by Contributed | Dec 12, 2020 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
As part of my work on the open source PostgreSQL team at Microsoft, I recently committed a new feature to track dependencies on collation versions, with help from co-author Julien Rouhaud and the many others who contributed ideas. It took a long time to build a consensus on how to tackle this thorny problem (work I began at EnterpriseDB and continued at Microsoft), and you can read about some of the details and considerations in the commit message below and the referenced discussion thread. Please note that some details may change by the time PostgreSQL 14 is released.
commit 257836a75585934cc05ed7a80bccf8190d41e056
Author: Thomas Munro <tmunro@postgresql.org>
Date: Mon Nov 2 19:50:45 2020 +1300
Track collation versions for indexes.
Record the current version of dependent collations in pg_depend when
creating or rebuilding an index. When accessing the index later, warn
that the index may be corrupted if the current version doesn’t match.
Thanks to Douglas Doole, Peter Eisentraut, Christoph Berg, Laurenz Albe,
Michael Paquier, Robert Haas, Tom Lane and others for very helpful
discussion.
Author: Thomas Munro <thomas.munro@gmail.com>
Author: Julien Rouhaud <rjuju123@gmail.com>
Reviewed-by: Peter Eisentraut <peter.eisentraut@2ndquadrant.com> (earlier versions)
Discussion: https://postgr.es/m/CAEepm%3D0uEQCpfq_%2BLYFBdArCe4Ot98t1aR4eYiYTe%3DyavQygiQ%40mail.gmail.com
I’m pretty happy with the result so far, but there is more to be done (see further down)! Now seems like a good time to walk you through the problem we needed to solve—that PostgreSQL indexes can get corrupted by changes in collations that occur naturally over time—and how the new feature makes things better in PostgreSQL 14. Plus, you’ll get a bit of background on collations, too.
What is a collation?
The term collation derives from a form of the Latin verb conferre meaning to confer, bring together, or compare. Book binders use the term collation to mean putting pages into the correct order. Outside special technical fields, collation may be better known as an old fashioned and formal name for a cold meal (cf. colazione, Italian for breakfast). That meaning comes to us from the same ultimate source, having developed a different meaning in 4th century monasteries though association with brown bag lunches, but I digress…
Many software systems including POSIX and Windows have locales that encapsulate language and cultural conventions. A collation is the component of a locale that controls the way text is sorted. Even though many languages share common writing systems, they don’t necessarily agree on how to sort words. Even within the same language, there can be differences in how words should be sorted in different countries or in specialised contexts.
Similarly, in the context of SQL, a COLLATION is a database object that identifies a set of rules for sorting character strings.
For example, in a Danish dictionary, “å” comes after “z”, and “aa” is considered to be an alternative spelling of “å”. PostgreSQL models the different possible sorting rules with different collations, and we can see this difference on most systems like so:
postgres=# create table words (word text);
CREATE TABLE
postgres=# insert into words values ('Aarhus'), ('Banana'), ('Cat');
INSERT 0 3
postgres=# select * from words order by word collate "en_NZ";
word
--------
Aarhus
Banana
Cat
(3 rows)
postgres=# select * from words order by word collate "da_DK";
word
--------
Banana
Cat
Aarhus
(3 rows)
This might affect where a user expects to find a value in drop-down list or contents page.
Collations are part of the static type system of SQL. If you’re working with text, you can’t escape them! You can mostly ignore them and just let your whole system use the collation named “default”, though. That’s how a lot of you probably consume collations, especially if you only deal with one language. That means you get the default for the database you’re connected to:
postgres=# l postgres
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges
----------+--------+----------+-------------+-------------+-------------------
postgres | tmunro | UTF8 | en_NZ.UTF-8 | en_NZ.UTF-8 |
(1 row)
Often the default collation is set by initdb when the PostgreSQL cluster is first created. The collation and other locale components can be set using defaults from the operating system environment, and then inherited by databases created later. However, they can also be explicitly specified, and changed in later CREATE DATABASE commands with certain restrictions. You can also opt for one of the special collations “C”, “POSIX”, or “ucs_basic” which sort in binary or code point order rather than following cultural conventions, avoiding the problems described below—fair warning though, the results might surprise a few humans if they are reflected in user interfaces.
