 365 Connected and all Yammer Files are stored in SharePoint Online. With the move to files in SharePoint, Yammer Files API started require using AAD tokens.
As Yammer continues its journey to integrate into the Microsoft 365 ecosystem, there will be even more shared Yammer experiences across Microsoft 365, such as with Teams, Outlook and other applications. All of these require using AAD tokens. Yammer’s OAuth token cannot be accepted to conduct these operations. Overtime all Yammer API endpoints will be changed to exclusively support AAD tokens.
Starting October 31, 2020, Yammer Group API endpoints that are used to Update, Delete Groups, and manage Group Membership and Group Admins will only support AAD tokens. Using Yammer OAuth tokens will result in a bad request response from the server. Create and Read operations will be supported with Yammer OAuth tokens, however using AAD tokens for all API scenarios with Yammer is strongly recommended.
Notes:
- All Connected Yammer Groups (including Yammer networks in Native Mode) will require AAD tokens. Using the Yammer OAuth tokens will return a rejected response.
- In non-Native Yammer networks, users without Group creation rights in AAD will be able to create unconnected Yammer Groups.
What should you do?
- Use MSAL to authenticate with Yammer: Microsoft recommends that customers and partners transition their apps to authenticate using the Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL) to acquire AAD tokens from the Microsoft Identity Platform to operate with the Yammer API. MSAL is available for .NET, JavaScript, Android, and iOS, which support many different application architectures and platforms. Learn about MSAL here.
- Set up AAD Client Application: Follow these instructions to set up a client application and assign Delegated Yammer API Permissions to access Yammer APIs.
Notes:
- Yammer supports Delegated Permissions in Azure Active Directory. This means that your application will access the Yammer API as the signed in user. Application permissions are currently not supported by Yammer in Azure Active Directory.
- Enabling user_impersonation allows the application to access the Yammer platform on behalf of the signed in user.
- Application permissions are currently not supported by Yammer in Azure Active Directory.
Application types:
- Client-side Single page JavaScript Application: If you are using a Single Page AAD App that uses the Implicit Grant Flow, then your AAD App will need to be mapped to its corresponding Yammer platform Application. Please provide details about your application in this form and our team will work with you on the process to map your Yammer and Azure Active Directory client applications. This is required to ensure that your application is not affected by Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) permissions issues. Learn about CORS here.
- Server-side application: Using the Microsoft identity platform implementation of OAuth 2.0, you can add sign in and API access to your mobile and desktop apps If you are running a server-side app that requires the usage of long-lived AAD tokens, then use the Microsoft Identity Platform OAuth 2.0 authorization code flow to acquire AAD Access Tokens, with a Refresh Token. This enables your app to request a new AAD access token without requiring any user interaction. Take a look at these sample apps that support MSAL 2.0.
Resources:
We’re committed to working with the developer community in transitioning to the new world of AAD tokens! Please check out the resources below, post your questions/comments here or email api@yammer.com.
by Scott Muniz | Aug 17, 2020 | Uncategorized
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Initial Update: Monday, 17 August 2020 18:28 UTC
We are aware of issues within Application Insights and are actively investigating. Some customers may experience the request getting stuck when attempting to register with the Microsoft.Insights resource provider.
- Work Around: None
- Next Update: Before 08/17 20:30 UTC
We are working hard to resolve this issue and apologize for any inconvenience.
-Jeff
by Scott Muniz | Aug 17, 2020 | Azure, Microsoft, Technology, Uncategorized
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
In a historic day, Microsoft today announced it has transitioned Azure HDInsight to the Microsoft engineered distribution of Apache Hadoop and Spark, specifically built to drastically improve the performance, improved release cadence of powerful Open Source data analytics frameworks and optimized to natively run at cloud scale in Azure. This transition will further help customers by establishing a common Open Source Analytics distribution across various Azure data services such as Azure Synapse & SQL Server Big Data Clusters.
Starting this week, customers creating Azure HDInsight clusters such as Apache Spark, Hadoop, Kafka & HBase in Azure HDInsight 4.0 will be created using Microsoft distribution of Hadoop and Spark.
