by Scott Muniz | Mar 29, 2021 | Security, Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
389-ds-base — 389-ds-base
|
When binding against a DN during authentication, the reply from 389-ds-base will be different whether the DN exists or not. This can be used by an unauthenticated attacker to check the existence of an entry in the LDAP database. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35518
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
askey — fiber_router
|
Askey Fiber Router RTF3505VW-N1 BR_SV_g000_R3505VWN1001_s32_7 devices allow Remote Code Execution and retrieval of admin credentials to log into the Dashboard or login via SSH, leading to code execution as root. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-28695
MISC |
basercms — basercms
|
Improper neutralization of JavaScript input in the page editing function of baserCMS versions prior to 4.4.5 allows remote authenticated attackers to inject an arbitrary script via unspecified vectors. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20681
MISC
MISC |
basercms — basercms
|
baserCMS versions prior to 4.4.5 allows a remote attacker with an administrative privilege to execute arbitrary OS commands via unspecified vectors. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20682
MISC
MISC |
basercms — basercms
|
Improper neutralization of JavaScript input in the blog article editing function of baserCMS versions prior to 4.4.5 allows remote authenticated attackers to inject an arbitrary script via unspecified vectors. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20683
MISC
MISC |
bluemonday — bluemonday
|
bluemonday before 1.0.5 allows XSS because certain Go lowercasing converts an uppercase Cyrillic character, defeating a protection mechanism against the “script” string. |
2021-03-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29272
MISC
MISC |
btcpay — server
|
BTCPay Server before 1.0.6.0, when the payment button is used, has a privacy vulnerability. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29249
MISC
MISC |
| ca — ehealth_performance_manager |
** UNSUPPORTED WHEN ASSIGNED ** CA eHealth Performance Manager through 6.3.2.12 is affected by Privilege Escalation via a setuid (and/or setgid) file. When a component is run as an argument of the runpicEhealth executable, the script code will be executed as the ehealth user. NOTE: This vulnerability only affects products that are no longer supported by the maintainer. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28250
MISC |
ca — ehealth_performance_manager
|
** UNSUPPORTED WHEN ASSIGNED ** CA eHealth Performance Manager through 6.3.2.12 is affected by Privilege Escalation via a Dynamically Linked Shared Object Library. A regular user must create a malicious library in the writable RPATH, to be dynamically linked when the emtgtctl2 executable is run. The code in the library will be executed as the ehealth user. NOTE: This vulnerability only affects products that are no longer supported by the maintainer. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28246
MISC |
ca — ehealth_performance_manager
|
** UNSUPPORTED WHEN ASSIGNED ** CA eHealth Performance Manager through 6.3.2.12 is affected by Cross Site Scripting (XSS). The impact is: An authenticated remote user is able to inject arbitrary web script or HTML due to incorrect sanitization of user-supplied data and perform a Reflected Cross-Site Scripting attack against the platform users. The affected endpoints are: cgi/nhWeb with the parameter report, aviewbin/filtermibobjects.pl with the parameter namefilter, and aviewbin/query.pl with the parameters System, SystemText, Group, and GroupText. NOTE: This vulnerability only affects products that are no longer supported by the maintainer. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28247
MISC |
ca — ehealth_performance_manager
|
** UNSUPPORTED WHEN ASSIGNED ** CA eHealth Performance Manager through 6.3.2.12 is affected by Improper Restriction of Excessive Authentication Attempts. An attacker is able to perform an arbitrary number of /web/frames/ authentication attempts using different passwords, and eventually gain access to a targeted account, NOTE: This vulnerability only affects products that are no longer supported by the maintainer. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28248
MISC |
ca — ehealth_performance_manager
|
** UNSUPPORTED WHEN ASSIGNED ** CA eHealth Performance Manager through 6.3.2.12 is affected by Privilege Escalation via a Dynamically Linked Shared Object Library. To exploit the vulnerability, the ehealth user must create a malicious library in the writable RPATH, to be dynamically linked when the FtpCollector executable is run. The code in the library will be executed as the root user. NOTE: This vulnerability only affects products that are no longer supported by the maintainer. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28249
MISC |
canpack — canpack
|
A flaw was found in upx canPack in p_lx_elf.cpp in UPX 3.96. This flaw allows attackers to cause a denial of service (SEGV or buffer overflow and application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impacts via a crafted ELF. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to system availability. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20285
MISC
MISC |
cisco — access_points_software
|
A vulnerability in the boot logic of Cisco Access Points Software could allow an authenticated, local attacker to execute unsigned code at boot time. The vulnerability is due to an improper check that is performed by the area of code that manages system startup processes. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by modifying a specific file that is stored on the system, which would allow the attacker to bypass existing protections. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute unsigned code at boot time and bypass the software image verification check part of the secure boot process of an affected device. Note: To exploit this vulnerability, the attacker would need to have access to the development shell (devshell) on the device. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1449
CISCO |
cisco — aironet_access_points
|
A vulnerability in the implementation of a CLI command in Cisco Aironet Access Points (AP) could allow an authenticated, local attacker to overwrite files in the flash memory of the device. This vulnerability is due to insufficient input validation for a specific command. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by issuing a command with crafted arguments. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to overwrite or create files with data that is already present in other files that are hosted on the affected device. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1423
CISCO |
cisco — aironet_access_points
|
A vulnerability in the multicast DNS (mDNS) gateway feature of Cisco Aironet Series Access Points Software could allow an unauthenticated, adjacent attacker to cause a denial of service (DoS) condition on an affected device. This vulnerability is due to insufficient input validation of incoming mDNS traffic. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a crafted mDNS packet to an affected device through a wireless network that is configured in FlexConnect local switching mode or through a wired network on a configured mDNS VLAN. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause the access point (AP) to reboot, resulting in a DoS condition. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1439
CISCO |
cisco — aironet_access_points
|
A vulnerability in the FlexConnect Upgrade feature of Cisco Aironet Series Access Points Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to obtain confidential information from an affected device. This vulnerability is due to an unrestricted Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) configuration. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a specific TFTP request to an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to download any file from the filesystem of the affected access point (AP). |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1437
CISCO |
cisco — ios_ios_and_ios_xe_software
|
A vulnerability in the CLI command permissions of Cisco IOS and Cisco IOS XE Software could allow an authenticated, local attacker to retrieve the password for Common Industrial Protocol (CIP) and then remotely configure the device as an administrative user. This vulnerability exists because incorrect permissions are associated with the show cip security CLI command. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by issuing the command to retrieve the password for CIP on an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to reconfigure the device. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1392
CISCO |
| cisco — ios_xe_sd-wan_software |
A vulnerability in the CLI of Cisco IOS XE SD-WAN Software could allow an authenticated, local attacker to execute arbitrary commands on the underlying operating system as the root user. The attacker must be authenticated on the affected device as a low-privileged user to exploit this vulnerability. This vulnerability is due to insufficient validation of user-supplied input. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by injecting arbitrary commands to a file as a lower-privileged user. The commands are then executed on the device by the root user. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary commands as the root user. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1432
CISCO |
| cisco — ios_xe_sd-wan_software |
A vulnerability in the CLI of Cisco IOS XE SD-WAN Software could allow an authenticated, local attacker to overwrite arbitrary files in the underlying file system. This vulnerability is due to insufficient validation of the parameters of a specific CLI command. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by issuing that command with specific parameters. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to overwrite the content of any arbitrary file that resides on the underlying host file system. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1434
CISCO |
| cisco — ios_xe_sd-wan_software |
A vulnerability in the role-based access control of Cisco IOS XE SD-WAN Software could allow an authenticated, local attacker with read-only privileges to obtain administrative privileges by using the console port when the device is in the default SD-WAN configuration. This vulnerability occurs because the default configuration is applied for console authentication and authorization. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by connecting to the console port and authenticating as a read-only user. A successful exploit could allow a user with read-only permissions to access administrative privileges. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1371
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_sd-wan_software
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in the CLI of Cisco IOS XE SD-WAN Software could allow an authenticated, local attacker to access the underlying operating system with root privileges. These vulnerabilities are due to insufficient input validation of certain CLI commands. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by authenticating to the device and submitting crafted input to the CLI. The attacker must be authenticated as an administrative user to execute the affected commands. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to access the underlying operating system with root privileges. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1383
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_sd-wan_software
|
A vulnerability in the CLI of Cisco IOS XE SD-WAN Software could allow an authenticated, local attacker to inject arbitrary commands to be executed with root privileges on the underlying operating system. This vulnerability is due to insufficient input validation on certain CLI commands. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by authenticating to the device and submitting crafted input to the CLI. The attacker must be authenticated as an administrative user to execute the affected commands. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute commands with root privileges. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1382
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_sd-wan_software
|
A vulnerability in the vDaemon process of Cisco IOS XE SD-WAN Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to cause a device to reload, resulting a denial of service (DoS) condition. This vulnerability is due to insufficient handling of malformed packets. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending crafted traffic to an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause the device to reload, resulting in a DoS condition. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1431
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_sd-wan_software
|
A vulnerability in the vDaemon process in Cisco IOS XE SD-WAN Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to cause a buffer overflow on an affected device. This vulnerability is due to insufficient bounds checking when the device processes traffic. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending crafted traffic to the device. The attacker must have a man-in-the-middle position between Cisco vManage and an associated device that is running an affected version of Cisco IOS XE SD-WAN Software. An exploit could allow the attacker to conduct a controllable buffer overflow attack (and possibly execute arbitrary commands as the root user) or cause a device reload, resulting in a denial of service (DoS) condition. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1433
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_sd-wan_software
|
A vulnerability in the CLI of Cisco IOS XE SD-WAN Software could allow an authenticated, local attacker to conduct path traversal attacks and obtain read access to sensitive files on an affected system. This vulnerability is due to insufficient validation of user-supplied input. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a crafted request to an affected system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to view arbitrary files on the affected system. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1436
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_sd-wan_software
|
A vulnerability in CLI management in Cisco IOS XE SD-WAN Software could allow an authenticated, local attacker to access the underlying operating system as the root user. This vulnerability is due to the way the software handles concurrent CLI sessions. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by authenticating to the device as an administrative user and executing a sequence of commands. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to obtain access to the underlying operating system as the root user. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1281