So what’s the catch?
To quote from Unicode Technical Standard #10:
Over time, collation order will vary: there may be fixes needed as more information becomes available about languages; there may be new government or industry standards for the language that require changes; and finally, new characters added to the Unicode Standard will interleave with the previously-defined ones. This means that collations must be carefully versioned.
The most obvious problem this causes for databases like PostgreSQL is that B-tree indexes can become corrupted if they are ordered by a collation that changes. Typical symptoms reported in the wild include rows that cannot be seen by one query but can be seen by another query that is using a different plan. Or sometimes, a unique index fails to prevent a duplicate value from being added to a table.
To see why collation changes could impact whether PostgreSQL is able to look things up, let’s use a phone book analogy. After all, a phone book is an ordered index with a lot of similarities to indexes in databases. So, imagine trying to look up your own name in an old-fashioned paper phone book—then imagine the phone book was created by someone who believes the alphabet goes in a slightly different order than you. There’s a chance you’ll conclude your name is not in the phone book, because your name is ordered in some unexpected place in the book, effectively hidden from you.
For a simple real-world example of a change in sort order on GNU/Linux that involves only ASCII characters, the sort order of the strings ‘a-a’ and ‘a+a’ flipped in glibc 2.28 (Debian 10, RHEL) compared to earlier releases.
Where does PostgreSQL’s collation logic come from?
PostgreSQL relies on external libraries to order strings. There are two “providers”:
libc, meaning the operating system locale facility (POSIX or Windows)
icu, meaning the ICU project, assuming PostgreSQL was built with ICU support
For now, only libc collations can be used as the database default, though ICU collations can be used explicitly, for example when defining the columns of a table. So which should you use?
One advantage of using libc collations is that the sorting behaviour matches other software on the same operating system.
Conversely, by using ICU it is possible to get software that is running on different operating systems to agree on sort order, if they’re also using ICU.
Another reason to use ICU: some operating systems provide only very rudimentary collation logic in their libc, especially when using the UTF-8 encoding.
And a 3rd reason to use ICU is that ICU supports a rich system of end-user customisation (see some simple examples in the PostgreSQL manual).
While the ICU project’s collation rules are based strictly on the Unicode Collation Algorithm and the ICU library version can be matched up with specific versions of Unicode and CLDR, things are a little murkier for libc, depending on your operating system. Many operating systems including FreeBSD, Windows 10, and GNU libc have migrated or are in the process of migrating from their own historical implementations of sorting rules to UCA-based logic and CLDR, so that eventually there will be fewer differences between systems, and between libc and ICU collations. Ironically it is this process that has caused many of the changes that we’ve seen in the past few years in libc collation definitions on popular operating systems. Even if all implementations eventually converged, CLDR itself is a moving target and it’s possible that the versions aren’t in sync.
The available set of collations on your system can be seen in the pg_collation catalog. You can add more with the CREATE COLLATION command, but you need to know how to form collcollate strings that are meaningful to your operating system or to ICU as appropriate. Note that collations often have names like “en_US”, which requires double quotes when you reference it in a COLLATE expression due their case-sensitivity.
Where does collation version information come from?
The ICU library can report an opaque version for the collations it provides. In PostgreSQL releases 10 to 13, versions of ICU collations were already captured in the pg_collation catalog table when they were first created. Typically that’s when the cluster is first set up. Then, when you use the collation (for example, by accessing an index that is ordered by it), a check is performed, and a warning is produced. This would alert you to rebuild all relevant indexes and then run ALTER COLLATION xxx REFRESH VERSION when done. This was a good start but it didn’t help many people for several reasons:
- it didn’t work for
libc collations (by far the more popular provider)
- it was difficult to see how to extend this model to cover the “default” collation (by far the most popular way to use collations, even if users may be unaware they’re doing it!)
