by Scott Muniz | Aug 30, 2021 | Security, Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
| adobe — acrobat_reader_dc |
Acrobat Reader DC versions versions 2021.001.20155 (and earlier), 2020.001.30025 (and earlier) and 2017.011.30196 (and earlier) are affected by an Use After Free vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28552
MISC |
adobe — acrobat_reader_dc
|
Acrobat Reader DC versions versions 2021.001.20155 (and earlier), 2020.001.30025 (and earlier) and 2017.011.30196 (and earlier) are affected by an Use After Free vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28632
MISC |
adobe — acrobat_reader_dc
|
Acrobat Reader DC versions versions 2021.001.20155 (and earlier), 2020.001.30025 (and earlier) and 2017.011.30196 (and earlier) are affected by an Out-of-bounds Read vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28554
MISC |
adobe — acrobat_reader_dc
|
Acrobat Reader DC versions versions 2021.001.20155 (and earlier), 2020.001.30025 (and earlier) and 2017.011.30196 (and earlier) are affected by an Out-of-bounds read vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28551
MISC |
adobe — acrobat_reader_dc
|
Acrobat Reader DC versions versions 2021.001.20155 (and earlier), 2020.001.30025 (and earlier) and 2017.011.30196 (and earlier) are affected by an Use After Free vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28631
MISC |
| adobe — after_effects |
Adobe After Effects version 18.2 (and earlier) is affected by an Our-of-bounds Read vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to disclose sensitive memory information and cause a denial of service in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28612
MISC |
| adobe — after_effects |
Adobe After Effects version 18.2 (and earlier) is affected by an Our-of-bounds Read vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to disclose sensitive memory information and cause a denial of service in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28611
MISC |
| adobe — after_effects |
Adobe After Effects version 18.2 (and earlier) is affected by an Out-of-bounds Read vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to disclose sensitive memory information in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28609
MISC |
| adobe — after_effects |
Adobe After Effects version 18.2 (and earlier) is affected by a heap corruption vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28607
MISC |
| adobe — after_effects |
Adobe After Effects version 18.2 (and earlier) is affected by an Our-of-bounds Read vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to disclose sensitive memory information in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28615
MISC |
| adobe — after_effects |
Adobe After Effects version 18.2 (and earlier) is affected by a memory corruption vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28605
MISC |
| adobe — after_effects |
Adobe After Effects version 18.2 (and earlier) is affected by a Heap-based Buffer Overflow vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28604
MISC |
| adobe — after_effects |
Adobe After Effects version 18.2 (and earlier) is affected by a memory corruption vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28602
MISC |
adobe — after_effects
|
Adobe After Effects version 18.2 (and earlier) is affected by an Our-of-bounds Read vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to disclose sensitive memory information and cause a denial of service in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28614
MISC |
adobe — after_effects
|
Adobe After Effects version 18.2 (and earlier) is affected by a Heap-based Buffer Overflow vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28608
MISC |
adobe — after_effects
|
Adobe After Effects version 18.2 (and earlier) is affected by a Heap-based Buffer Overflow vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28603
MISC |
adobe — after_effects
|
Adobe After Effects version 18.2 (and earlier) is affected by a Heap-based Buffer Overflow vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28610
MISC |
adobe — after_effects
|
Adobe After Effects version 18.2 (and earlier) is affected by a Null pointer dereference vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve an application denial-of-service in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28601
MISC |
adobe — after_effects
|
Adobe After Effects version 18.2 (and earlier) is affected by an Out-of-bounds Read vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to disclose sensitive memory information in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28600
MISC |
adobe — after_effects
|
Adobe After Effects version 18.2 (and earlier) is affected by an Our-of-bounds Read vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to disclose sensitive memory information and cause a denial of service in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28616
MISC |
adobe — after_effects
|
Adobe After Effects version 18.2 (and earlier) is affected by a Stack-based Buffer Overflow vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28606
MISC |
| adobe — animate |
Adobe Animate version 21.0.6 (and earlier) is affected by an Out-of-bounds Read vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to disclose potential sensitive information in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28630
MISC |
| adobe — animate |
Adobe Animate version 21.0.6 (and earlier) is affected by an Out-of-bounds Write vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28622
MISC |
| adobe — animate |
Adobe Animate version 21.0.6 (and earlier) is affected by an Out-of-bounds Read vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to disclose sensitive memory information in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28618
MISC |
adobe — animate
|
Adobe Animate version 21.0.6 (and earlier) is affected by an Out-of-bounds Read vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to disclose sensitive memory information in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28617
MISC |
adobe — animate
|
Adobe Animate version 21.0.6 (and earlier) is affected by an Out-of-bounds Read vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to disclose sensitive memory information in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28619
MISC |
adobe — animate
|
Adobe Animate version 21.0.6 (and earlier) is affected by a Heap-based Buffer Overflow vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28620
MISC |
adobe — animate
|
Adobe Animate version 21.0.6 (and earlier) is affected by an Out-of-bounds Read vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28621
MISC |
adobe — animate
|
Adobe Animate version 21.0.6 (and earlier) is affected by a Heap-based Buffer Overflow vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28629
MISC |
adobe — creative_cloud_desktop_application
|