As part of today’s release, we are adding following new capabilities to HDInsight 4.0
SparkCruise: Queries in production workloads and interactive data analytics are often overlapping, i.e., multiple queries share parts of the computation. These redundancies increase the processing time and total cost for the users. To reuse computations, many big data processing systems support materialized views. However, it is challenging to manually select common computations in the workload given the size and evolving nature of the query workloads. In this release, we are introducing a new Spark capability called “SparkCruise” that will significantly improve the performance of Spark SQL.
SparkCruise is an automatic computation reuse system that selects the most useful common subexpressions to materialize based on the past query workload. SparkCruise materializes these subexpressions as part of query processing, so you can continue with their query processing just as before and computation reuse is automatically applied in the background — all without any modifications to the Spark code. SparkCruise has shown to improve the overall runtime of a benchmark derived from TPC-DS benchmark queries by 30%.
SparkCruise: Automatic Computation Reuse in Apache Spark
Hive View: Hive is a data warehouse infrastructure built on top of Hadoop. It provides tools to enable
data ETL, a mechanism to put structures on the data, and the capability to query and analyze large data sets that are stored in Hadoop. Hive View is designed to help you to author, optimize, and execute Hive queries. We are bringing Hive View natively to HDInsight 4.0 as part of this release.
Tez View: Tez is a framework for building high-performance batch and interactive data processing applications. When you run a job such as a Hive query Tez, you can use Tez View to track and debug the execution of that job. Tez View is now available in HDInsight 4.0
Frequently asked questions
What is Microsoft distribution of Hadoop & Spark (MDH)?
Microsoft engineered distribution of Apache Hadoop and Spark. Please read the motivation behind this step here
• Apache analytics projects built, delivered, and supported completely by Microsoft
• Apache projects enhanced with Microsoft’s years of experience with Cloud-Scale Big Data analytics
• Innovations by Microsoft offered back to the community
What can I do with HDInsight with MDH?
Easily run popular open-source frameworks—including Apache Hadoop, Spark, and Kafka—using Azure HDInsight, cost-effective, enterprise-grade service for open-source analytics. Effortlessly process massive amounts of data and get all the benefits of the broad open-source ecosystem with the global scale of Azure.
What versions of Apache frameworks available as part of MDH?
|
Component
|
HDInsight 4.0
|
|
Apache Hadoop and YARN
|
3.1.1
|
|
Apache Tez
|
0.9.1
|
|
Apache Pig
|
0.16.0
|
|
Apache Hive
|
3.1.0
|
|
Apache Ranger
|
1.1.0
|
|
Apache HBase
|
2.1.6
|
|
Apache Sqoop
|
1.4.7
|
|
Apache Oozie
|
4.3.1
|
|
Apache Zookeeper
|
3.4.6
|
|
Apache Phoenix
|
5
|
|
Apache Spark
|
2.4.4
|
|
Apache Livy
|
0.5
|
|
Apache Kafka
|
2.1.1
|
|
Apache Ambari
|
2.7.0
|
|
Apache Zeppelin
|
0.8.0
|
In which region Azure HDInsight with MDH is available?
HDInsight with MDH is available in all HDInsight supported regions
What version of HDInsight with MDH will map to?
HDInsight with MDH maps to HDInsight 4.0. We expect 100% compatibility with HDInsight 4.0
Do you support Azure Data Lake Store Gen 2? How about Azure Data Lake Store Gen 1?
Yes, we support storage services such as ADLS Gen 2, ADLS Gen1 and BLOB store
What happens to the existing running cluster created with the HDP distribution?
Existing clusters created with HDP distribution runs without any change.
How can I verify if my cluster is leveraging MDH?
You can verify the stack version (HDInsight 4.1) in Ambari (Ambari–>User–>Versions)
How do I get support?
Support mechanisms are not changing, customers continue to engage support channels such as Microsoft support
Is there a cost difference?
There is no cost or billing change with HDInsight with Microsoft supported distribution of Hadoop & Spark.
Is Microsoft trying to benefit from the open-source community without contributing back?