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_sd-wan_software
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in the CLI of Cisco IOS XE SD-WAN Software could allow an authenticated, local attacker to access the underlying operating system with root privileges. These vulnerabilities are due to insufficient input validation of certain CLI commands. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by authenticating to the device and submitting crafted input to the CLI. The attacker must be authenticated as an administrative user to execute the affected commands. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to access the underlying operating system with root privileges. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1454
CISCO |
| cisco — ios_xe_software |
A vulnerability in the web UI of Cisco IOS XE Software could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to inject arbitrary commands that can be executed as the root user. This vulnerability is due to insufficient input validation. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a crafted request to the web UI of an affected device with arbitrary commands injected into a portion of the request. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary commands as the root user. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1435
CISCO |
| cisco — ios_xe_software |
A vulnerability in the DECnet Phase IV and DECnet/OSI protocol processing of Cisco IOS XE Software could allow an unauthenticated, adjacent attacker to cause a denial of service (DoS) condition on an affected device. The vulnerability is due to insufficient input validation of DECnet traffic that is received by an affected device. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending DECnet traffic to an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause the affected device to reload, resulting in a DoS condition. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1352
CISCO |
| cisco — ios_xe_software |
A vulnerability in Cisco IOS XE Software could allow an authenticated, local attacker with high privileges or an unauthenticated attacker with physical access to the device to open a debugging console. The vulnerability is due to insufficient command authorization restrictions. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by running commands on the hardware platform to open a debugging console. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to access a debugging console. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1381
CISCO |
| cisco — ios_xe_software |
A vulnerability in the web UI feature of Cisco IOS XE Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to conduct a cross-site WebSocket hijacking (CSWSH) attack and cause a denial of service (DoS) condition on an affected device. This vulnerability is due to insufficient HTTP protections in the web UI on an affected device. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by persuading an authenticated user of the web UI to follow a crafted link. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to corrupt memory on the affected device, forcing it to reload and causing a DoS condition. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1403
CISCO |
| cisco — ios_xe_software |
A vulnerability in the dragonite debugger of Cisco IOS XE Software could allow an authenticated, local attacker to escalate from privilege level 15 to root privilege. The vulnerability is due to the presence of development testing and verification scripts that remained on the device. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by bypassing the consent token mechanism with the residual scripts on the affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to escalate from privilege level 15 to root privilege. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1391
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_software
|
A vulnerability in the boot logic of Cisco IOS XE Software could allow an authenticated, local attacker with level 15 privileges or an unauthenticated attacker with physical access to execute arbitrary code on the underlying Linux operating system of an affected device. This vulnerability is due to incorrect validations of specific function arguments that are passed to the boot script. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by tampering with a specific file, which an affected device would process during the initial boot process. On systems that are protected by the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) secure boot feature, a successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute unsigned code at boot time and bypass the image verification check in the secure boot process of the affected device. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1398
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_software
|
A vulnerability in the Easy Virtual Switching System (VSS) feature of Cisco IOS XE Software for Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series Switches and Cisco Catalyst 4500-X Series Switches could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary code on the underlying Linux operating system of an affected device. The vulnerability is due to incorrect boundary checks of certain values in Easy VSS protocol packets that are destined for an affected device. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending crafted Easy VSS protocol packets to UDP port 5500 while the affected device is in a specific state. When the crafted packet is processed, a buffer overflow condition may occur. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to trigger a denial of service (DoS) condition or execute arbitrary code with root privileges on the underlying Linux operating system of the affected device. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1451
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_software
|
A vulnerability in the DNS application layer gateway (ALG) functionality used by Network Address Translation (NAT) in Cisco IOS XE Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to cause an affected device to reload. The vulnerability is due to a logic error that occurs when an affected device inspects certain DNS packets. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending crafted DNS packets through an affected device that is performing NAT for DNS packets. A successful exploit could allow an attacker to cause the device to reload, resulting in a denial of service (DoS) condition on an affected device. The vulnerability can be exploited only by traffic that is sent through an affected device via IPv4 packets. The vulnerability cannot be exploited via IPv6 traffic. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1446
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_software
|
A vulnerability in the web UI of Cisco IOS XE Software could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary code with root privileges on the underlying operating system of an affected device. The vulnerability exists because the affected software improperly sanitizes values that are parsed from a specific configuration file. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by tampering with a specific configuration file and then sending an API call. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to inject arbitrary code that would be executed on the underlying operating system of the affected device. To exploit this vulnerability, the attacker would need to have a privileged set of credentials to the device. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1443
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_software
|
A vulnerability in the ROM Monitor (ROMMON) of Cisco IOS XE Software for Cisco Catalyst IE3200, IE3300, and IE3400 Rugged Series Switches, Cisco Catalyst IE3400 Heavy Duty Series Switches, and Cisco Embedded Services 3300 Series Switches could allow an unauthenticated, physical attacker to execute unsigned code at system boot time. This vulnerability is due to incorrect validations of specific function arguments passed to a boot script when specific ROMMON variables are set. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by setting malicious values for a specific ROMMON variable. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute unsigned code and bypass the image verification check during the secure boot process of an affected device. To exploit this vulnerability, the attacker would need to have unauthenticated, physical access to the device or obtain privileged access to the root shell on the device. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1452
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_software
|
A vulnerability in the software image verification functionality of Cisco IOS XE Software for the Cisco Catalyst 9000 Family of switches could allow an unauthenticated, physical attacker to execute unsigned code at system boot time. The vulnerability is due to an improper check in the code function that manages the verification of the digital signatures of system image files during the initial boot process. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by loading unsigned software on an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to boot a malicious software image or execute unsigned code and bypass the image verification check part of the secure boot process of an affected device. To exploit this vulnerability, the attacker would need to have unauthenticated physical access to the device or obtain privileged access to the root shell on the device. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1453
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_software
|
A vulnerability in one of the diagnostic test CLI commands of Cisco IOS XE Software could allow an authenticated, local attacker to execute arbitrary code on an affected device. To exploit this vulnerability, the attacker would need to have valid user credentials at privilege level 15. This vulnerability exists because the affected software permits modification of the run-time memory of an affected device under specific circumstances. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by authenticating to the affected device and issuing a specific diagnostic test command at the CLI. A successful exploit could trigger a logic error in the code that was designed to restrict run-time memory modifications. The attacker could take advantage of this logic error to overwrite system memory locations and execute arbitrary code on the underlying Linux operating system (OS) of the affected device. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1390
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_software
|
A vulnerability in the ingress traffic manager of Cisco IOS XE Software for Cisco Network Convergence System (NCS) 520 Routers could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to cause a denial of service (DoS) condition in the web management interface of an affected device. This vulnerability is due to incorrect processing of certain IPv4 TCP traffic that is destined to an affected device. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a large number of crafted TCP packets to the affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause the web management interface to become unavailable, resulting in a DoS condition. Note: This vulnerability does not impact traffic that is going through the device or going to the Management Ethernet interface of the device. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1394
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_software
|
A vulnerability in a diagnostic command for the Plug-and-Play (PnP) subsystem of Cisco IOS XE Software could allow an authenticated, local attacker to elevate privileges to the level of an Administrator user (level 15) on an affected device. The vulnerability is due to insufficient protection of sensitive information. An attacker with low privileges could exploit this vulnerability by issuing the diagnostic CLI show pnp profile when a specific PnP listener is enabled on the device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to obtain a privileged authentication token. This token can be used to send crafted PnP messages and execute privileged commands on the targeted system. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1442
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_software
|
A vulnerability in Cisco IOx application hosting environment of Cisco IOS XE Software could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to inject commands into the underlying operating system as the root user. This vulnerability is due to incomplete validation of fields in the application packages loaded onto IOx. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by creating a crafted application .tar file and loading it onto the device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to perform command injection into the underlying operating system as the root user. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1384
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_software
|
A vulnerability in Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) management of Cisco IOS Software and Cisco IOS XE Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to prevent an affected device from resolving ARP entries for legitimate hosts on the connected subnets. This vulnerability exists because ARP entries are mismanaged. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by continuously sending traffic that results in incomplete ARP entries. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause ARP requests on the device to be unsuccessful for legitimate hosts, resulting in a denial of service (DoS) condition. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1377
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_software
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in the fast reload feature of Cisco IOS XE Software running on Cisco Catalyst 3850, Cisco Catalyst 9300, and Cisco Catalyst 9300L Series Switches could allow an authenticated, local attacker to either execute arbitrary code on the underlying operating system, install and boot a malicious software image, or execute unsigned binaries on an affected device. These vulnerabilities are due to improper checks performed by system boot routines. To exploit these vulnerabilities, the attacker would need privileged access to the CLI of the device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to either execute arbitrary code on the underlying operating system or execute unsigned code and bypass the image verification check part of the secure boot process. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1376