Adobe Creative Cloud Desktop Application (installer) version 2.4 (and earlier) is affected by an Uncontrolled Search Path Element vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28594
MISC |
adobe — creative_cloud_desktop_application
|
Adobe Creative Cloud Desktop Application (installer) version 2.4 (and earlier) is affected by an Insecure temporary file creation vulnerability. An attacker could leverage this vulnerability to cause arbitrary file overwriting in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires physical interaction to the system. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28633
MISC |
| adobe — experience_manager_cloud_service |
Adobe Experience Manager Cloud Service offering, as well as versions 6.5.8.0 (and below) is affected by a Server-side Request Forgery. An authenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to contact systems blocked by the dispatcher. Exploitation of this issue does not require user interaction. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28627
MISC |
| adobe — experience_manager_cloud_service |
Adobe Experience Manager Cloud Service offering, as well as versions 6.5.8.0 (and below) is affected by a Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability that could be abused by an attacker to inject malicious scripts into vulnerable form fields. Malicious JavaScript may be executed in a victim’s browser when they browse to the page containing the vulnerable field. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28628
MISC |
adobe — experience_manager_cloud_service
|
Adobe Experience Manager Cloud Service offering, as well as versions 6.5.8.0 (and below) is affected by a Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability that could be abused by an attacker to inject malicious scripts into vulnerable form fields. Malicious JavaScript may be executed in a victim’s browser when they browse to the page containing the vulnerable field. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28625
MISC |
adobe — experience_manager_cloud_service
|
Adobe Experience Manager Cloud Service offering, as well as versions 6.5.8.0 (and below) is affected by an Improper Authorization vulnerability allowing users to create nodes under a location. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to cause an application denial-of-service. Exploitation of this issue does not require user interaction. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28626
MISC |
adobe — framemaker
|
Adobe Framemaker version 2020.0.1 (and earlier) and 2019.0.8 (and earlier) are affected by an Out-of-bounds Write vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28596
MISC |
adobe — media_encoder
|
Adobe Media Encoder version 15.2 (and earlier) is affected by an Out-of-bounds Read vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-36013
MISC |
apache — nifi_minifi
|
From Apache NiFi MiNiFi C++ version 0.5.0 the c2 protocol implements an “agent-update” command which was designed to patch the application binary. This “patching” command defaults to calling a trusted binary, but might be modified to an arbitrary value through a “c2-update” command. Said command is then executed using the same privileges as the application binary. This was addressed in version 0.10.0 |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33191
MISC
MLIST
MLIST |
aruba — airwave_management_platform
|
A remote cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability was discovered in Aruba AirWave Management Platform version(s): Prior to 8.2.13.0. Aruba has released upgrades for the Aruba AirWave Management Platform that address this security vulnerability. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37715
MISC |
atlassian — jira_server_and_data_center
|
Affected versions of Atlassian Jira Server and Data Center allow remote attackers to redirect users to a malicious URL via a reverse tabnapping vulnerability in the Project Shortcuts feature. The affected versions are before version 8.5.15, from version 8.6.0 before 8.13.7, from version 8.14.0 before 8.17.1, and from version 8.18.0 before 8.18.1. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39112
MISC |
axis — device_manager
|
A user with permission to log on to the machine hosting the AXIS Device Manager client could under certain conditions extract a memory dump from the built-in Windows Task Manager application. The memory dump may potentially contain credentials of connected Axis devices. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-31989
MISC |
basercms — basercms
|
baserCMS is an open source content management system with a focus on Japanese language support. In affected versions there is a cross-site scripting vulnerability in the file upload function of the management system of baserCMS. Users are advised to update as soon as possible. No workaround are available to mitigate this issue. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39136
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC
JVN |
bento4 — bento4
|
The AP4_CttsAtom class in Core/Ap4CttsAtom.cpp in Bento4 1.5.1.0 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash), related to a memory allocation failure, as demonstrated by mp2aac. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2018-10790
MISC
MISC |
binderhub — binderhub
|
BinderHub is a kubernetes-based cloud service that allows users to share reproducible interactive computing environments from code repositories. In affected versions a remote code execution vulnerability has been identified in BinderHub, where providing BinderHub with maliciously crafted input could execute code in the BinderHub context, with the potential to egress credentials of the BinderHub deployment, including JupyterHub API tokens, kubernetes service accounts, and docker registry credentials. This may provide the ability to manipulate images and other user created pods in the deployment, with the potential to escalate to the host depending on the underlying kubernetes configuration. Users are advised to update to version 0.2.0-n653. If users are unable to update they may disable the git repo provider by specifying the `BinderHub.repo_providers` as a workaround. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39159
CONFIRM
MISC |
blog_mini — blog_mini
|
Cross Site Scripting (XSS) in Blog_mini v1.0 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via the component ‘/admin/custom/blog-plugin/add’. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18998
MISC |
blog_mini — blog_mini
|
Cross Site Scripting (XSS) in Blog_mini v1.0 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via the component ‘/admin/submit-articles’. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18999
MISC |
| braun — spacecom2 |
An improper sanitization of input vulnerability in B. Braun SpaceCom2 prior to 012U000062 allows a remote unauthenticated attacker to gain user-level command-line access by passing a raw external string straight through to printf statements. The attacker is required to be on the same network as the device. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33886