No. Azure customers are demanding the ability to build and operate analytics applications based on the most innovative open-source analytics projects on the state-of-the-art enterprise features in the Azure platform. Microsoft is committed to meeting the requirements of such customers in the best and fastest way possible. Microsoft is investing deeply in the most popular open-source projects and driving innovations into the same. Microsoft will work with the open-source community to contribute the relevant changes back to the Apache project itself.
Will customers who use the Microsoft distribution get locked into Azure or other Microsoft offerings?
The Microsoft distribution of Apache projects is optimized for the cloud and will be tested extensively to ensure that they work best on Azure. Where needed, the changes will be based on open or industry-standard APIs.
How will Microsoft decide which open-source projects to include in its distribution?
To start with, the Microsoft distribution contains the open-source projects supported in the latest version of Azure HDInsight. Additional projects will be included in the distribution based on feedback from customers, partners, and the open-source community.
Get started
by Scott Muniz | Aug 17, 2020 | Uncategorized
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
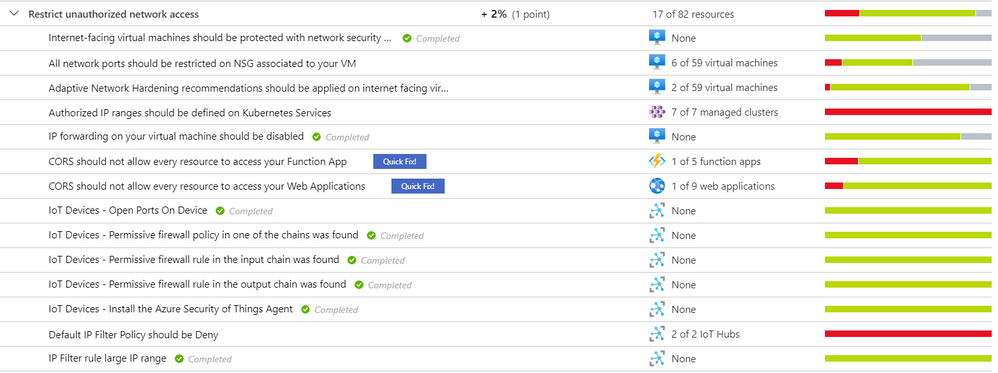
As part of our recent Azure Security Center (ASC) Blog Series, we are diving into the different controls within ASC’s Secure Score. In this post we will be discussing the control of “Restrict Unauthorized Network Access”.
There are many ways to protect your data nowadays; it is all about finding the best tools that adhere to your infrastructure and integrating them in the most efficient and effective way. Azure Security Center has an Enhanced Secure Score which brings specific security recommendations of your hybrid workloads in the cloud (Azure or others) as well as on premises. These advices are meant to keep your resources safe and improve your security hygiene where a continuous teamwork must be placed.
Gaining network access should be based on IP and device restrictions, firewall policies, network ports control, network security rules and more according to your business’s needs. Azure Security Center’s security control “Restrict Unauthorized Network Access” has a series of recommendations for this type of scenario. For a reference on this security control’s definition and others, visit this article.

The type of resources that you have in your infrastructure will dictate the kind of recommendations that are going to appear under “Restrict Unauthorized Network Access” security control. The sections that follows will cover some of the most common security recommendations that belong to this security control.