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_software
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in the fast reload feature of Cisco IOS XE Software running on Cisco Catalyst 3850, Cisco Catalyst 9300, and Cisco Catalyst 9300L Series Switches could allow an authenticated, local attacker to either execute arbitrary code on the underlying operating system, install and boot a malicious software image, or execute unsigned binaries on an affected device. These vulnerabilities are due to improper checks performed by system boot routines. To exploit these vulnerabilities, the attacker would need privileged access to the CLI of the device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to either execute arbitrary code on the underlying operating system or execute unsigned code and bypass the image verification check part of the secure boot process. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1375
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_software
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web UI of Cisco IOS XE Software could allow an authenticated, remote attacker with read-only privileges to cause the web UI software to become unresponsive and consume vty line instances, resulting in a denial of service (DoS) condition. These vulnerabilities are due to insufficient error handling in the web UI. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending crafted HTTP packets to an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause the web UI software to become unresponsive and consume all available vty lines, preventing new session establishment and resulting in a DoS condition. Manual intervention would be required to regain web UI and vty session functionality. Note: These vulnerabilities do not affect the console connection. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1356
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_software
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web UI of Cisco IOS XE Software could allow an authenticated, remote attacker with read-only privileges to cause the web UI software to become unresponsive and consume vty line instances, resulting in a denial of service (DoS) condition. These vulnerabilities are due to insufficient error handling in the web UI. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending crafted HTTP packets to an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause the web UI software to become unresponsive and consume all available vty lines, preventing new session establishment and resulting in a DoS condition. Manual intervention would be required to regain web UI and vty session functionality. Note: These vulnerabilities do not affect the console connection. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1220
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_software
|
A vulnerability in the hardware initialization routines of Cisco IOS XE Software for Cisco 1100 Series Industrial Integrated Services Routers and Cisco ESR6300 Embedded Series Routers could allow an authenticated, local attacker to execute unsigned code at system boot time. This vulnerability is due to incorrect validations of parameters passed to a diagnostic script that is executed when the device boots up. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by tampering with an executable file stored on a device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute unsigned code at boot time and bypass the software image verification check part of the secure boot process of an affected device. To exploit this vulnerability, the attacker would need administrative level credentials (level 15) on the device. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1441
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_wireless_controller
|
A vulnerability in the web-based management interface of Cisco IOS XE Wireless Controller software for the Catalyst 9000 Family of switches could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to conduct a cross-site scripting (XSS) attack against another user of the web-based management interface of an affected device. The vulnerability is due to insufficient validation of user-supplied input by the web-based management interface of an affected device. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by authenticating to the device as a high-privileged user, adding certain configurations with malicious code in one of its fields, and persuading another user to click on it. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary script code in the context of the affected interface or to access sensitive, browser-based information. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1374
CISCO |
cisco — ios_xe_wireless_controller
|
A vulnerability in the Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP) protocol processing of Cisco IOS XE Wireless Controller Software for the Cisco Catalyst 9000 Family Wireless Controllers could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to cause a denial of service (DoS) condition of an affected device. The vulnerability is due to insufficient validation of CAPWAP packets. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a malformed CAPWAP packet to an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause the affected device to crash and reload, resulting in a DoS condition. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1373
CISCO |
cisco — iox_application_framework
|
A vulnerability in the Cisco IOx Application Framework of Cisco 809 Industrial Integrated Services Routers (Industrial ISRs), Cisco 829 Industrial ISRs, Cisco CGR 1000 Compute Module, and Cisco IC3000 Industrial Compute Gateway could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to cause a denial of service (DoS) condition on an affected device. This vulnerability is due to insufficient error handling during packet processing. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a high and sustained rate of crafted TCP traffic to the IOx web server on an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause the IOx web server to stop processing requests, resulting in a DoS condition. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1460
CISCO |
| cisco — jabber |
Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco Jabber for Windows, Cisco Jabber for MacOS, and Cisco Jabber for mobile platforms could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary programs on the underlying operating system with elevated privileges, access sensitive information, intercept protected network traffic, or cause a denial of service (DoS) condition. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1417
CISCO |
| cisco — jabber |
Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco Jabber for Windows, Cisco Jabber for MacOS, and Cisco Jabber for mobile platforms could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary programs on the underlying operating system with elevated privileges, access sensitive information, intercept protected network traffic, or cause a denial of service (DoS) condition. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1418
CISCO |
cisco — jabber
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco Jabber for Windows, Cisco Jabber for MacOS, and Cisco Jabber for mobile platforms could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary programs on the underlying operating system with elevated privileges, access sensitive information, intercept protected network traffic, or cause a denial of service (DoS) condition. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1471
CISCO |
cisco — jabber
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco Jabber for Windows, Cisco Jabber for MacOS, and Cisco Jabber for mobile platforms could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary programs on the underlying operating system with elevated privileges, access sensitive information, intercept protected network traffic, or cause a denial of service (DoS) condition. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1469
CISCO |
cisco — jabber
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco Jabber for Windows, Cisco Jabber for MacOS, and Cisco Jabber for mobile platforms could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary programs on the underlying operating system with elevated privileges, access sensitive information, intercept protected network traffic, or cause a denial of service (DoS) condition. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1411
CISCO |
cisco — multiple_products
|
A vulnerability in the Cisco IOx application hosting environment of multiple Cisco platforms could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to conduct directory traversal attacks and read and write files on the underlying operating system or host system. This vulnerability occurs because the device does not properly validate URIs in IOx API requests. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a crafted API request that contains directory traversal character sequences to an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to read or write arbitrary files on the underlying operating system. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1385
CISCO |
clienthello — clienthello
|
An OpenSSL TLS server may crash if sent a maliciously crafted renegotiation ClientHello message from a client. If a TLSv1.2 renegotiation ClientHello omits the signature_algorithms extension (where it was present in the initial ClientHello), but includes a signature_algorithms_cert extension then a NULL pointer dereference will result, leading to a crash and a denial of service attack. A server is only vulnerable if it has TLSv1.2 and renegotiation enabled (which is the default configuration). OpenSSL TLS clients are not impacted by this issue. All OpenSSL 1.1.1 versions are affected by this issue. Users of these versions should upgrade to OpenSSL 1.1.1k. OpenSSL 1.0.2 is not impacted by this issue. Fixed in OpenSSL 1.1.1k (Affected 1.1.1-1.1.1j). |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3449
MLIST
MLIST
MLIST
MLIST
CONFIRM
MISC
CONFIRM
CISCO
DEBIAN
CONFIRM |
containernetworking/cni — containernetworking/cni
|
An improper limitation of path name flaw was found in containernetworking/cni in versions before 0.8.1. When specifying the plugin to load in the ‘type’ field in the network configuration, it is possible to use special elements such as “../” separators to reference binaries elsewhere on the system. This flaw allows an attacker to execute other existing binaries other than the cni plugins/types, such as ‘reboot’. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to confidentiality, integrity, as well as system availability. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20206
MISC
MISC |
esri — arcgis_server
|
Multiple buffer overflow vulnerabilities when parsing a specially crafted file in Esri ArcGIS Server 10.8.1 (and earlier) allows an authenticated attacker with specialized permissions to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the service account. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29094
CONFIRM |
esri — arcgis_server
|
A use-after-free vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file in Esri ArcGIS Server 10.8.1 (and earlier) allows an authenticated attacker with specialized permissions to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the service account. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29093
CONFIRM |
| esri — multiple_products |
A use-after-free vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file in Esri ArcReader, ArcGIS Desktop, ArcGIS Engine 10.8.1 (and earlier) and ArcGIS Pro 2.7 (and earlier) allows an unauthenticated attacker to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29096
CONFIRM |
forgerock — openam
|
ForgeRock OpenAM before 13.5.1 allows LDAP injection via the Webfinger protocol. For example, an unauthenticated attacker can perform character-by-character retrieval of password hashes, or retrieve a session token or a private key. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29156
MISC
MISC |
| freebsd — freebsd |
In FreeBSD 12.2-STABLE before r369334, 11.4-STABLE before r369335, 12.2-RELEASE before p4 and 11.4-RELEASE before p8 when a process, such as jexec(8) or killall(1), calls jail_attach(2) to enter a jail, the jailed root can attach to it using ptrace(2) before the current working directory is changed. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-25582
MISC |
| freebsd — freebsd |
In FreeBSD 12.2-STABLE before r365767, 11.4-STABLE before r365769, 12.1-RELEASE before p10, 11.4-RELEASE before p4 and 11.3-RELEASE before p14 a number of AMD virtualization instructions operate on host physical addresses, are not subject to nested page table translation, and guest use of these instructions was not trapped. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-7467
MISC |
| freebsd — freebsd |
In FreeBSD 12.2-STABLE before r365772, 11.4-STABLE before r365773, 12.1-RELEASE before p10, 11.4-RELEASE before p4 and 11.3-RELEASE before p14 a ftpd(8) bug in the implementation of the file system sandbox, combined with capabilities available to an authenticated FTP user, can be used to escape the file system restriction configured in ftpchroot(5). Moreover, the bug allows a malicious client to gain root privileges. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-7468
MISC |
| freebsd — freebsd |
In 11.4-PRERELEASE before r360733 and 11.3-RELEASE before p13, improper mbuf handling in the kernel causes a use-after-free bug by sending IPv6 Hop-by-Hop options over the loopback interface. The use-after-free situation may result in unintended kernel behaviour including a kernel panic. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-7462
MISC |
| freebsd — freebsd |
In FreeBSD 12.2-STABLE before r369312, 11.4-STABLE before r369313, 12.2-RELEASE before p4 and 11.4-RELEASE before p8 due to a race condition in the jail_remove(2) implementation, it may fail to kill some of the processes. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-25581
MISC |
freebsd — freebsd
|
In FreeBSD 12.2-STABLE before r368969, 11.4-STABLE before r369047, 12.2-RELEASE before p3, 12.1-RELEASE before p13 and 11.4-RELEASE before p7 several file systems were not properly initializing the d_off field of the dirent structures returned by VOP_READDIR. In particular, tmpfs(5), smbfs(5), autofs(5) and mqueuefs(5) were failing to do so. As a result, eight uninitialized kernel stack bytes may be leaked to userspace by these file systems. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-25578
MISC |
freebsd — freebsd
|
In FreeBSD 12.2-STABLE before r368969, 11.4-STABLE before r369047, 12.2-RELEASE before p3, 12.1-RELEASE before p13 and 11.4-RELEASE before p7 msdosfs(5) was failing to zero-fill a pair of padding fields in the dirent structure, resulting in a leak of three uninitialized bytes. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-25579