MISC
MISC |
braun — spacecom2
|
A Missing Authentication for Critical Function vulnerability in B. Braun SpaceCom2 prior to 012U000062 allows a remote attacker to reconfigure the device from an unknown source because of lack of authentication on proprietary networking commands. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33882
MISC
MISC |
braun — spacecom2
|
A Cleartext Transmission of Sensitive Information vulnerability in B. Braun SpaceCom2 prior to 012U000062 allows a remote attacker to obtain sensitive information by snooping on the network traffic. The exposed data includes critical values for a pump’s internal configuration. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33883
MISC
MISC |
braun — spacecom2
|
An Unrestricted Upload of File with Dangerous Type vulnerability in B. Braun SpaceCom2 prior to 012U000062 allows remote attackers to upload any files to the /tmp directory of the device through the webpage API. This can result in critical files being overwritten. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33884
MISC
MISC |
braun — spacecom2
|
An Insufficient Verification of Data Authenticity vulnerability in B. Braun SpaceCom2 prior to 012U000062 allows a remote unauthenticated attacker to send the device malicious data that will be used in place of the correct data. This results in full system command access and execution because of the lack of cryptographic signatures on critical data sets. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33885
MISC
MISC |
| cachet — cachet |
Cachet is an open source status page system. Prior to version 2.5.1 authenticated users, regardless of their privileges (User or Admin), can trick Cachet and install the instance again, leading to arbitrary code execution on the server. This issue was addressed in version 2.5.1 by improving the middleware `ReadyForUse`, which now performs a stricter validation of the instance name. As a workaround, only allow trusted source IP addresses to access to the administration dashboard. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39173
MISC
CONFIRM |
cachet — cachet
|
Cachet is an open source status page system. Prior to version 2.5.1, authenticated users, regardless of their privileges (User or Admin), can exploit a new line injection in the configuration edition feature (e.g. mail settings) and gain arbitrary code execution on the server. This issue was addressed in version 2.5.1 by improving `UpdateConfigCommandHandler` and preventing the use of new lines characters in new configuration values. As a workaround, only allow trusted source IP addresses to access to the administration dashboard. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39172
MISC
CONFIRM |
cachet — cachet
|
Cachet is an open source status page. With Cachet prior to and including 2.3.18, there is a SQL injection which is in the `SearchableTrait#scopeSearch()`. Attackers without authentication can utilize this vulnerability to exfiltrate sensitive data from the database such as administrator’s password and session. The original repository of Cachet <https://github.com/CachetHQ/Cachet> is not active, the stable version 2.3.18 and it’s developing 2.4 branch is affected. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39165
MISC
CONFIRM |
cachet — cachet
|
Cachet is an open source status page system. Prior to version 2.5.1, authenticated users, regardless of their privileges (User or Admin), can leak the value of any configuration entry of the dotenv file, e.g. the application secret (`APP_KEY`) and various passwords (email, database, etc). This issue was addressed in version 2.5.1 by improving `UpdateConfigCommandHandler` and preventing the use of nested variables in the resulting dotenv configuration file. As a workaround, only allow trusted source IP addresses to access to the administration dashboard. |
2021-08-28 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39174
MISC
CONFIRM |
cacti — cacti
|
Multiple Cross Site Scripting (XSS) vulneratiblities exist in Cacti 1.2.12 in (1) reports_admin.php, (2) data_queries.php, (3) datat.ph_inpup, (4) graph_templates.php, (5) graphs.php, (6) reports_admin.php, and (7) data_input.php. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-23226
MISC |
canon — oce_print_exec_workgroup
|
Canon Oce Print Exec Workgroup 1.3.2 allows Host header injection. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39367
MISC |
care2x — hospital_information_management
|
Stored cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in Care2x Hospital Information Management 2.7 Alpha. The vulnerability has found POST requests in /modules/registration_admission/patient_register.php page with “name_middle”, “addr_str”, “station”, “name_maiden”, “name_2”, “name_3” parameters. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-36352
MISC
MISC |
cerner — mobile_care
|
A SQL Injection vulnerability in Cerner Mobile Care 5.0.0 allows remote unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary SQL commands via a Fullwidth Apostrophe (aka U+FF07) in the default.aspx User ID field. Arbitrary system commands can be executed through the use of xp_cmdshell. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-36385
MISC
MISC
MISC |
cisco — application_policy_infrastructure_controller
|
A vulnerability in an API endpoint of Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller (APIC) and Cisco Cloud Application Policy Infrastructure Controller (Cloud APIC) could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to read or write arbitrary files on an affected system. This vulnerability is due to improper access control. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by using a specific API endpoint to upload a file to an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to read or write arbitrary files on an affected device. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1577
CISCO |
cisco — application_policy_infrastructure_controller
|
A vulnerability in an API endpoint of Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller (APIC) and Cisco Cloud Application Policy Infrastructure Controller (Cloud APIC) could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to elevate privileges to Administrator on an affected device. This vulnerability is due to an improper policy default setting. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by using a non-privileged credential for Cisco ACI Multi-Site Orchestrator (MSO) to send a specific API request to a managed Cisco APIC or Cloud APIC device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to obtain Administrator credentials on the affected device. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1578
CISCO |
cisco — cisco — application_policy_infrastructure_controller
|