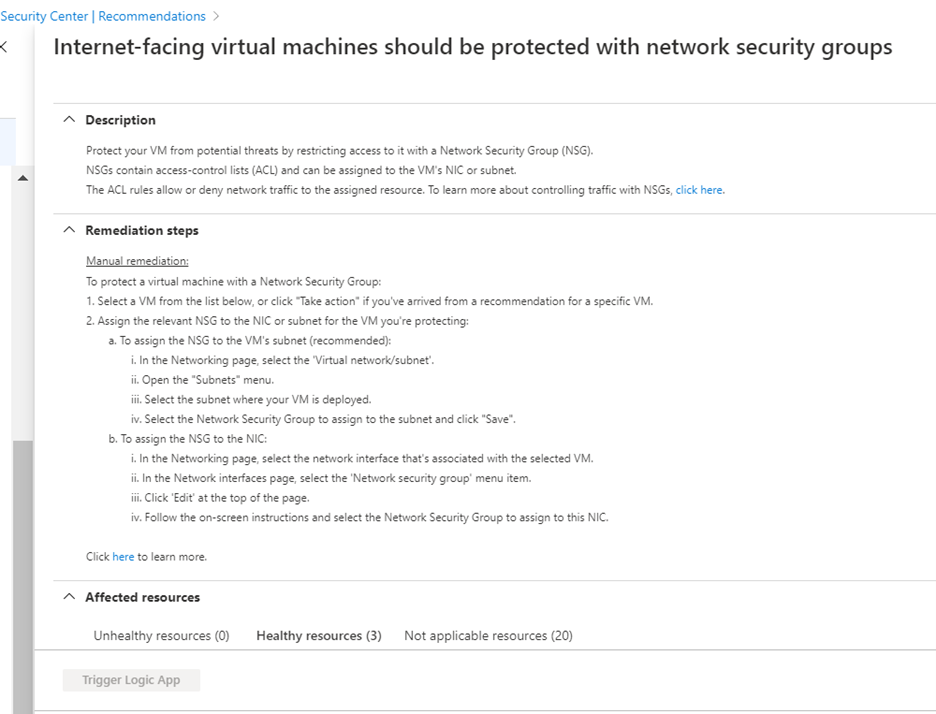
Internet-facing virtual machines should be protected with network security groups
Azure Security Center identifies virtual machines that are exposed to the Internet without a network security group (NSG) to filter the traffic. Although there are some other options to protect your internet-facing virtual machines, for the purpose of ASC, this is the security recommendation that needs to be remediated. When you go and click that recommendation, there will be a manual remediation you can follow. Once all the VMs have NSGs assigned, the task would be completed.
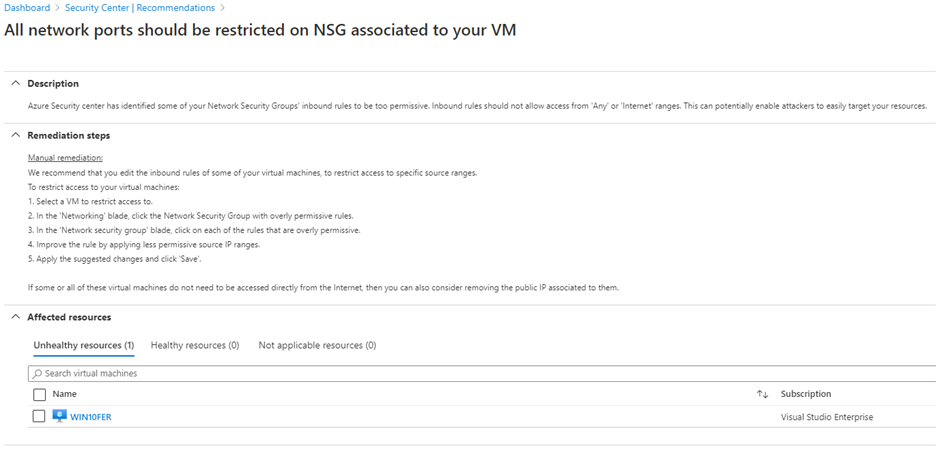
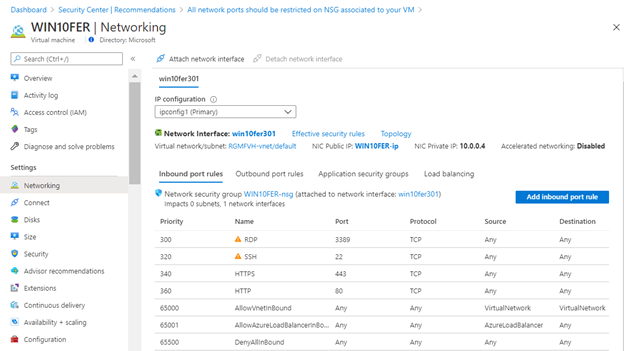
All network ports should be restricted on NSG associated to your VM
This recommendation appears when Azure Security Center identifies that some of your Network Security Groups’ inbound rules are too permissive. Which means, you have inbound rules that are too broad, for example from “Any” to “Any”. This recommendation is relevant only for virtual machines protected by a network security group, so even if you have virtual machines on NSGs but are not-internet-facing, they will appear in the “Not applicable resources” tab. The manual procedure indicates that you should improve the network security group rule by applying less permissive source IP ranges. Once this is performed, it would appear as completed.