MISC |
freebsd — freebsd
|
In FreeBSD 12.1-STABLE before r365010, 11.4-STABLE before r365011, 12.1-RELEASE before p9, 11.4-RELEASE before p3, and 11.3-RELEASE before p13, dhclient(8) fails to handle certain malformed input related to handling of DHCP option 119 resulting a heap overflow. The heap overflow could in principle be exploited to achieve remote code execution. The affected process runs with reduced privileges in a Capsicum sandbox, limiting the immediate impact of an exploit. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-7461
MISC |
freebsd — freebsd
|
In FreeBSD 12.2-STABLE before r369346, 11.4-STABLE before r369345, 12.2-RELEASE before p4 and 11.4-RELEASE before p8 a regression in the login.access(5) rule processor has the effect of causing rules to fail to match even when they should not. This means that rules denying access may be ignored. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-25580
MISC |
freebsd — freebsd
|
In FreeBSD 12.1-STABLE before r364644, 11.4-STABLE before r364651, 12.1-RELEASE before p9, 11.4-RELEASE before p3, and 11.3-RELEASE before p13, improper handling in the kernel causes a use-after-free bug by sending large user messages from multiple threads on the same SCTP socket. The use-after-free situation may result in unintended kernel behaviour including a kernel panic. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-7463
MISC |
freebsd — freebsd
|
In FreeBSD 12.2-STABLE before r365730, 11.4-STABLE before r365738, 12.1-RELEASE before p10, 11.4-RELEASE before p4, and 11.3-RELEASE before p14, a programming error in the ure(4) device driver caused some Realtek USB Ethernet interfaces to incorrectly report packets with more than 2048 bytes in a single USB transfer as having a length of only 2048 bytes. An adversary can exploit this to cause the driver to misinterpret part of the payload of a large packet as a separate packet, and thereby inject packets across security boundaries such as VLANs. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-7464
MISC |
fuji — multiple_devices
|
Fuji Xerox multifunction devices and printers (DocuCentre-VII C7773/C6673/C5573/C4473/C3373/C3372/C2273, DocuCentre-VII C7788/C6688/C5588, ApeosPort-VII C7773/C6673/C5573/C4473/C3373/C3372 C2273, ApeosPort-VII C7788/C6688/C5588, ApeosPort C7070/C6570/C5570/C4570/C3570/C3070/C7070G/C6570G/C5570G/C4570G/C3570G/C3070G, ApeosPort-VII C4421/C3321, ApeosPort C3060/C2560/C2060/C3060G/C2560G/C2060G, ApeosPort-VII CP4421, ApeosPort Print C5570, ApeosPort 5570/4570/5570G/4570G, ApeosPort 3560/3060/2560/3560G/3060G/2560G, ApeosPort-VII 5021/ 4021, ApeosPort-VII P5021, DocuPrint CP 555 d/505 d, DocuPrint P505 d, PrimeLink C9065/C9070, DocuPrint CP475AP, and DocuPrint P475AP) allow an attacker to cause a denial of service (DoS) condition and abnormal end (ABEND) of the affected products via sending a specially crafted command. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20679
MISC
MISC
MISC |
ge — mu320e
|
The software contains a hard-coded password that could allow an attacker to take control of the merging unit using these hard-coded credentials on the MU320E (all firmware versions prior to v04A00.1). |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27452
MISC |
ge — mu320e
|
A miscommunication in the file system allows adversaries with access to the MU320E to escalate privileges on the MU320E (all firmware versions prior to v04A00.1). |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27448
MISC |
ge — mu320e
|
SSH server configuration file does not implement some best practices. This could lead to a weakening of the SSH protocol strength, which could lead to additional misconfiguration or be leveraged as part of a larger attack on the MU320E (all firmware versions prior to v04A00.1). |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27450
MISC |
| ge — reason_dr60 |
The software contains a hard-coded password it uses for its own inbound authentication or for outbound communication to external components on the Reason DR60 (all firmware versions prior to 02A04.1). |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27438
MISC |
ge — reason_dr60
|
The software contains a hard-coded password it uses for its own inbound authentication or for outbound communication to external components on the Reason DR60 (all firmware versions prior to 02A04.1). |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27440
MISC |
ge — reason_dr60
|
The software performs an operation at a privilege level higher than the minimum level required, which creates new weaknesses or amplifies the consequences of other weaknesses on the Reason DR60 (all firmware versions prior to 02A04.1). |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27454
MISC |
gitlab — gitlab
|
In all versions of GitLab starting from 13.7, marshalled session keys were being stored in Redis. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22194
CONFIRM
MISC |
gitlab — gitlab
|
An information disclosure issue in GitLab starting from version 12.8 allowed a user with access to the server logs to see sensitive information that wasn’t properly redacted. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22184
CONFIRM
MISC |
gitlab — gitlab
|
An issue has been discovered in GitLab affecting all versions starting from 13.4. Improper access control allows unauthorized users to access details on analytic pages. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22180
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
gitlab — gitlab
|
Improper authorization in GitLab 12.8+ allows a guest user in a private project to view tag data that should be inaccessible on the releases page |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22172
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
gnu — binutils
|
A flaw was found in GNU Binutils 2.35.1, where there is a heap-based buffer overflow in _bfd_elf_slurp_secondary_reloc_section in elf.c due to the number of symbols not calculated correctly. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to system availability. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20284
MISC
MISC |
gnu — binutils
|
There is an open race window when writing output in the following utilities in GNU binutils version 2.35 and earlier:ar, objcopy, strip, ranlib. When these utilities are run as a privileged user (presumably as part of a script updating binaries across different users), an unprivileged user can trick these utilities into getting ownership of arbitrary files through a symlink. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20197
MISC
MISC |
gnu — tar
|
A flaw was found in the src/list.c of tar 1.33 and earlier. This flaw allows an attacker who can submit a crafted input file to tar to cause uncontrolled consumption of memory. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to system availability. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20193
MISC
MISC
MISC |
grafana — enterprise
|
Grafana Enterprise 7.2.x and 7.3.x before 7.3.10 and 7.4.x before 7.4.5 allows a dashboard editor to bypass a permission check concerning a data source they should not be able to access. |
2021-03-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27962
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
imagemagik — imagemagik
|
A heap based buffer overflow in coders/tiff.c may result in program crash and denial of service in ImageMagick before 7.0.10-45. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-27829
MISC
MISC |
jasper_project — jasper
|
A NULL pointer dereference flaw was found in the way Jasper versions before 2.0.26 handled component references in CDEF box in the JP2 image format decoder. A specially crafted JP2 image file could cause an application using the Jasper library to crash when opened. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3467
MISC
FEDORA |
jasper_project — jasper
|
A NULL pointer dereference flaw was found in the way Jasper versions before 2.0.27 handled component references in the JP2 image format decoder. A specially crafted JP2 image file could cause an application using the Jasper library to crash when opened. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3443
MISC |
kde — discover
|
libdiscover/backends/KNSBackend/KNSResource.cpp in KDE Discover before 5.21.3 automatically creates links to potentially dangerous URLs (that are neither https:// nor http://) based on the content of the store.kde.org web site. (5.18.7 is also a fixed version.) |
2021-03-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28117
MISC
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
MISC |
kongchuanhujiao/server — kongchuanhujiao/server
|
In github.com/kongchuanhujiao/server before version 1.3.21 there is an authentication Bypass by Primary Weakness vulnerability. All users are impacted. This is fixed in version 1.3.21. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21403
MISC
CONFIRM |
librit — librit
|
app/views_mod/user/user.py in LibrIT PaSSHport through 2.5 is affected by LDAP Injection. There is an information leak through the crafting of special queries, escaping the provided search filter because user input gets no sanitization. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3027
MISC |
linux — linux_kernel
|
A flaw possibility of race condition and incorrect initialization of the process id was found in the Linux kernel child/parent process identification handling while filtering signal handlers. A local attacker is able to abuse this flaw to bypass checks to send any signal to a privileged process. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35508
MISC
MISC |
linux — linux_kernel
|
An issue was discovered in the Linux kernel before 5.11.7. usbip_sockfd_store in drivers/usb/usbip/stub_dev.c allows attackers to cause a denial of service (GPF) because the stub-up sequence has race conditions during an update of the local and shared status, aka CID-9380afd6df70. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29265
MISC
MISC |
linux — linux_kernel
|
An issue was discovered in the Linux kernel through 5.11.10. drivers/net/ethernet/freescale/gianfar.c in the Freescale Gianfar Ethernet driver allows attackers to cause a system crash because a negative fragment size is calculated in situations involving an rx queue overrun when jumbo packets are used and NAPI is enabled, aka CID-d8861bab48b6. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29264
MISC |
linux — linux_kernel
|
An issue was discovered in the Linux kernel before 5.11.9. drivers/vhost/vdpa.c has a use-after-free because v->config_ctx has an invalid value upon re-opening a character device, aka CID-f6bbf0010ba0. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29266
MISC
MISC |
| mcafee — epolicy_orchestrator |
Cross-Site Scripting vulnerability in McAfee ePolicy Orchestrator (ePO) prior to 5.10 Update 10 allows ePO administrators to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via multiple parameters where the administrator’s entries were not correctly sanitized. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-23889
CONFIRM |
| mcafee — epolicy_orchestrator |
Information leak vulnerability in the Agent Handler of McAfee ePolicy Orchestrator (ePO) prior to 5.10 Update 10 allows an unauthenticated user to download McAfee product packages (specifically McAfee Agent) available in ePO repository and install them on their own machines to have it managed and then in turn get policy details from the ePO server. This can only happen when the ePO Agent Handler is installed in a Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) to service machines not connected to the network through a VPN. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-23890
CONFIRM |
mcafee — epolicy_orchestrator
|
Unvalidated client-side URL redirect vulnerability in McAfee ePolicy Orchestrator (ePO) prior to 5.10 Update 10 could cause an authenticated ePO user to load an untrusted site in an ePO iframe which could steal information from the authenticated user. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-23888
CONFIRM |
micro_focus — access_manager
|
Advance configuration exposing Information Leakage vulnerability in Micro Focus Access Manager product, affects all versions prior to version 5.0. The vulnerability could cause information leakage. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22506
MISC |
micro_focus — access_manager
|
Cross-Site scripting vulnerability in Micro Focus Access Manager product, affects all version prior to version 5.0. The vulnerability could cause configuration destruction. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-25840
MISC |
microseven — mym71080i-b_devices
|
MicroSeven MYM71080i-B 2.0.5 through 2.0.20 devices send admin credentials in cleartext to pnp.microseven.com TCP port 7007. An attacker on the same network as the device can capture these credentials. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29255
MISC
MISC |
mifos-mobile — mifosx
|
Mifos-Mobile Android Application for MifosX is an Android Application built on top of the MifosX Self-Service platform. Mifos-Mobile before commit e505f62 disables HTTPS hostname verification of its HTTP client. Additionally it accepted any self-signed certificate as valid. Hostname verification is an important part when using HTTPS to ensure that the presented certificate is valid for the host. Disabling it can allow for man-in-the-middle attacks. Accepting any certificate, even self-signed ones allows man-in-the-middle attacks. This problem is fixed in mifos-mobile commit e505f62. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21385
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
| mulesoft — mulesoft |
MuleSoft is aware of a XML External Entity (XXE) vulnerability affecting certain versions of a Mule runtime component that may affect both CloudHub and on-premise customers. Affected versions: Mule 4.x runtime released before February 2, 2021. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1628
MISC |
mulesoft — mulesoft
|
MuleSoft is aware of a Server Side Request Forgery vulnerability affecting certain versions of a Mule runtime component that may affect both CloudHub and on-premise customers. This affects: Mule 3.8.x,3.9.x,4.x runtime released before February 2, 2021. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1627
MISC |
mulesoft — mulesoft
|
MuleSoft is aware of a Remote Code Execution vulnerability affecting certain versions of a Mule runtime component that may affect both CloudHub and on-premise customers. Versions affected: Mule 4.1.x and 4.2.x runtime released before February 2, 2021. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1626
MISC |
nanopb — nanopb
|