A vulnerability in an API endpoint of Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller (APIC) and Cisco Cloud Application Policy Infrastructure Controller (Cloud APIC) could allow an authenticated, remote attacker with Administrator read-only credentials to elevate privileges on an affected system. This vulnerability is due to an insufficient role-based access control (RBAC). An attacker with Administrator read-only credentials could exploit this vulnerability by sending a specific API request using an app with admin write credentials. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to elevate privileges to Administrator with write privileges on the affected device. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1579
CISCO |
cisco — cisco — application_policy_infrastructure_controller
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web UI and API endpoints of Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller (APIC) or Cisco Cloud APIC could allow a remote attacker to perform a command injection or file upload attack on an affected system. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1580
CISCO |
cisco — cisco — application_policy_infrastructure_controller
|
Multiple vulnerabilities in the web UI and API endpoints of Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller (APIC) or Cisco Cloud APIC could allow a remote attacker to perform a command injection or file upload attack on an affected system. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1581
CISCO |
cisco — cisco — application_policy_infrastructure_controller
|
A vulnerability in the web UI of Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller (APIC) or Cisco Cloud APIC could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to perform a stored cross-site scripting attack on an affected system. This vulnerability is due to improper input validation in the web UI. An authenticated attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending malicious input to the web UI. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary script code in the context of the web-based interface or access sensitive, browser-based information. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1582
CISCO |
cisco — cisco — nexus_9000_series_fabric_switches
|
A vulnerability in the Multi-Pod or Multi-Site network configurations for Cisco Nexus 9000 Series Fabric Switches in Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) mode could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to unexpectedly restart the device, resulting in a denial of service (DoS) condition. This vulnerability exists because TCP traffic sent to a specific port on an affected device is not properly sanitized. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending crafted TCP data to a specific port that is listening on a public-facing IP address for the Multi-Pod or Multi-Site configuration. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause the device to restart unexpectedly, resulting in a DoS condition. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1586
CISCO |
cisco — nexus_9000_series_fabric_switches
|
A vulnerability in Cisco Nexus 9000 Series Fabric Switches in Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) Mode could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to cause a queue wedge on a leaf switch, which could result in critical control plane traffic to the device being dropped. This could result in one or more leaf switches being removed from the fabric. This vulnerability is due to mishandling of ingress TCP traffic to a specific port. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a stream of TCP packets to a specific port on a Switched Virtual Interface (SVI) configured on the device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause a specific packet queue to queue network buffers but never process them, leading to an eventual queue wedge. This could cause control plane traffic to be dropped, resulting in a denial of service (DoS) condition where the leaf switches are unavailable. Note: This vulnerability requires a manual intervention to power-cycle the device to recover. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1523
CISCO |
cisco — nexus_9000_series_fabric_switches
|
A vulnerability in the fabric infrastructure file system access control of Cisco Nexus 9000 Series Fabric Switches in Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) mode could allow an authenticated, local attacker to read arbitrary files on an affected system. This vulnerability is due to improper access control. An attacker with Administrator privileges could exploit this vulnerability by executing a specific vulnerable command on an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to read arbitrary files on the file system of the affected device. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1583
CISCO |
cisco — nexus_9000_series_fabric_switches
|
A vulnerability in Cisco Nexus 9000 Series Fabric Switches in Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) mode could allow an authenticated, local attacker to elevate privileges on an affected device. This vulnerability is due to insufficient restrictions during the execution of a specific CLI command. An attacker with administrative privileges could exploit this vulnerability by performing a command injection attack on the vulnerable command. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to access the underlying operating system as root. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1584
CISCO |
| cisco — nexus_9500_series_switches |
A vulnerability in the EtherChannel port subscription logic of Cisco Nexus 9500 Series Switches could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to bypass access control list (ACL) rules that are configured on an affected device. This vulnerability is due to oversubscription of resources that occurs when applying ACLs to port channel interfaces. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by attempting to access network resources that are protected by the ACL. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to access network resources that would be protected by the ACL that was applied on the port channel interface. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1591
CISCO |
| cisco — nx-os_software |
A vulnerability in the MPLS Operation, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) feature of Cisco NX-OS Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to cause a denial of service (DoS) condition on an affected device. This vulnerability is due to improper input validation when an affected device is processing an MPLS echo-request or echo-reply packet. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending malicious MPLS echo-request or echo-reply packets to an interface that is enabled for MPLS forwarding on the affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause the MPLS OAM process to crash and restart multiple times, causing the affected device to reload and resulting in a DoS condition. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1588