CORS should not allow every resource to access your Function App/Web App
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) allows restricted resources on a web page to be requested from another domain. This recommendation aims to harden the list of required domains that can interact with your Function App/Web App. It has the Quick Fix button, which triggers an automatic script (modifiable) to remediate.
Note: The allowedOrigins parameter should be in the format:
["http://localhost","https://functions-staging.azure.com","https://functions.azure.com"]
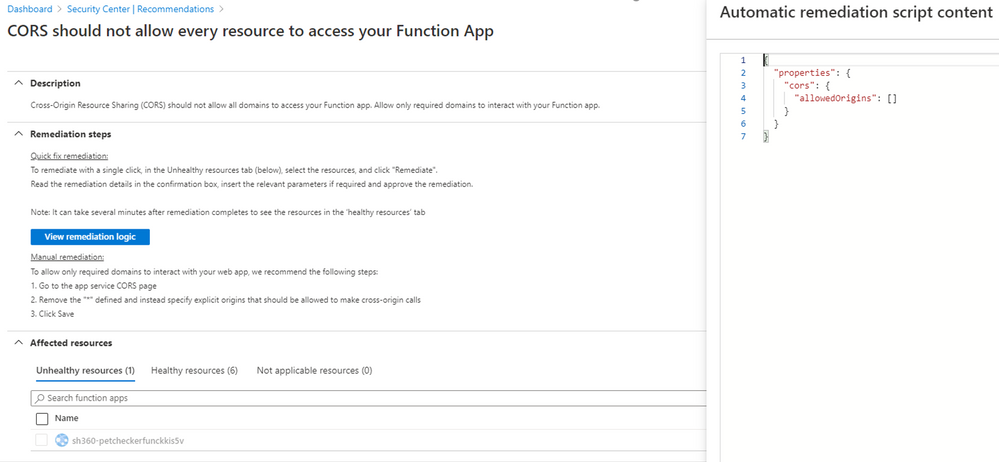
The manual remediation requires that you go to your app service CORS section so you remove the “*” and specify explicit origins that should be allowed to make cross-origin calls.
Default IP Filter Policy should be Deny
When you have any IoT solution based on Azure IoT Hub and the IP Filter grid is by default (a rule that accepts the 0.0.0.0/0 IP address range), your hub will accept connections from any IP address. That is when this recommendation will be displayed.