Nanopb is a small code-size Protocol Buffers implementation in ansi C. In Nanopb before versions 0.3.9.8 and 0.4.5, decoding a specifically formed message can cause invalid `free()` or `realloc()` calls if the message type contains an `oneof` field, and the `oneof` directly contains both a pointer field and a non-pointer field. If the message data first contains the non-pointer field and then the pointer field, the data of the non-pointer field is incorrectly treated as if it was a pointer value. Such message data rarely occurs in normal messages, but it is a concern when untrusted data is parsed. This has been fixed in versions 0.3.9.8 and 0.4.5. See referenced GitHub Security Advisory for more information including workarounds. |
2021-03-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21401
MISC
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
| netop — vision_pro |
Cleartext transmission of sensitive information in Netop Vision Pro up to and including 9.7.1 allows a remote unauthenticated attacker to gather credentials including Windows login usernames and passwords. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27194
MISC |
netop — vision_pro
|
Local privilege escalation vulnerability in Windows clients of Netop Vision Pro up to and including 9.7.1 allows a local user to gain administrator privileges whilst using the clients. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27192
MISC |
netop — vision_pro
|
Improper Authorization vulnerability in Netop Vision Pro up to and including to 9.7.1 allows an attacker to replay network traffic. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27195
MISC |
netop — vision_pro
|
Incorrect default permissions vulnerability in the API of Netop Vision Pro up to and including 9.7.1 allows a remote unauthenticated attacker to read and write files on the remote machine with system privileges resulting in a privilege escalation. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27193
MISC |
| nimble — nimble |
Nimble is a package manager for the Nim programming language. In Nim release versions before versions 1.2.10 and 1.4.4, “nimble refresh” fetches a list of Nimble packages over HTTPS without full verification of the SSL/TLS certificate due to the default setting of httpClient. An attacker able to perform MitM can deliver a modified package list containing malicious software packages. If the packages are installed and used the attack escalates to untrusted code execution. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21374
MISC
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
nimble — nimble
|
Nimble is a package manager for the Nim programming language. In Nim release version before versions 1.2.10 and 1.4.4, Nimble doCmd is used in different places and can be leveraged to execute arbitrary commands. An attacker can craft a malicious entry in the packages.json package list to trigger code execution. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21372
MISC
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
nimble — nimble
|
Nimble is a package manager for the Nim programming language. In Nim release versions before versions 1.2.10 and 1.4.4, “nimble refresh” fetches a list of Nimble packages over HTTPS by default. In case of error it falls back to a non-TLS URL http://irclogs.nim-lang.org/packages.json. An attacker able to perform MitM can deliver a modified package list containing malicious software packages. If the packages are installed and used the attack escalates to untrusted code execution. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21373
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
nokia — netact
|
An issue was discovered in Nokia NetAct 18A. A malicious user can change a filename of an uploaded file to include JavaScript code, which is then stored and executed by a victim’s web browser. The most common mechanism for delivering malicious content is to include it as a parameter in a URL that is posted publicly or e-mailed directly to victims. Here, the /netact/sct filename parameter is used. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-26596
MISC
MISC |
nokia — netact
|
An issue was discovered in Nokia NetAct 18A. A remote user, authenticated to the NOKIA NetAct Web Page, can visit the Site Configuration Tool web site section and arbitrarily upload potentially dangerous files without restrictions via the /netact/sct dir parameter in conjunction with the operation=upload value. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-26597
MISC
MISC |
oauth2-proxy — oauth2-proxy
|
OAuth2-Proxy is an open source reverse proxy that provides authentication with Google, Github or other providers. The `–gitlab-group` flag for group-based authorization in the GitLab provider stopped working in the v7.0.0 release. Regardless of the flag settings, authorization wasn’t restricted. Additionally, any authenticated users had whichever groups were set in `–gitlab-group` added to the new `X-Forwarded-Groups` header to the upstream application. While adding GitLab project based authorization support in #630, a bug was introduced where the user session’s groups field was populated with the `–gitlab-group` config entries instead of pulling the individual user’s group membership from the GitLab Userinfo endpoint. When the session groups where compared against the allowed groups for authorization, they matched improperly (since both lists were populated with the same data) so authorization was allowed. This impacts GitLab Provider users who relies on group membership for authorization restrictions. Any authenticated users in your GitLab environment can access your applications regardless of `–gitlab-group` membership restrictions. This is patched in v7.1.0. There is no workaround for the Group membership bug. But `–gitlab-project` can be set to use Project membership as the authorization checks instead of groups; it is not broken. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21411
MISC
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
openid — connect_server
|
The OpenID Connect server implementation for MITREid Connect through 1.3.3 contains a Server Side Request Forgery (SSRF) vulnerability. The vulnerability arises due to unsafe usage of the logo_uri parameter in the Dynamic Client Registration request. An unauthenticated attacker can make a HTTP request from the vulnerable server to any address in the internal network and obtain its response (which might, for example, have a JavaScript payload for resultant XSS). The issue can be exploited to bypass network boundaries, obtain sensitive data, or attack other hosts in the internal network. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-26715
MISC
MISC |
openssl — openssl
|
The X509_V_FLAG_X509_STRICT flag enables additional security checks of the certificates present in a certificate chain. It is not set by default. Starting from OpenSSL version 1.1.1h a check to disallow certificates in the chain that have explicitly encoded elliptic curve parameters was added as an additional strict check. An error in the implementation of this check meant that the result of a previous check to confirm that certificates in the chain are valid CA certificates was overwritten. This effectively bypasses the check that non-CA certificates must not be able to issue other certificates. If a “purpose” has been configured then there is a subsequent opportunity for checks that the certificate is a valid CA. All of the named “purpose” values implemented in libcrypto perform this check. Therefore, where a purpose is set the certificate chain will still be rejected even when the strict flag has been used. A purpose is set by default in libssl client and server certificate verification routines, but it can be overridden or removed by an application. In order to be affected, an application must explicitly set the X509_V_FLAG_X509_STRICT verification flag and either not set a purpose for the certificate verification or, in the case of TLS client or server applications, override the default purpose. OpenSSL versions 1.1.1h and newer are affected by this issue. Users of these versions should upgrade to OpenSSL 1.1.1k. OpenSSL 1.0.2 is not impacted by this issue. Fixed in OpenSSL 1.1.1k (Affected 1.1.1h-1.1.1j). |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3450
MLIST
MLIST
MLIST
MLIST
CONFIRM
MISC
CONFIRM
CISCO
CONFIRM |
oria — gridx
|
Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in tests/support/stores/test_grid_filter.php in oria gridx 1.3, allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code, via crafted value to the $query parameter. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-19625
MISC
MISC |
privoxy — privoxy
|
A flaw was found in Privoxy in versions before 3.0.29. Dereference of a NULL-pointer that could result in a crash if accept-intercepted-requests was enabled, Privoxy failed to get the request destination from the Host header and a memory allocation failed. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20213
MISC
MISC |
qemu — qemu
|
The patch for CVE-2020-17380/CVE-2020-25085 was found to be ineffective, thus making QEMU vulnerable to the out-of-bounds read/write access issues previously found in the SDHCI controller emulation code. This flaw allows a malicious privileged guest to crash the QEMU process on the host, resulting in a denial of service or potential code execution. QEMU up to (including) 5.2.0 is affected by this. |
2021-03-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3409
MISC
MISC |
qemu — qemu
|
A use-after-free flaw was found in the MegaRAID emulator of QEMU. This issue occurs while processing SCSI I/O requests in the case of an error mptsas_free_request() that does not dequeue the request object ‘req’ from a pending requests queue. This flaw allows a privileged guest user to crash the QEMU process on the host, resulting in a denial of service. Versions between 2.10.0 and 5.2.0 are potentially affected. |
2021-03-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3392
MISC
MISC |
realtek — xpon_rtl9601D_sdk_devices
|
Realtek xPON RTL9601D SDK 1.9 stores passwords in plaintext which may allow attackers to possibly gain access to the device with root permissions via the build-in network monitoring tool and execute arbitrary commands. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27372
MISC |
| red_hat — red_hat |
An insecure modification vulnerability in the /etc/passwd file was found in the operator-framework/hadoop as shipped in Red Hat Openshift 4. An attacker with access to the container could use this flaw to modify /etc/passwd and escalate their privileges. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2019-19354
MISC
MISC
MISC |
red_hat — red_hat
|
An insecure modification vulnerability in the /etc/passwd file was found in the container operator-framework/operator-metering as shipped in Red Hat Openshift 4. An attacker with access to the container could use this flaw to modify /etc/passwd and escalate their privileges. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2019-19349
MISC
MISC |
red_hat — red_hat
|
An insecure modification vulnerability in the /etc/passwd file was found in the openshift/ansible-service-broker as shipped in Red Hat Openshift 4 and 3.11. An attacker with access to the container could use this flaw to modify /etc/passwd and escalate their privileges. |
2021-03-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2019-19350
MISC
MISC |
remark42 — remark42
|
remark42 before 1.6.1 allows XSS, as demonstrated by “Locator: Locator{URL:” followed by an XSS payload. This is related to backend/app/store/comment.go and backend/app/store/service/service.go. |
2021-03-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29271
MISC |
resteasy — resteasy
|
A flaw was found in RESTEasy in all versions of RESTEasy up to 4.6.0.Final. The endpoint class and method names are returned as part of the exception response when RESTEasy cannot convert one of the request URI path or query values to the matching JAX-RS resource method’s parameter value. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data confidentiality. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20289
MISC |
rocket.chat — rocket.chat
|
Rocket.Chat before 3.11, 3.10.5, 3.9.7, 3.8.8 is vulnerable to persistent cross-site scripting (XSS) using nested markdown tags allowing a remote attacker to inject arbitrary JavaScript in a message. This flaw leads to arbitrary file read and RCE on Rocket.Chat desktop app. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22886
MISC
MISC
MISC |
rockwell_automation — micrologix
|
Rockwell Automation MicroLogix 1400 Version 21.6 and below may allow a remote unauthenticated attacker to send a specially crafted Modbus packet allowing the attacker to retrieve or modify random values in the register. If successfully exploited, this may lead to a buffer overflow resulting in a denial-of-service condition. The FAULT LED will flash RED and communications may be lost. Recovery from denial-of-service condition requires the fault to be cleared by the user. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22659
MISC
MISC |
rpm — rpm
|
A flaw was found in RPM’s signature check functionality when reading a package file. This flaw allows an attacker who can convince a victim to install a seemingly verifiable package, whose signature header was modified, to cause RPM database corruption and execute code. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data integrity, confidentiality, and system availability. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20271
MISC
MISC |
samsung — account
|
Improper Access Control in EmailValidationView in Samsung Account prior to version 10.7.0.7 and 12.1.1.3 allows physically proximate attackers to log out user account on device without user password. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25351
MISC
MISC |
samsung — account
|
Information Exposure vulnerability in Samsung Account prior to version 12.1.1.3 allows physically proximate attackers to access user information via log. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25350
MISC
CONFIRM |
samsung — bixby_voice
|
Using PendingIntent with implicit intent in Bixby Voice prior to version 3.0.52.14 allows attackers to execute privileged action by hijacking and modifying the intent. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25352
MISC
CONFIRM |
samsung — cloud
|
Hijacking vulnerability in Samsung Cloud prior to version 4.7.0.3 allows attackers to intercept when the provider is executed. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25368
MISC
CONFIRM |
samsung — galazy_themes
|
Using empty PendingIntent in Galaxy Themes prior to version 5.2.00.1215 allows local attackers to read/write private file directories of Galaxy Themes application without permission via hijacking the PendingIntent. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25353
MISC
CONFIRM |
samsung — internet
|