CISCO |
cisco — nx-os_software
|
A vulnerability in the VXLAN Operation, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) feature of Cisco NX-OS Software, known as NGOAM, could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to cause a denial of service (DoS) condition on an affected device. This vulnerability is due to improper handling of specific packets with a Transparent Interconnection of Lots of Links (TRILL) OAM EtherType. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending crafted packets, including the TRILL OAM EtherType of 0x8902, to a device that is part of a VXLAN Ethernet VPN (EVPN) fabric. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause an affected device to experience high CPU usage and consume excessive system resources, which may result in overall control plane instability and cause the affected device to reload. Note: The NGOAM feature is disabled by default. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1587
CISCO |
cisco — nx-os_software
|
A vulnerability in the implementation of the system login block-for command for Cisco NX-OS Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to cause a login process to unexpectedly restart, causing a denial of service (DoS) condition. This vulnerability is due to a logic error in the implementation of the system login block-for command when an attack is detected and acted upon. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by performing a brute-force login attack on an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause a login process to reload, which could result in a delay during authentication to the affected device. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1590
CISCO |
cisco — ucs_manager
|
A vulnerability in the way Cisco UCS Manager software handles SSH sessions could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to cause a denial of service (DoS) condition on an affected device. This vulnerability is due to improper resource management for established SSH sessions. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by opening a significant number of SSH sessions on an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause a crash and restart of internal Cisco UCS Manager software processes and a temporary loss of access to the Cisco UCS Manager CLI and web UI. Note: The attacker must have valid user credentials to authenticate to the affected device. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-1592
CISCO |
codesys — codesys
|
An unsafe deserialization vulnerability exists in the Engine.plugin ProfileInformation ProfileData functionality of CODESYS GmbH CODESYS Development System 3.5.16 and 3.5.17. A specially crafted file can lead to arbitrary command execution. An attacker can provide a malicious file to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21869
MISC |
| cscape — cscape |
Cscape (All Versions prior to 9.90 SP5) lacks proper validation of user-supplied data when parsing project files. This could lead to an out-of-bounds write via an uninitialized pointer. An attacker could leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33015
MISC |
cscape — cscape
|
Cscape (All Versions prior to 9.90 SP5) lacks proper validation of user-supplied data when parsing project files. This could lead to an out-of-bounds read. An attacker could leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32975
MISC |
cscape — cscape
|
Cscape (All Versions prior to 9.90 SP5) lacks proper validation of user-supplied data when parsing project files. This could lead to an out-of-bounds write. An attacker could leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32995
MISC |
cxuucms — cxuucms
|
Multiple Cross Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities exists in CXUUCMS 3.1 in the search and c parameters in (1) public/search.php and in the (2) c parameter in admin.php. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39599
MISC |
cxuucms — cxuucms
|
SQL Injection vulnerability in cxuucms 3.1 ivia the pid parameter in public/admin.php. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3264
MISC |
d-link — dsr-500n
|
** UNSUPPORTED WHEN ASSIGNED ** D-Link DSR-500N version 1.02 contains hard-coded credentials for undocumented user accounts in the ‘/etc/passwd’ file.If an attacker succeeds in recovering the cleartext password of the identified hash value, he will be able to log in via SSH or Telnet and thus gain access to the underlying embedded Linux operating system on the device. Fixed in version 2.12/2. NOTE: This vulnerability only affects products that are no longer supported by the maintainer. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39615
MISC
MISC
MISC |
d-link — dvg-3104ms
|
** UNSUPPORTED WHEN ASSIGNED ** D-Link DVG-3104MS version 1.0.2.0.3, 1.0.2.0.4, and 1.0.2.0.4E contains hard-coded credentials for undocumented user accounts in the ‘/etc/passwd’ file. As weak passwords have been used, the plaintext passwords can be recovered from the hash values. NOTE: This vulnerability only affects products that are no longer supported by the maintainer. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39613
MISC
MISC
MISC |
d-link — dvx-2000ms
|
D-Link DVX-2000MS contains hard-coded credentials for undocumented user accounts in the ‘/etc/passwd’ file. As weak passwords have been used, the plaintext passwords can be recovered from the hash values. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39614
MISC
MISC
MISC |
d-link — multiple_devices
|
An issue was discovered in D-Link DIR816_A1_FW101CNB04 750m11ac wireless router via the HTTP request parameter in the handler function of /goform/form2userconfig.cgi route, which can construct the user name string to delete the user function. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39510
MISC
MISC |
d-link — multiple_devices
|
An issue was discovered in D-Link DIR-816 DIR-816A2_FWv1.10CNB05_R1B011D88210 750m11ac wireless router via the HTTP request parameter in the handler function of /goform/form2userconfig.cgi route, which can construct the user name string to delete the user function. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39509
MISC
MISC |
dedecms — dedecms
|
An arbitrary file upload vulnerability in the /uploads/dede component of DedeCMS V5.7SP2 allows attackers to upload a webshell in HTM format. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18114
MISC |
dedecms — dedecms
|
The plus/search.php component in DedeCMS 5.7 SP2 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary PHP code via the typename parameter because the contents of typename.inc are under an attacker’s control. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18917
MISC |
detect-charachter-encoding — detect-charachter-encoding
|