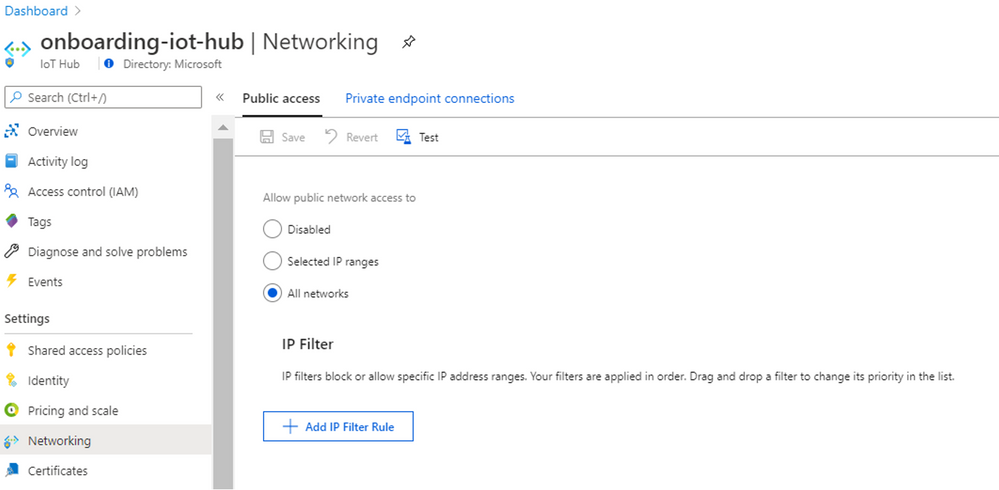
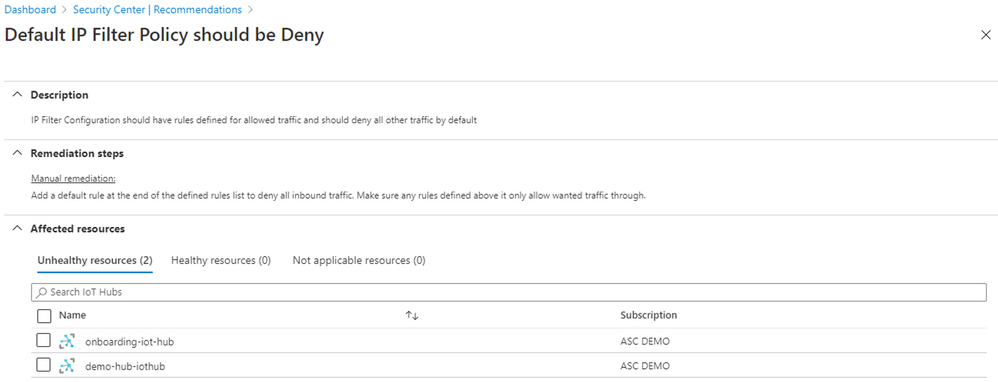
The manual remediation is to go to your IoT solution and edit your IP Filter. Read this article to learn how to add/edit/delete an IP filter rule and more.
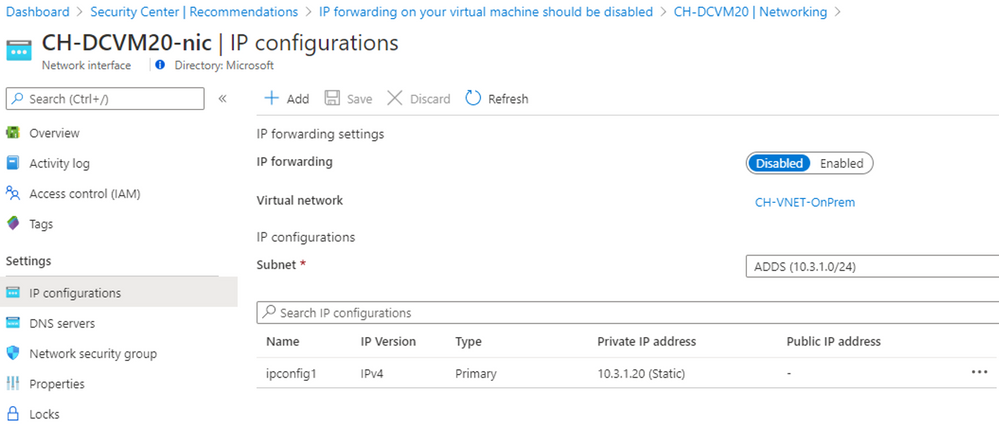
IP forwarding on your virtual machine should be disabled
Azure Security Center will show this recommendation when it discovers that IP forwarding is enabled on some of your virtual machines. This allows the VM to accept incoming network packets that should be send to another network. The Azure Security Center GitHub community page has a Logic App Playbook and a PowerShell script sample to resolve the recommendation.
The manual remediation is to go to the VM’s networking blade and under NIC click in IP Configurations to disable “IP Forwarding”.
Conclusion
It is imperative to constantly review your Secure Score and act in the recommendations provided specifically for your infrastructure. You can always disable the recommendations that do not apply to your environment, in fact, it is quite easy; nevertheless, we encourage you to get every team involved in this to analyze the behaviors that should be allowed for each resource.