Improper access control in Samsung Internet prior to version 13.2.1.70 allows physically proximate attackers to bypass the secret mode’s authentication. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25366
MISC
CONFIRM |
samsung — internet
|
Improper input check in Samsung Internet prior to version 13.2.1.46 allows attackers to launch non-exported activity in Samsung Browser via malicious deeplink. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25354
MISC
CONFIRM |
| samsung — multiple_products |
A vulnerability in DSP driver prior to SMR Mar-2021 Release 1 allows attackers load arbitrary ELF libraries inside DSP. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25371
MISC
CONFIRM |
samsung — multiple_products
|
An improper boundary check in DSP driver prior to SMR Mar-2021 Release 1 allows out of bounds memory access. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25372
MISC
CONFIRM |
samsung — multiple_products
|
An incorrect implementation handling file descriptor in dpu driver prior to SMR Mar-2021 Release 1 results in memory corruption leading to kernel panic. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25370
MISC
CONFIRM |
samsung — multiple_products
|
An improper access control vulnerability in sec_log file prior to SMR MAR-2021 Release 1 exposes sensitive kernel information to userspace. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25369
MISC
CONFIRM |
samsung — notes
|
Using unsafe PendingIntent in Samsung Notes prior to version 4.2.00.22 allows local attackers unauthorized action without permission via hijacking the PendingIntent. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25355
MISC
CONFIRM |
samsung — notes
|
Path Traversal vulnerability in Samsung Notes prior to version 4.2.00.22 allows attackers to access local files without permission. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25367
MISC
CONFIRM |
samsung — slow_motion_editor
|
Using unsafe PendingIntent in Slow Motion Editor prior to version 3.5.18.5 allows local attackers unauthorized action without permission via hijacking the PendingIntent. |
2021-03-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-25349
MISC
CONFIRM |
solarwinds — orion_platform
|
SolarWinds Orion Platform before 2020.2.5 allows stored XSS attacks by an administrator on the Customize View page. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-35856
CONFIRM
MISC |
solarwinds — orion_platform
|
The custom menu item options page in SolarWinds Orion Platform before 2020.2.5 allows Reverse Tabnabbing in the context of an administrator account. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3109
CONFIRM
MISC |
synapse — synapse
|
Synapse is a Matrix reference homeserver written in python (pypi package matrix-synapse). Matrix is an ecosystem for open federated Instant Messaging and VoIP. In Synapse before version 1.27.0, the notification emails sent for notifications for missed messages or for an expiring account are subject to HTML injection. In the case of the notification for missed messages, this could allow an attacker to insert forged content into the email. The account expiry feature is not enabled by default and the HTML injection is not controllable by an attacker. This is fixed in version 1.27.0. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21333
MISC
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
synapse — synapse
|
Synapse is a Matrix reference homeserver written in python (pypi package matrix-synapse). Matrix is an ecosystem for open federated Instant Messaging and VoIP. In Synapse before version 1.27.0, the password reset endpoint served via Synapse was vulnerable to cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. The impact depends on the configuration of the domain that Synapse is deployed on, but may allow access to cookies and other browser data, CSRF vulnerabilities, and access to other resources served on the same domain or parent domains. This is fixed in version 1.27.0. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21332
MISC
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
tableau — server
|
Tableau Server fails to validate certain URLs that are embedded in emails sent to Tableau Server users. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1629
MISC |
| tibco — rendezvous |
The Windows Installation component of TIBCO Software Inc.’s TIBCO ActiveSpaces – Community Edition, TIBCO ActiveSpaces – Developer Edition, and TIBCO ActiveSpaces – Enterprise Edition contains a vulnerability that theoretically allows a low privileged attacker with local access on some versions of the Windows operating system to insert malicious software. The affected component can be abused to execute the malicious software inserted by the attacker with the elevated privileges of the component. This vulnerability results from a lack of access restrictions on certain files and/or folders in the installation. Affected releases are TIBCO Software Inc.’s TIBCO ActiveSpaces – Community Edition: versions 4.5.0 and below, TIBCO ActiveSpaces – Developer Edition: versions 4.5.0 and below, and TIBCO ActiveSpaces – Enterprise Edition: versions 4.5.0 and below. |
2021-03-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28824
CONFIRM |
tibco — rendezvous
|
The Rendezvous Routing Daemon (rvrd), Rendezvous Secure Routing Daemon (rvrsd), Rendezvous Secure Daemon (rvsd), Rendezvous Cache (rvcache), Rendezvous Secure C API, Rendezvous Java API, and Rendezvous .Net API components of TIBCO Software Inc.’s TIBCO Rendezvous and TIBCO Rendezvous Developer Edition contain a vulnerability that theoretically allows a low privileged attacker with local access on the Windows operating system to insert malicious software. The affected component can be abused to execute the malicious software inserted by the attacker with the elevated privileges of the component. This vulnerability results from the affected component searching for run-time artifacts outside of the installation hierarchy. Affected releases are TIBCO Software Inc.’s TIBCO Rendezvous: versions 8.5.1 and below and TIBCO Rendezvous Developer Edition: versions 8.5.1 and below. |
2021-03-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28818
CONFIRM |
tibco — rendezvous
|
The FTL Server (tibftlserver), FTL C API, FTL Golang API, FTL Java API, and FTL .Net API components of TIBCO Software Inc.’s TIBCO FTL – Community Edition, TIBCO FTL – Developer Edition, and TIBCO FTL – Enterprise Edition contain a vulnerability that theoretically allows a low privileged attacker with local access on the Windows operating system to insert malicious software. The affected component can be abused to execute the malicious software inserted by the attacker with the elevated privileges of the component. This vulnerability results from the affected component searching for run-time artifacts outside of the installation hierarchy. Affected releases are TIBCO Software Inc.’s TIBCO FTL – Community Edition: versions 6.5.0 and below, TIBCO FTL – Developer Edition: versions 6.5.0 and below, and TIBCO FTL – Enterprise Edition: versions 6.5.0 and below. |
2021-03-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28820
CONFIRM |
tibco — rendezvous
|
The Windows Installation component of TIBCO Software Inc.’s TIBCO Enterprise Message Service, TIBCO Enterprise Message Service – Community Edition, and TIBCO Enterprise Message Service – Developer Edition contains a vulnerability that theoretically allows a low privileged attacker with local access on some versions of the Windows operating system to insert malicious software. The affected component can be abused to execute the malicious software inserted by the attacker with the elevated privileges of the component. This vulnerability results from a lack of access restrictions on certain files and/or folders in the installation. Affected releases are TIBCO Software Inc.’s TIBCO Enterprise Message Service: versions 8.5.1 and below, TIBCO Enterprise Message Service – Community Edition: versions 8.5.1 and below, and TIBCO Enterprise Message Service – Developer Edition: versions 8.5.1 and below. |
2021-03-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28821
CONFIRM |
tibco — rendezvous
|
The Enterprise Message Service Server (tibemsd), Enterprise Message Service Central Administration (tibemsca), Enterprise Message Service JSON configuration generator (tibemsconf2json), and Enterprise Message Service C API components of TIBCO Software Inc.’s TIBCO Enterprise Message Service, TIBCO Enterprise Message Service – Community Edition, and TIBCO Enterprise Message Service – Developer Edition contain a vulnerability that theoretically allows a low privileged attacker with local access on the Windows operating system to insert malicious software. The affected component can be abused to execute the malicious software inserted by the attacker with the elevated privileges of the component. This vulnerability results from the affected component searching for run-time artifacts outside of the installation hierarchy. Affected releases are TIBCO Software Inc.’s TIBCO Enterprise Message Service: versions 8.5.1 and below, TIBCO Enterprise Message Service – Community Edition: versions 8.5.1 and below, and TIBCO Enterprise Message Service – Developer Edition: versions 8.5.1 and below. |
2021-03-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28822
CONFIRM |
tibco — rendezvous
|
The Windows Installation component of TIBCO Software Inc.’s TIBCO eFTL – Community Edition, TIBCO eFTL – Developer Edition, and TIBCO eFTL – Enterprise Edition contains a vulnerability that theoretically allows a low privileged attacker with local access on some versions of the Windows operating system to insert malicious software. The affected component can be abused to execute the malicious software inserted by the attacker with the elevated privileges of the component. This vulnerability results from a lack of access restrictions on certain files and/or folders in the installation. Affected releases are TIBCO Software Inc.’s TIBCO eFTL – Community Edition: versions 6.5.0 and below, TIBCO eFTL – Developer Edition: versions 6.5.0 and below, and TIBCO eFTL – Enterprise Edition: versions 6.5.0 and below. |
2021-03-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28823
CONFIRM |
tp-link — multiple_products
|
Unauthenticated stored cross-site scripting (XSS) exists in multiple TP-Link products including WIFI Routers (Wireless AC routers), Access Points, ADSL + DSL Gateways and Routers, which affects TD-W9977v1, TL-WA801NDv5, TL-WA801Nv6, TL-WA802Nv5, and Archer C3150v2 devices through the improper validation of the hostname. Some of the pages including dhcp.htm, networkMap.htm, dhcpClient.htm, qsEdit.htm, and qsReview.htm and use this vulnerable hostname function (setDefaultHostname()) without sanitization. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3275
MISC
MISC
FULLDISC
MISC |
univerge — aspire_series_devices
|
UNIVERGE Aspire series PBX (UNIVERGE Aspire WX from 1.00 to 3.51, UNIVERGE Aspire UX from 1.00 to 9.70, UNIVERGE SV9100 from 1.00 to 10.70, and SL2100 from 1.00 to 3.00) allows a remote authenticated attacker to cause system down and a denial of service (DoS) condition by sending a specially crafted command. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20677
MISC
MISC |
vscode-sass-lint — vscode-sass-lint
|
** UNSUPPORTED WHEN ASSIGNED ** The unofficial vscode-sass-lint (aka Sass Lint) extension through 1.0.7 for Visual Studio Code allows attackers to execute arbitrary binaries if the user opens a crafted workspace. NOTE: This vulnerability only affects products that are no longer supported by the maintainer. |
2021-03-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28956
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
wire-server — wire-server
|
wire-server is an open-source back end for Wire, a secure collaboration platform. In wire-server from version 2021-02-16 and before version 2021-03-02, the client metadata of all users was exposed in the `GET /users/list-clients` endpoint. The endpoint could be used by any logged in user who could request client details of any other user (no connection required) as far as they can find their User ID. The exposed metadata included id, class, type, location, time, and cookie. A user on a Wire backend could use this endpoint to find registration time and location for each device for a given list of users. As a workaround, remove `/list-clients` from nginx config. This has been fixed in version 2021-03-02. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21396
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
wordpress — wordpress
|
BuddyPress is an open source WordPress plugin to build a community site. In releases of BuddyPress from 5.0.0 before 7.2.1 it’s possible for a non-privileged, regular user to obtain administrator rights by exploiting an issue in the REST API members endpoint. The vulnerability has been fixed in BuddyPress 7.2.1. Existing installations of the plugin should be updated to this version to mitigate the issue. |
2021-03-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21389
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
by Contributed | Mar 29, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Let’s start with some basics…
Cost optimization is one of the most common requirements for cloud workloads. How to implement a cost optimization framework will depend on the type of service, scenario, purchase model, and a few other aspects of Your environment. It’s worth noting that, when it comes to frameworks, Microsoft has been developing its own framework for Azure. The Azure Well-Architected Framework (WAF) is a set of guiding tenets that can be used to improve the quality of a workload. The framework consists of five pillars of architecture excellence:
- Cost Optimization
- Operational Excellence
- Performance Efficiency
- Reliability
- Security
Following the best practices and the specific business priorities that are relevant to you and your cloud journey, you can effectively and consistently optimize your workload costs against Azure. You can find more information about Microsoft Azure Well-Architected Framework by going to:
Now, after You have grown a little more with the WAF, it’s time to start the journey. Diving deeper down the cost optimization pillar we can identify several areas:
- Right resources, the right size
- Aim for scalable costs |Pay for consumption
- Keep within the cost constraints
- Monitor and optimize
These four areas are your anchor for the further steps. The thing to keep in mind is that, as any other framework, the WAF only provides broad recommendations. To implement it, You will need concrete details pertinent to a particular solution, workload, and even the service level. With this in mind, let’s go one level deeper and focus on the cost optimization aspect for Azure SQL Managed Instance.