detect-character-encoding is an open source character encoding inspection library. In detect-character-encoding v0.6.0 and earlier, data matching no charset causes the Node.js process to crash. The problem has been patched in [detect-character-encoding v0.7.0](https://github.com/sonicdoe/detect-character-encoding/releases/tag/v0.7.0). No workaround are available and all users should update to resolve this issue. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39157
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
discourse — discourse
|
Discourse is an open source platform for community discussion. In affected versions category names can be used for Cross-site scripting(XSS) attacks. This is mitigated by Discourse’s default Content Security Policy and this vulnerability only affects sites which have modified or disabled or changed Discourse’s default Content Security Policy have allowed for moderators to modify categories. This issue is patched in the latest stable, beta and tests-passed versions of Discourse. Users are advised to ensure that the Content Security Policy is enabled, and has not been modified in a way which would make it more vulnerable to XSS attacks. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39161
CONFIRM |
doyocms — doyocms
|
A SQL injection vulnerability in admin.php of DOYOCMS 2.3 allows attackers to execute arbitrary SQL commands via the orders[] parameter. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-19821
MISC |
dzzoffice — dzzoffice
|
A cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the referer parameter of Dzzoffice 2.02 allows attackers to execute arbitrary web scripts or HTML via a crafted payload. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-19703
MISC |
earclink — espcms-p8
|
EARCLINK ESPCMS-P8 was discovered to contain a SQL injection vulnerability in the espcms_web/Search.php component via the attr_array parameter. This vulnerability allows attackers to access sensitive database information. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18913
MISC |
eclipse_cyclone — eclipse_cyclone
|
A stack buffer overflow in /ddsi/q_bitset.h of Eclipse IOT Cyclone DDS Project v0.1.0 causes the DDS subscriber server to crash. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18734
MISC
MISC
MISC |
eclipse_cyclone — eclipse_cyclone
|
A heap buffer overflow in /src/dds_stream.c of Eclipse IOT Cyclone DDS Project v0.1.0 causes the DDS subscriber server to crash. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18735
MISC
MISC
MISC |
elf-g10hn — elf-g10hn
|
There is a logic vulnerability in Elf-G10HN 1.0.0.608. An unauthenticated attacker could perform specific operations to exploit this vulnerability. Due to insufficient security design, successful exploit could allow an attacker to add users to be friends without prompting in the target device. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22449
MISC |
emtec — zoc
|
EmTec ZOC before 8.02.2 allows e[201~ pastes, a different vulnerability than CVE-2021-32198. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40147
MISC |
| envoy — envoy |
Envoy is an open source L7 proxy and communication bus designed for large modern service oriented architectures. In affected versions after Envoy sends a locally generated response it must stop further processing of request or response data. However when local response is generated due the internal buffer overflow while request or response is processed by the filter chain the operation may not be stopped completely and result in accessing a freed memory block. A specifically constructed request delivered by an untrusted downstream or upstream peer in the presence of extensions that modify and increase the size of request or response bodies resulting in a Denial of Service when using extensions that modify and increase the size of request or response bodies, such as decompressor filter. Envoy versions 1.19.1, 1.18.4, 1.17.4, 1.16.5 contain fixes to address incomplete termination of request processing after locally generated response. As a workaround disable Envoy’s decompressor, json-transcoder or grpc-web extensions or proprietary extensions that modify and increase the size of request or response bodies, if feasible. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32781
MISC
CONFIRM |
| envoy — envoy |
Envoy is an open source L7 proxy and communication bus designed for large modern service oriented architectures. In affected versions when ext-authz extension is sending request headers to the external authorization service it must merge multiple value headers according to the HTTP spec. However, only the last header value is sent. This may allow specifically crafted requests to bypass authorization. Attackers may be able to escalate privileges when using ext-authz extension or back end service that uses multiple value headers for authorization. A specifically constructed request may be delivered by an untrusted downstream peer in the presence of ext-authz extension. Envoy versions 1.19.1, 1.18.4, 1.17.4, 1.16.5 contain fixes to the ext-authz extension to correctly merge multiple request header values, when sending request for authorization. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32777
CONFIRM
MISC |
envoy — envoy
|
Envoy is an open source L7 proxy and communication bus designed for large modern service oriented architectures. In affected versions Envoy transitions a H/2 connection to the CLOSED state when it receives a GOAWAY frame without any streams outstanding. The connection state is transitioned to DRAINING when it receives a SETTING frame with the SETTINGS_MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS parameter set to 0. Receiving these two frames in the same I/O event results in abnormal termination of the Envoy process due to invalid state transition from CLOSED to DRAINING. A sequence of H/2 frames delivered by an untrusted upstream server will result in Denial of Service in the presence of untrusted **upstream** servers. Envoy versions 1.19.1, 1.18.4 contain fixes to stop processing of pending H/2 frames after connection transition to the CLOSED state. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32780
CONFIRM
MISC |
envoy — envoy
|
Envoy is an open source L7 proxy and communication bus designed for large modern service oriented architectures. In affected versions envoy’s procedure for resetting a HTTP/2 stream has O(N^2) complexity, leading to high CPU utilization when a large number of streams are reset. Deployments are susceptible to Denial of Service when Envoy is configured with high limit on H/2 concurrent streams. An attacker wishing to exploit this vulnerability would require a client opening and closing a large number of H/2 streams. Envoy versions 1.19.1, 1.18.4, 1.17.4, 1.16.5 contain fixes to reduce time complexity of resetting HTTP/2 streams. As a workaround users may limit the number of simultaneous HTTP/2 dreams for upstream and downstream peers to a low number, i.e. 100. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32778
MISC
CONFIRM |