- it didn’t know which indexes needed to be rebuilt after an upgrade, and relied on a human to figure that out
The first step to making things better and to tracking collation version dependencies was to figure out how to get version information from the operating system for libc collations. No relevant standard provides such an interface, but patches have now been committed to do that for GNU/Linux, FreeBSD 13+, and Windows using non-standard interfaces provided by those systems. Here are some example values, as returned by the pg_collation_actual_version() function in PostgreSQL 14-devel:
OS |
Provider |
Collation |
Version |
|---|
Linux |
libc |
en_NZ |
2.28 |
FreeBSD |
libc |
en_NZ |
34.0 |
Windows |
libc |
en_NZ |
1538.14,1538.14 |
(All) |
icu |
en-NZ-x-icu |
153.88 |
Patches for other operating systems are welcome! These version strings are not interpreted in any way by PostgreSQL, except to check if they have changed. Note that on Linux we fall back to the glibc library version, for lack of anything better.
What do we do with these new collation versions (starting in PostgreSQL 14)?
PostgreSQL tracks the dependencies between database objects in the pg_depend catalog. This is used for various purposes, including stopping you from dropping things that other things reference, dropping dependent things automatically, and dumping objects in the correct order.
The new refobjversion column provides a place for us to record the collation version that was in effect at the time an index was created. For example:
postgres=# create table city (name text primary key);
CREATE TABLE
And now, after inserting some data, suppose we upgrade the operating system, or use a streaming replica server which has a newer operating system version:
postgres=# select * from city where name between 'Aarhus' and 'Antioch';
WARNING: index "city_pkey" depends on collation "default" version "34.0", but the current version is "36.0"
DETAIL: The index may be corrupted due to changes in sort order.
HINT: REINDEX to avoid the risk of corruption.
This is just a warning, and will only be given once per index, per session. The primary way to stop the warning is with the REINDEX command, as mentioned in the HINT. It’s also possible to tell the system that you have independently verified that the index has not been corrupted by the change in version with ALTER INDEX name ALTER COLLATION name REFRESH VERSION. One way to verify that is to use the amcheck module.
What else could we do with the new collation version infrastructure?
Currently, warnings advising you to rebuild indexes are raised, but you need to take action one by one to clear the warnings. It would be nice to have a new view and a new REINDEX variant to see and address all problems at once, before PostgreSQL 14 is released; work is underway to do that.
So far I talked about indexes, because PostgreSQL indexes are the most likely source of problems when ordering functions change. Equivalent problems exist in other places, for example:
range partitions might now classify a key as belonging to a different partition after a collation change
check constraints that perform string comparisons might previously have passed, but now fail
While proof-of-concept patches have been drafted to provide similar warnings for those cases, it’s a little less clear what the user should do about these warnings, so these proof-of-concept ideas remain under discussion.
Mutating IMMUTABLE functions
PostgreSQL requires every function or operator involved in the definition of an index to be marked IMMUTABLE. The case of mutating collations can be thought of as a violation of that requirement, because the string comparison function (for example, bttextcmp) fails to guarantee that it’ll return the same value given the same inputs for the rest of eternity. The same applies to user-defined functions that are declared IMMUTABLE, but don’t meet that requirement due to, say, a dependency on the time, a GUC setting, or any other information that is not derivable only from the inputs.
There is a class of functions that change infrequently and at known times, however. Perhaps it would be possible to create a system of declarative versions for those, using the new refobjversion system: the index would depend on a named version of the function.
Other external things that could affect indexes
Consider the example of the unaccent function. A version for the unaccent() function itself would be a little too simplistic, because there is a second object besides the function that affects its results: the rules file. The rules file can be modified or replaced by the user, either directly or by supplying a pathname as an extra argument to the function.
Another example of functions that are used in indexes but depend on objects that might change is the full text search system. The dictionaries, stopwords, and stemmers can all change over time. In theory, some kind of system could be devised to cover those objects too.
TL;DR for collation versioning in PostgreSQL 14
PostgreSQL 14 will warn you about collation changes that might otherwise cause subtle, silent corruption such as failure to look up keys or prevent duplicate keys. This has been a persistent source of user complaint over the years; the new warnings in PostgreSQL 14 should help you avoid the risks by alerting you to changes in collation versions, either when upgrading machines or moving databases between machines.
Collations and dependencies are nerdy topics a bit like like leap seconds and time zones: you know, the kinds of obscure things you don’t normally have to worry about until something is broken. If you like gory details, the UCA is both fascinating and terrifying (my favourite part is “backward accent ordering” which shows up in some French variants but not others).