The next level starts here…
Right resources, right size…and the right location
The first and one of the most important steps in cost optimization is to choose the right resources that are aligned with Your business goals and can deliver the required performance of the planned workload. An inappropriate or misconfigured service can adversely impact the cost.
With SQL Managed Instance You can choose between General Purpose (GP) and Business Critical (BC) tiers. Obviously, there is a price difference between these two tiers because each tier was designed differently.
The General Purpose service tier is based on the separation of computing and storage, while the Business Critical service tier model is based on a cluster of database engine processes. The choice between these architectural models affects the availability, reliability, performance, and cost. In the GP tier, Azure Blob Storage transparently replicates database files and guarantees no data loss. Business Critical, on the other hand, relies on the fact that there is always a quorum of available database engine nodes which ensure minimal performance impact on your workload even during maintenance activities. Of course, there are other differences between the two tiers which affect their bottom line pricing, e.g. storage latency between 5 and 10 m in GP and 1-2 ms SSD storage in BC.
The SKU Recommendations feature which is available in Data Migration Assistant tool allows you to identify the minimum recommended Azure SQL Managed Instance SKU based on performance counters collected from the computer(s) hosting your databases. Make sure to check how easily identify the right Azure SQL Database SKU for your on-premises database (Data Migration Assistant)
If You need more details about the SQL MI tiers please visit:
Below you can find a sample comparison between the same SQL MI configuration running in GP and BC tiers.

Figure 1 General Purpose Sample Pricing vs Business Critical Sample Pricing
Once you identify the appropriate service tier, there are few more things to consider which can allow reducing cost:
- Check service prices in different Azure datacenter locations. Azure has regions located all over the world. Prices between regions for the same service can be different. Below You can find a sample comparison of SQL MI cost deployed in different regions in Europe with the following configuration : General Purpose, 4 vCores, Pay-as-you-go:
Figure 2 Sample SQL MI cost per Azure region in Europe comparison
Region
|
Monthly cost (~ 730h)
|
Difference to West Europe [in percent]
|
West Europe
|
$780.82
|
N/A
|
North Europe
|
$745.27
|
~ – 4 %
|
France Central
|
$847.49
|
~+ 9 %
|
France South
|
$1,014.17
|
~+ 30 %
|
Germany North (public)
|
$927.50
|
~ + 19 %
|
Germany West Central (public)
|
$780.82
|
0%
|
- Deploy the database/instances in the same region as your application to prevent data transfer costs. Deploying SQL MI in one region and other services, like App Service, in another region, can generate additional cross-region data transfer costs. Although in most cases this cost will not be significant, it’s worth following the pattern of keeping the related services in the same region.
Figure 3 Sample bandwidth cost for 1 TB
- Building a multi-region service when the service levels don’t require high-availability or geo-redundancy will increase the cost without a reasonable business justification. There are many options to increase the availability of your solution. One of them is multi-region deployment. In the case of SQL MI You can achieve this by using Auto-failover groups – SQL Managed Instance. Auto-failover groups are superior to having a secondary instance deployed in another region as a fully paid instance, which doubles the cost of the solution.
Figure 4 Failover groups – secondary replica is fully paid
As an alternative approach, if you still need geo-region deployment with reduced costs you can consider using Auto-failover groups – SQL Managed Instance with secondary instance configuration lower than primary one – in this case make sure performance of secondary instance is enough to follow the primary instance synchronization needs and scale it up if needed.
- If your Business Continuity strategy requires geo-region deployment but there are no strict requirements for auto-failover and some RTO,RPO values can be relaxed consider using backup with geo-replicated storage as well as the geo-restore option, you can also automate the process with a simple script to Restore geo-backup for Azure SQL Managed Instance – Azure SQL Managed Instance. Geo-restore is the most basic disaster-recovery solution available in SQL Database and SQL Managed Instance. It relies on automatically created geo-replicated backups with a recovery point objective (RPO) up to 1 hour and an estimated recovery time of up to 12 hours. Depends on a need this can be a good option to keep Business Continuity policies in place at lower cost.
Note! Remember to choose the service tier based on a thorough analysis rather than a superficial comparison of service prices. Always make a clear analysis of your HA/DR (RTO, RPO), performance, and feature requirements to set up your service accordingly. Please visit the following pages to get more information about SQL MI tiers:
Aim for scalable costs | Pay for consumption
The workload cost should scale with the demand. A key benefit of the cloud is the ability to scale dynamically. You can save costs through automatic/on-demand scaling. Although SQL Managed Instance doesn’t have a built-in autoscaling option, like other services it follows a common cloud pattern in which You can access APIs to turn on/off, scale-up/down, or even drop and re-deploy workloads. Such an approach allows You to manage the overall costs depending on the changing business needs. Although scaling up/down or drop/re-deployment of the service aren’t instantaneous, they can be some of the easiest ways to control SQL Managed Instance cost over longer periods of time. Make sure You check the following links for details and examples of automation (including progress tracking):
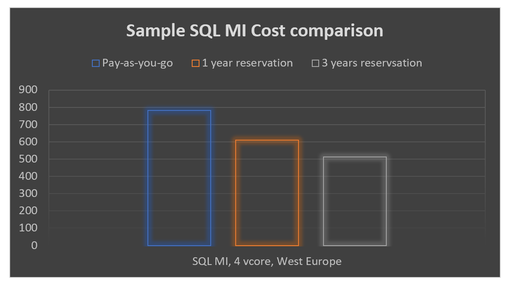
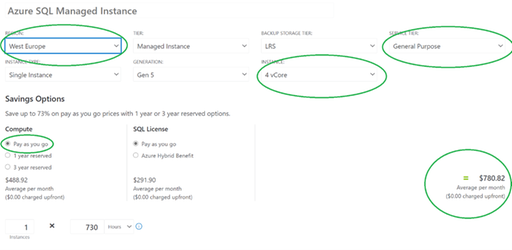
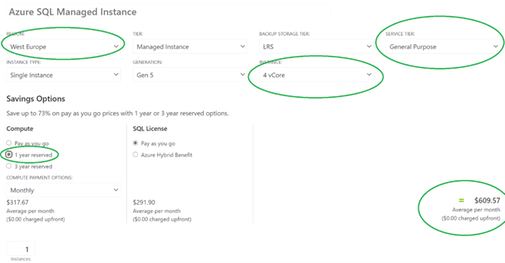
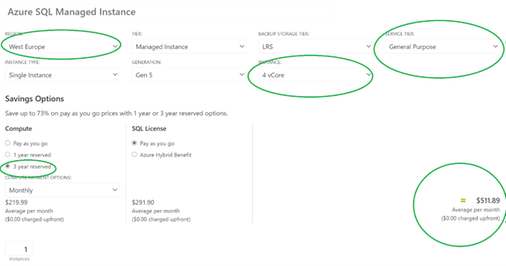
Figure 6 Sample SQL MI Cost Pay-as-you-go vs Reservations
Make sure You check more details how to Save compute costs with reserved capacity – Azure SQL Database & SQL Managed Instance
Keep within the cost constraints
Every design choice has cost implications. Thus, no matter if You are just planning the deployment or the deployment was already done, there are some points to verify and focus on in order to fit within the budget constraints. In the case of SQL Managed Instance, licensing can be one of the most important areas to consider:
Cost structure has a huge impact on the ongoing costs. Although we are talking about cloud services we have to follow specific licensing rules. In the case of SQL MI there are few rules of thumb that help you manage cost-effectively:
- Compute is provisioned in virtual cores (vCores). A vCore represents a logical CPU and its main cost factor when choosing Your Managed Instance configuration as you pay for computing (number of cores) and license needed to cover deployed cores – BY DEFAULT LICENSE COST IS TRANSPARENT FOR YOU AS A CUSTOMER AND IS INCLUDED IN THE SERVICE PRICE
- In some cases, You can already have SQL Server licenses in Your organization which can be used to run SQL MI and reduce its cost. SQL Managed Instance is eligible for Azure Hybrid Use Benefit (AHUB), which is a licensing benefit that works by letting you use your on-premises SQL Server licenses with Software Assurance on Azure based on the following pattern:
On-premises license
|
Azure usage
|
SQL Server Enterprise Edition core customers with Software Assurance
|
1 core on-premises = 4 cores in General Purpose SKU
1 core on-premises = 1 core in Business Critical SKU
|
SQL Server Standard Edition core customers with Software Assurance
|
1 core on-premises = 1 core in General Purpose SKU
4 core on-premises = 1 core in Business Critical SKU
|
It’s important to remember if you decide to use AHUB you need to cover whole SQL MI configuration (it isn’t possible to cover only part of vCores used in SQL MI with AHUB and using rest in license-included model). The same rule applies if you plan to scale up your instance – you must have eligible number of SQL license with SA to cover whole instance after scaling up. To find more information about Azure Hybrid Use Benefit, visit Azure Hybrid Benefit – Azure SQL Database & SQL Managed Instance
Azure Hybrid Use Benefit for SQL MI can be enabled during or after instance deployment and it’s possible to do it using Azure Portal, PowerShell, CLI, or REST API. Below You can find the sample snapshot from Azure Portal for running SQL MI which shows how to activate AHUB and the potential savings – in this case, 39.6% (value can vary between Azure offering, Azure regions).