envoy — envoy
|
Envoy is an open source L7 proxy and communication bus designed for large modern service oriented architectures. In affected versions envoy incorrectly handled a URI ‘#fragment’ element as part of the path element. Envoy is configured with an RBAC filter for authorization or similar mechanism with an explicit case of a final “/admin” path element, or is using a negative assertion with final path element of “/admin”. The client sends request to “/app1/admin#foo”. In Envoy prior to 1.18.0, or 1.18.0+ configured with path_normalization=false. Envoy treats fragment as a suffix of the query string when present, or as a suffix of the path when query string is absent, so it evaluates the final path element as “/admin#foo” and mismatches with the configured “/admin” path element. In Envoy 1.18.0+ configured with path_normalization=true. Envoy transforms this to /app1/admin%23foo and mismatches with the configured /admin prefix. The resulting URI is sent to the next server-agent with the offending “#foo” fragment which violates RFC3986 or with the nonsensical “%23foo” text appended. A specifically constructed request with URI containing ‘#fragment’ element delivered by an untrusted client in the presence of path based request authorization resulting in escalation of Privileges when path based request authorization extensions. Envoy versions 1.19.1, 1.18.4, 1.17.4, 1.16.5 contain fixes that removes fragment from URI path in incoming requests. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32779
MISC
CONFIRM |
| exiv2 — exiv2 |
A float point exception in the printLong function in tags_int.cpp of Exiv2 0.27.99.0 allows attackers to cause a denial of service (DOS) via a crafted tif file. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18774
MISC |
exiv2 — exiv2
|
Exiv2 0.27.99.0 has a global buffer over-read in Exiv2::Internal::Nikon1MakerNote::print0x0088 in nikonmn_int.cpp which can result in an information leak. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18771
MISC |
exiv2 — exiv2
|
An invalid memory access in the decode function in iptc.cpp of Exiv2 0.27.99.0 allows attackers to cause a denial of service (DOS) via a crafted tif file. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18773
MISC |
feehicms — feehicms
|
Insufficient filtering of the tag parameters in feehicms 0.1.3 allows attackers to execute arbitrary web or HTML via a crafted payload. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-19709
MISC |
ffmpeg — ffmpeg
|
adts_decode_extradata in libavformat/adtsenc.c in FFmpeg 4.4 does not check the init_get_bits return value, which is a necessary step because the second argument to init_get_bits can be crafted. |
2021-08-21 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-38171
MISC
MISC |
flatcore-cms — flatcore-cms
|
Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerabilty exists in FlatCore-CMS 2.0.7 via the upload addon plugin, which could let a remote malicious user exeuct arbitrary php code. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39608
MISC |
flatcore-cms — flatcore-cms
|
Cross Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability exiss in FlatCore-CMS 2.0.7 via the upload image function. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39609
MISC |
forgerock — access_management
|
ForgeRock Access Management (AM) before 7.0.2, when configured with Active Directory as the Identity Store, has an authentication-bypass issue. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37153
MISC
CONFIRM |
forgerock — access_management
|
In ForgeRock Access Management (AM) before 7.0.2, the SAML2 implementation allows XML injection, potentially enabling a fraudulent SAML 2.0 assertion. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37154
MISC
CONFIRM |
gd — graphics_library
|
** DISPUTED ** gdImageGd2Ptr in gd_gd2.c in the GD Graphics Library (aka LibGD) through 2.3.2 has a double free. NOTE: the vendor’s position is “The GD2 image format is a proprietary image format of libgd. It has to be regarded as being obsolete, and should only be used for development and testing purposes.” |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40145
MISC
MISC
MISC |
gecos — gecos
|
opensysusers through 0.6 does not safely use eval on files in sysusers.d that may contain shell metacharacters. For example, it allows command execution via a crafted GECOS field whereas systemd-sysusers (a program with the same specification) does not do that. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40084
MISC
MISC |
| gitlab — ce/ee |
Improper authorization in GitLab CE/EE affecting all versions since 12.6 allowed guest users to create issues for Sentry errors and track their status |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22256
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
| gitlab — ce/ee |
Under specialized conditions, GitLab CE/EE versions starting 7.10 may allow existing GitLab users to use an invite URL meant for another email address to gain access into a group. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22243
CONFIRM
MISC |
| gitlab — ce/ee |
Improper authorization in GitLab EE affecting all versions since 13.4 allowed a user who previously had the necessary access to trigger deployments to protected environments under specific conditions after the access has been removed |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22253
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
| gitlab — ce/ee |
A confusion between tag and branch names in GitLab CE/EE affecting all versions since 13.7 allowed a Developer to access protected CI variables which should only be accessible to Maintainers |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22252
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
| gitlab — ce/ee |
Improper authorization in GitLab CE/EE affecting all versions since 13.3 allowed users to view and delete impersonation tokens that administrators created for their account |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22250
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
| gitlab — ce/ee |
Under specialized conditions, GitLab may allow a user with an impersonation token to perform Git actions even if impersonation is disabled. This vulnerability is present in GitLab CE/EE versions before 13.12.9, 14.0.7, 14.1.2 |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22237
MISC
CONFIRM |
| gitlab — ce/ee |
Improper validation of commit author in GitLab CE/EE affecting all versions allowed an attacker to make several pages in a project impossible to view |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22245
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
gitlab — ce/ee
|
Due to improper handling of OAuth client IDs, new subscriptions generated OAuth tokens on an incorrect OAuth client application. This vulnerability is present in GitLab CE/EE since version 14.1. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22236