All of these things—time zones, leap seconds, collations—are gnarly details of the real world around us. And they can, and do, change. Collations matter to PostgreSQL because people want to be able to use natural language strings in database indexes (and use these indexes to drive user-visible ordering.) Hence, PostgreSQL needs to be able to cope with the fact that the underlying collation rules change over time—and that the providers are external libraries we don’t control.
Thanks for reading. I hope you found this deep dive into the new collation version tracking feature in PostgreSQL 14 interesting!
by Contributed | Dec 12, 2020 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
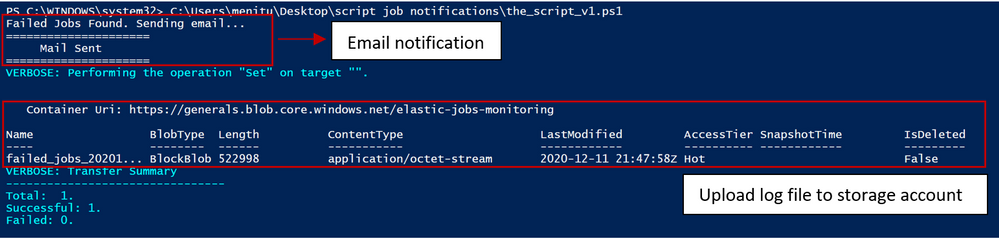
Alerts can be sent for any particular state of an elastic job. In this article, we discuss the case of ‘Failed’ jobs, however the solution can be easily extended to other scenarios. The script can be executed on client machines in background on a schedule or in Azure Automation Runbook. If failed jobs are identified, email notifications are sent, with an attachment of a log file containing only the failed jobs.
Elastic Jobs are currently in public preview and the monitoring capabilities are resuming for now to ad-hoc executions of T-SQL / PowerShell commands to retrieve the elastic job execution status, with no embedded option for sending alerts in case of a job failure.
This need has been addressed through a PowerShell script that filters job executions based on their status and sends the output to a log file, that is further sent as an attachment in a notification email and in the same time the log file is stored in an Azure Storage Account for further reference.
 script output when executed on client machine
script output when executed on client machine
The jobs are filtered with the below T-SQL, that can be modified as per the requirements:
SELECT * FROM jobs.job_executions WHERE lifecycle = 'Failed' ORDER BY start_time DESC
Other possible values for job execution states are Created, InProgress, WaitingForRetry, Succeeded, SucceededWithSkipped, Failed, TimedOut, Canceled, Skipped and WaitingForChildJobExecutions.
Generated log file:
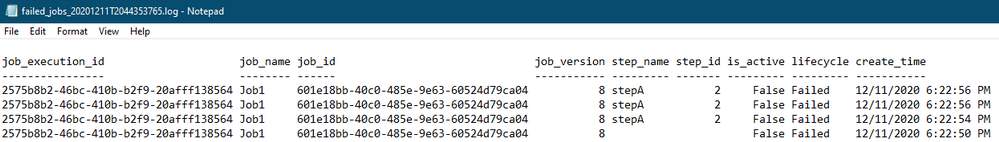 log file snippet
log file snippet
Save log file to storage account:
# Get key to storage account
$acctKey = (Get-AzStorageAccountKey -Name generals -ResourceGroupName general).Value[0]
# Map to the reports BLOB context
$storageContext = New-AzStorageContext -StorageAccountName $StorageAccountName -StorageAccountKey $acctKey
# Copy the file to the storage account
Set-AzStorageBlobContent -File $output_file -Container StorageContainerName -BlobType "Block" -Context $storageContext -Verbose
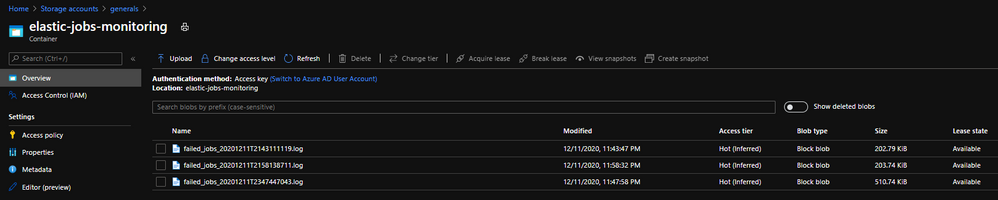 save log to storage account
save log to storage account
The email functionality can be leveraged through any Simple Mail Transfer Protocol server. The proposed script is using smtp.mail.yahoo.com on port 587.