Figure 7 SQL MI Cost comparison in Pay-as-you-go vs Azure Hybrid Use Benefit
Note! One of best practices to reduce cost is instances consolidation with right sizing to ensure the least amount of vCores is required.
- An additional cost-saving option is directly related to the scenario in which SQL MI is used. If your workload is not a production one. Consider using Dev/Test licensing model which is available for SQL Database Managed Instance as part of the dev/test offer. It is a highly cost-effective way to run your development and testing workloads and can easily help save up to 55% off the list price. To make it clear Dev/Test licensing model means you pay only for compute, license cost is reduced to zero. There are three offers that allow reducing SQL MI cost used for development and testing:
- Individual one: Monthly Azure credits for Visual Studio subscribers
Azure credits are included in your Visual Studio subscription and depend on the Visual Subscription level. When you run out of the credit that’s allotted for the month, you won’t be able to continue using it until it resets the next month.
Figure 8 Azure Credits in Visual Subscriptions
This is offer doesn’t require any separate payment, it’s just using the funds already in your Enterprise Agreement. It requires creating a subscription that is marked as Dev/Test or changing the existing one. More details can be found here: Enabling and Creating EA Dev/Test Subscriptions through the EA Portal | Enterprise Azure Portal | Channel 9 (msdn.com).Please remember that only active Visual Studio subscribers with standard subscriptions can use the Azure resources running within an Enterprise Dev/Test subscription. End users can also access the application to provide feedback or perform acceptance tests.
This offer works similar to Enterprise Dev/Test. The difference is that it doesn’t require You to have an Enterprise Agreement in place. This scenario also requires users to have an active Visual Studio subscription to be able to use the Azure resources running within a Dev/Test subscription.
Just to show how the dev/test pricing looks like, below You will find a comparison between the same SQL MI configuration running in standard and dev/test model.
Figure 9 Commercial to Dev/Test cost comparision
- Last but not least is taking the advantage of the appropriate subscription offer types. Azure usage rates and billing periods can differ between Enterprise, Web Direct, and Cloud Solution Provider (CSP). It’s worth evaluating this option to make sure your pricing is relevant to your business needs.
Monitor and optimize
Resource monitoring can be a great opportunity to optimize costs. Treat it as a process, rather than a point-in-time activity. Conduct regular reviews and forecast the capacity needs so that you can provision resources dynamically and scale with demand – for more information please back to section Right resources, right size…and right location and Aim for scalable costs | Pay for consumption
There are few steps which can help you optimize the overall cost:
- collect and visualize key performance metrics to determine the right resource level usage (vCore, memory, IOPS, etc.). Verify if your database requires a specific number of cores, memory, IOPS and use it to determine the right service tier (General Purpose or Business Critical). Follow the best practice in monitoring SQL MI by using solutions like SQL Insights. Make sure to explore monitoring options available for Azure SQL Managed Instance
- use built-in features like Query Store or index usage statistics to optimize SQL workload which can allow you to optimize the sizing of your SQL MI and help to reduce the ongoing costs: Performance tuning guidance for applications and databases – Azure SQL Database & Azure SQL Managed Instance | Microsoft Docs
- consider using compression (row, page), column store indexes where possible to keep storage footprint small and reduce storage size needs.
- define and enforce data retention, archival requirements, or data offloading (e.g. to a storage account) strategy, as not all data typically needs to be available for online processing)
- reduce the billing charges for excess usage of the backup storage space beyond the free backup storage space provided. You can control the backup consumption using these general approaches:
- Choosing the backup storage type that is right for you
- Optimize database backup retention period
- Maximize your free backup storage space
- Optimize your apps and workloads
- Alternative considerations
Dive into details about backup cost optimization by @Danimir Ljepava
Fine tuning backup storage costs on SQL Managed Instance
Backup storage consumption on Managed Instance explained
What’s next?
Once you go through the most common cost optimization hints described in this post, remember to treat them as a process. Implement, revisit, and follow them regularly. Also stay tuned as more articles about Azure Well-Architected Framework (WAF) for SQL Managed Instance workload is coming.
Disclaimer
Please note that options presented in this article are subject to change. This article reflects the state of cost optimization options available for Azure SQL Managed Instance in March, 2021 but is not limited to them and can changed over time
Closing remarks
If you find this article useful, please like it on this page and share through social media.
To share this article, you can use the Share button below, or this short link: https://aka.ms/sqlmi-waf-cost-optimization
by Contributed | Mar 29, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Microsoft provides three main Identity services – Active Directory, Azure Active Directory and Microsoft Accounts. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between Azure Active Directory and Microsoft Accounts.
Interested in the difference between Active Directory and Azure Active Directory? Check out this article I wrote for A Cloud Guru.
 Microsoft’s three main Identity platforms
Microsoft’s three main Identity platforms
What is a Microsoft Account?
A Microsoft Account is the modern name given to the Identity system that provides authentication and authorization to Microsoft’s consumer services. It’s had other former names, like Microsoft Passport or a Microsoft Live Account and is sometimes referred to as a personal account. A Microsoft Account can be used to sign in to Outlook.com, Office subscriptions, Skype, OneDrive, XBox Live, Bing, the Microsoft Store, Windows and MSN:
 Consumer services that use a Microsoft Account
Consumer services that use a Microsoft Account
Here are some common scenarios:
A Microsoft Account can be created with a new email address and mailbox at Outlook.com. You can even choose Hotmail.com as a valid domain name for this service.
A Microsoft Account can be created when you sign into a new Windows 10 computer for the first time.
A Microsoft Account can be used to sign into Microsoft 365 home plans such as Microsoft 365 Personal, for access to Office applications, including the consumer version of OneDrive.
With a Microsoft Account, Microsoft controls and manages all of the configuration and settings of the Identity platform. It’s designed to scale to a broad base of consumer users across the globe, all in the one system. So, you will have a conflict if you try and create a Microsoft Account with a username that has already been taken.
You don’t need to create a new email account or use the outlook.com or hotmail.com domains for your new Microsoft Account. In fact, you can even use a Gmail address to register for a Microsoft Account:
 gmail.com address used for a Microsoft Account
gmail.com address used for a Microsoft Account
You used to be able to create a Microsoft Account using the same email address as your work or school account, but Microsoft have now blocked this to stop confusion between the two different identity services. There is no organizational-level management of user accounts for creating and viewing users, resetting passwords etc.
What is a work or school account with Azure Active Directory?
A work or school account is created by an organization using a business service that has Azure Active Directory as the authentication and authorization platform. This includes business plans for Microsoft 365 including Outlook Web Access and OneDrive for Business, Microsoft Intune and Windows 10 devices that are connected to your organization’s Azure Active Directory domain, as well as Microsoft Azure resources.
With Azure Active Directory, Microsoft provides the identity platform as a service but you can modify some of the configuration and settings, such as adding your own custom domain name (to get @yourorg.com) or requiring multi-factor authentication. Your Azure Active Directory instance is available via the Azure Portal and other management tools like PowerShell, the Azure CLI and the REST API. And you can also monitor and investigate advanced security events with integration into tools like Azure Sentinel.
 User management with Azure Active Directory in the Azure portal
User management with Azure Active Directory in the Azure portal
The sign-in experience
Previously, the Microsoft sign-in interface would get you to choose personal account or a work or school account before entering your details. Now the sign-in screen detects the account type for you, presenting you with an agnostic sign-in window:
 A sign-in window for a Microsoft service
A sign-in window for a Microsoft service
If you visit Outlook.com and sign in with your work account that has an Exchange Online mailbox via Microsoft 365, you’ll automatically be redirected to the outlook.office365.com mailbox.
And if you try to sign into a business service that needs a work or school account (like portal.office.com), you’ll receive an error:
 You can’t sign in here with a personal account. Use your work or school account instead.
You can’t sign in here with a personal account. Use your work or school account instead.
Interoperability
Lets look at some difference scenarios that might involve these two services together.
Synchronization
There is no synchronization of user account information between Microsoft Accounts and Azure Active Directory, like you can achieve with Active Directory and Azure Active Directory. This is due to the separation of that consumer versus business identity platform.
Guest accounts
Even though you can’t synchronize Microsoft accounts into your Azure AD (or vice versa), you can invite someone as a guest user into Azure with their Microsoft Account email address. They’ll appear in your directory with Microsoft Account listed at the source and you won’t be able to perform any user administration on their account such as renaming them or resetting their password. This is useful though for inviting external people to collaborate and is the method behind the scenes if someone’s Microsoft Account is invited to be a guest in Microsoft 365 services like Teams.
Azure AD B2C
In addition, Microsoft provides a service called Azure Active Directory B2C which DOES support using Microsoft Accounts as an authentication source for access to your applications, as well as other consumer identity directories like Facebook, Twitter, Google, Amazon and OIDC compliant business and government identity providers. For more information, visit What is Azure Active Directory B2C?
 Azure Active Directory B2C allows consumer and OIDC identities to be authentication sources for Azure.
Azure Active Directory B2C allows consumer and OIDC identities to be authentication sources for Azure.
Azure service errors
I’ve recently become aware of errors like this example, accessing Azure Key Vault with Visual Studio, that may indicate a conflict between a Microsoft Account and an Azure Active Directory account: “Azure Key Vault is configured for use by Azure Active Directory users only. Please do not use the /consumers endpoint to serve this request.” It is possible to create a new Azure tenancy and have a Microsoft Account as the login.
In fact, that’s a common process when you set up Azure for the first time:
From Azure, create a Free or Pay as you Go account using your Outlook.com email address (such as personal0321@outlook.com).
This creates an Azure subscription with a new Azure Active Directory and your account as the first user. Note it takes your email address to form the new directory’s default domain name (personal0321outlook.onmicrosoft.com) and you can add a custom domain name next.
 First Azure User created from a Microsoft Account
First Azure User created from a Microsoft Account
Note the Source is listed as Microsoft Account.
 Microsoft Account signed in to access Azure
Microsoft Account signed in to access Azure
In this case, it’s recommended that you create a new user in Azure Active Directory and grant them the Owner role to the subscription, and use that identity to authenticate with. In this example, I’ve also made them a Global Administrator for Azure Active Directory. For more information visit Add or change Azure subscription administrators.
 The new user has Azure Active Directory as the Source
The new user has Azure Active Directory as the Source Creating a new Azure user as a global administrator
Creating a new Azure user as a global administrator
Learn more:
Secure access to your applications by using Azure identity services – Microsoft Learn
What’s new in Azure Active Directory?
What is the Azure Active Directory architecture?
Microsoft Accounts in the Enterprise



Recent Comments