This blog was written as a collaboration with @Yuri Diogenes
by Scott Muniz | Aug 17, 2020 | Uncategorized
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
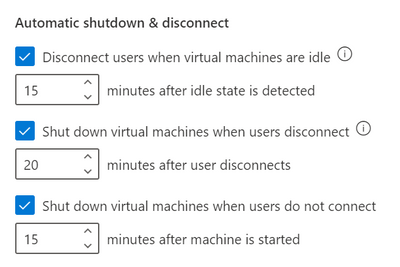
I’m excited to announce new cost control features that will proactively prevent waste of virtual machine usage hours inside the labs! The combination of these three automatic shutdown and disconnect features will now catch most of the cases where users accidentally leave their virtual machines running:

These settings can be configured at both the lab account level and the lab level. If the settings are enabled at the lab account level, they will be applied to all labs within the lab account. Any changes to the settings made at the lab level will override the lab account level configuration. For all new lab accounts, these settings will be turned on by default.
Let’s look at what each setting does in detail.
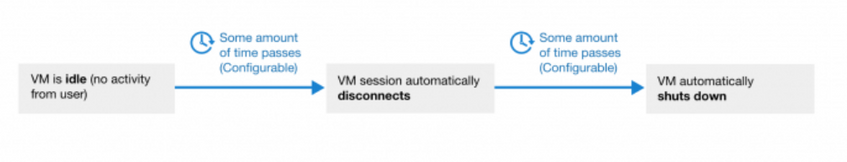
1. Automatically disconnect users from virtual machines that the OS deems idle (Windows-only)
This is a setting that is only available for Windows virtual machines. When the setting is turned on, any machines in the lab, including the template virtual machine, will automatically disconnect the user when the Windows OS deems the session to be idle. Windows OS’s definition of idle uses two criteria:
- User absence – no keyboard or mouse input
- Lack of resource consumption – all the processors and all the disks were idle for a certain % of time
Users will see a message like this inside the virtual machines before they are disconnected:
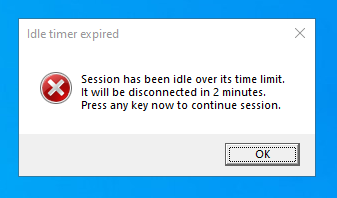
Please note that the virtual machine is still running when the user is disconnected. If the user reconnects to the virtual machine by signing in, windows or files that were open or unsaved work previous to the disconnect will still be there. In this state, because the virtual machine is running, it still counts as active and accrues cost.
To automatically shut down the idle Windows virtual machines that are disconnected, use the combination of “Disconnect users when virtual machines are idle” and “Shut down virtual machines when users disconnect” settings.
For example, if you configure the settings as follows:
- Disconnect users when virtual machines are idle – 15 minutes after idle state is detected
- Shut down virtual machines when users disconnect” – 5 minutes after user disconnects
The Windows virtual machines will automatically shutdown 20 minutes after the user stops using them.
2. Automatically shut down virtual machines when users disconnect (Windows & Linux)
This setting now supports both Windows and Linux virtual machines. When this setting is on, automatic shutdown will occur when:
- For Windows, Remote Desktop (RDP) connection is disconnected
- For Linux, SSH connection is disconnected
This feature utilizes the Linux Diagnostic Extension and is available for only the specific distributions and versions of Linux that the Linux Diagnostic Extension supports.
You can specify how long the virtual machines should wait for the user to reconnect before automatically shutting down.
3. Automatically shut down virtual machines that are started but users don’t connect
Inside a lab, a user might start a virtual machine but never connect to it. For example:
- A schedule in the lab starts all virtual machines for a class session, but some students do not show up and don’t connect to their machines.
- A user starts a virtual machine, but forgets to connect.
The “Shut down virtual machines when users do not connect” setting will catch these cases and automatically shut down the virtual machines.
—-
Please enable these settings to minimize waste in your labs. I’m looking forward to hearing any feedback or questions you have.
Thank you!




Recent Comments