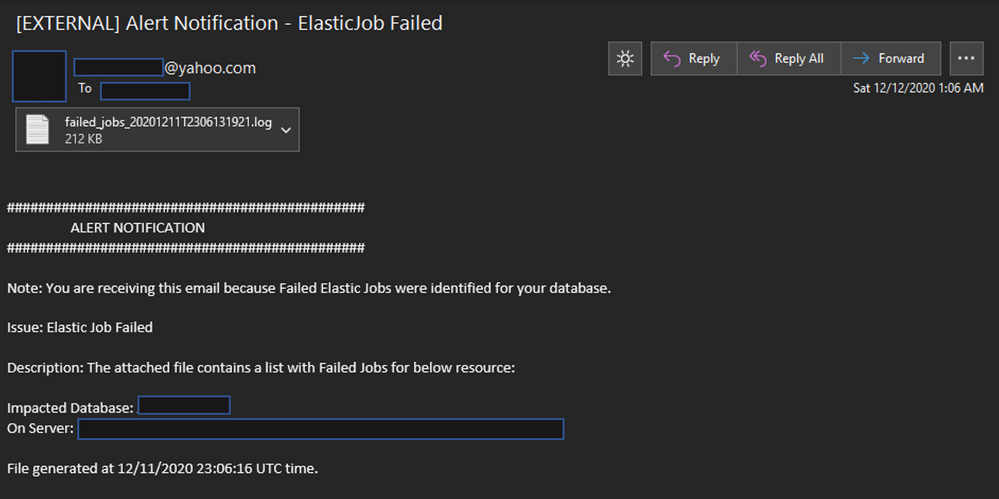 email notification alert
email notification alert
How to run and automate alerts
As elastic jobs can be scheduled to run on a regular basis from both PowerShell and T-SQL, so our alert script can. Depending on the desired deployment type you choose, there are several options. For any of the below options, you have to set the required parameters in the script: Insert SQL Server Details, Credentials & SMTP server details:
$server = '.database.windows.net' # Set the name of the server
$jobDB = '' # Set the name of the job database you wish to test
$user = '' # Set the login username you wish to use
$passw = '' # Set the login password you wish to use
$FromEmail = 'xxxxxxxxxxxx@yahoo.com' # "from" field's account must match the smtp server domain
$FromEmailPassw = '' # use app/server access token - it works with account passw
$ToEmail = 'xxxxxxxxxxxx@yyyyy.com'
$SMTPServer = "smtp.mail.yahoo.com" #insert SMTP server
$SMTPPort = "587" # or port 465
$StorageAccountName = ''
$StorageContainerName = ''
OPTION#1
Run the script on schedule in background on client machine
In order to run it you need to:
Open Windows PowerShell ISE in Administrator mode
Open a New Script window
Paste the content in script window
Run it
If failed jobs are found, an alert email will be triggered and the log file containing details on the failed jobs will be attached to the email and either saved locally or sent to a storage account. The result of the script can be followed in the output window.
To run the script in background on a schedule, you can use the following commands:
## =========================================================================
## Schedule Commands for Client Machines
## =========================================================================
## To schedule script execution in background, please see below options
#insert parameter values
$script = 'script.ps1' # insert script path
$Time= 'MM/DD/YYYY HH:MM' # insert desired start time for schedule
$jobName = 'Job1'#insert desired job name
# display all scheduled jobs
Get-ScheduledJob
# add new job to run at schedule
Register-ScheduledJob -Name $jobName -FilePath $script -Trigger (New-JobTrigger -Once -At $Time `
-RepetitionInterval (New-TimeSpan -Minutes 1) -RepetitionDuration ([TimeSpan]::MaxValue))
# command to remove a scheduled job
Unregister-ScheduledJob $jobName
OPTION#2
Run the script from Azure Runbook
- Create a new Automation Account as described here and make sure you choose “YES” for option “Create Azure Run As Account”.
- Import the following Azure Modules by browsing the gallery:
Az.Accounts (≥ 2.2.2)
Az.Storage
Az.Automation
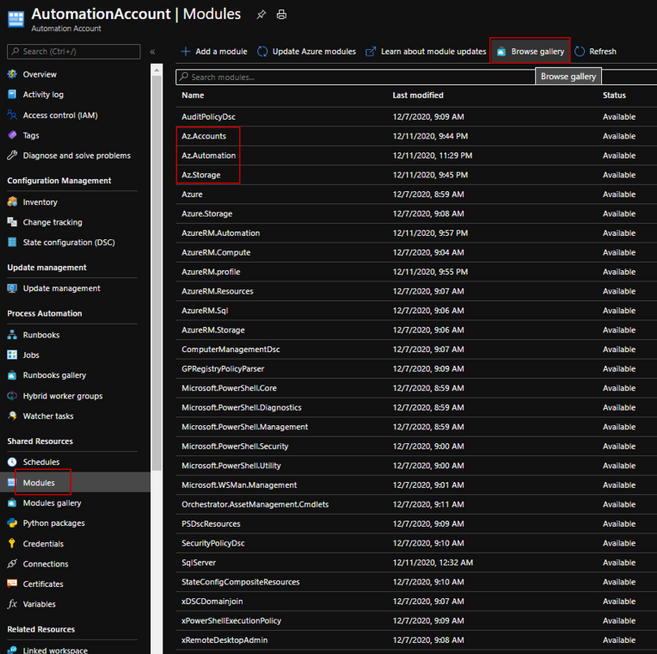 browse gallery – add module
browse gallery – add module
- Create a runbook to run the script and make sure you choose Powershell runbook type.
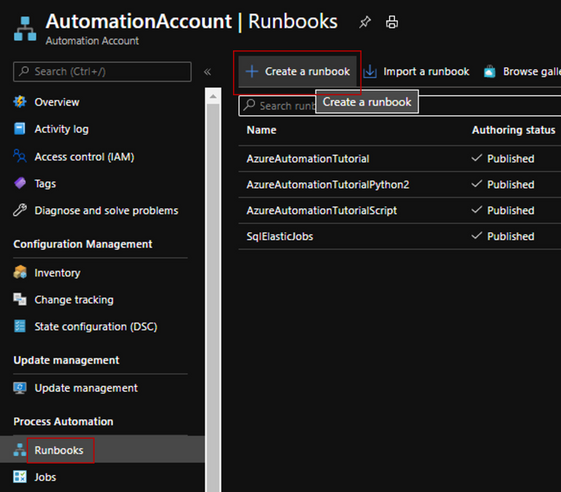 add a runbook
add a runbook
- Add the following login section when connecting from a Runbook
## =========================================================================
## Login when running from a Runbook
## =========================================================================
## Enable this code section when running from Azure Runbook
## Get the connection "AzureRunAsConnection" when run from automation account
$connection = Get-AutomationConnection -Name AzureRunAsConnection
Connect-AzAccount `
-ServicePrincipal `
-Tenant $connection.TenantID `
-ApplicationId $connection.ApplicationID `
-CertificateThumbprint $connection.CertificateThumbprint
"Login successful..."
 schedule task
schedule task
Note: Script execution can be monitored in the portal and alerts can be set for any script execution failure.
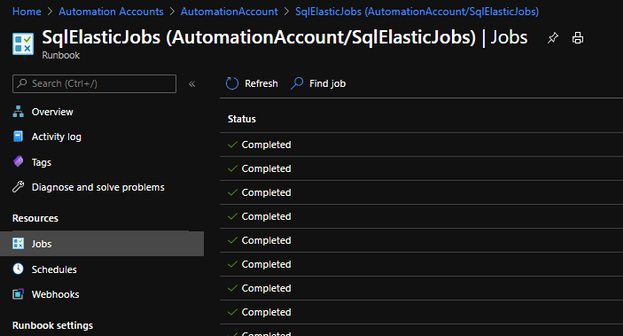 job execution monitor
job execution monitor
The script can be found in the following Git repository. This project welcomes contributions and suggestions.


Recent Comments