CONFIRM
MISC |
gitlab — ce/ee
|
Insufficient input sanitization in Mermaid markdown in GitLab CE/EE version 11.4 and up allows an attacker to exploit a stored cross-site scripting vulnerability via a specially-crafted markdown |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22242
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
gitlab — ce/ee
|
Improper authorization in GitLab CE/EE affecting all versions since 13.0 allows guests in private projects to view CI/CD analytics |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22247
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
gitlab — ce/ee
|
Improper authorization in the vulnerability report feature in GitLab EE affecting all versions since 13.1 allowed a reporter to access vulnerability data |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22244
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
gnome — evolution-rss
|
In GNOME evolution-rss through 0.3.96, network-soup.c does not enable TLS certificate verification on the SoupSessionSync objects it creates, leaving users vulnerable to network MITM attacks. NOTE: this is similar to CVE-2016-20011. |
2021-08-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39361
MISC
MISC |
gnome — grilo
|
In GNOME grilo though 0.3.13, grl-net-wc.c does not enable TLS certificate verification on the SoupSessionAsync objects it creates, leaving users vulnerable to network MITM attacks. NOTE: this is similar to CVE-2016-20011. |
2021-08-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39365
MISC
MISC
DEBIAN |
gnome — libzapojit
|
In GNOME libzapojit through 0.0.3, zpj-skydrive.c does not enable TLS certificate verification on the SoupSessionSync objects it creates, leaving users vulnerable to network MITM attacks. NOTE: this is similar to CVE-2016-20011. |
2021-08-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39360
MISC
MISC |
go-ethereum — go-ethereum
|
go-ethereum is the official Go implementation of the Ethereum protocol. In affected versions a consensus-vulnerability in go-ethereum (Geth) could cause a chain split, where vulnerable versions refuse to accept the canonical chain. Further details about the vulnerability will be disclosed at a later date. A patch is included in the upcoming `v1.10.8` release. No workaround are available. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39137
MISC
CONFIRM |
gotenberg — gotenberg
|
It is possible to inject HTML and/or JavaScript in the HTML to PDF conversion in Gotenberg through 6.2.1 via the /convert/html endpoint. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-14161
MISC
MISC
MISC |
gotenberg — gotenberg
|
An SSRF vulnerability in Gotenberg through 6.2.1 exists in the remote URL to PDF conversion, which results in a remote attacker being able to read local files or fetch intranet resources. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-14160
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| gpac_project — advanced_content_library |
An exploitable integer overflow vulnerability exists within the MPEG-4 decoding functionality of the GPAC Project on Advanced Content library v1.0.1. A specially crafted MPEG-4 input using the “ctts” FOURCC code can cause an integer overflow due to unchecked arithmetic resulting in a heap-based buffer overflow that causes memory corruption. An attacker can convince a user to open a video to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21836
MISC |
| gpac_project — advanced_content_library |
An exploitable integer overflow vulnerability exists within the MPEG-4 decoding functionality of the GPAC Project on Advanced Content library v1.0.1. A specially crafted MPEG-4 input can cause an integer overflow when the library encounters an atom using the “trun” FOURCC code due to unchecked arithmetic resulting in a heap-based buffer overflow that causes memory corruption. An attacker can convince a user to open a video to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21850
MISC |
| gpac_project — advanced_content_library |
An exploitable integer overflow vulnerability exists within the MPEG-4 decoding functionality of the GPAC Project on Advanced Content library v1.0.1. A specially crafted MPEG-4 input can cause an integer overflow when the library encounters an atom using the “tfra” FOURCC code due to unchecked arithmetic resulting in a heap-based buffer overflow that causes memory corruption. An attacker can convince a user to open a video to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21849
MISC |
| gpac_project — advanced_content_library |
An exploitable integer overflow vulnerability exists within the MPEG-4 decoding functionality of the GPAC Project on Advanced Content library v1.0.1. The library will actually reuse the parser for atoms with the “stsz” FOURCC code when parsing atoms that use the “stz2” FOURCC code and can cause an integer overflow due to unchecked arithmetic resulting in a heap-based buffer overflow that causes memory corruption. An attacker can convince a user to open a video to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21848
MISC |
gpac_project — advanced_content_library
|
An exploitable integer overflow vulnerability exists within the MPEG-4 decoding functionality of the GPAC Project on Advanced Content library v1.0.1. A specially crafted MPEG-4 input used to process an atom using the “saio” FOURCC code cause an integer overflow due to unchecked arithmetic resulting in a heap-based buffer overflow that causes memory corruption. An attacker can convince a user to open a video to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21840
MISC |
gpac_project — advanced_content_library
|
An exploitable integer overflow vulnerability exists within the MPEG-4 decoding functionality of the GPAC Project on Advanced Content library v1.0.1. A specially crafted MPEG-4 input when reading an atom using the ‘sbgp’ FOURCC code can cause an integer overflow due to unchecked arithmetic resulting in a heap-based buffer overflow that causes memory corruption. An attacker can convince a user to open a video to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21841
MISC |
gpac_project — advanced_content_library
|
An exploitable integer overflow vulnerability exists within the MPEG-4 decoding functionality of the GPAC Project on Advanced Content library v1.0.1. A specially crafted MPEG-4 input when decoding the atom for the “co64” FOURCC can cause an integer overflow due to unchecked arithmetic resulting in a heap-based buffer overflow that causes memory corruption. An attacker can convince a user to open a video to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21834
MISC |
gpac_project — advanced_content_library
|
An exploitable integer overflow vulnerability exists within the MPEG-4 decoding functionality of the GPAC Project on Advanced Content library v1.0.1. A specially crafted MPEG-4 input when decoding the atom associated with the “csgp” FOURCC can cause an integer overflow due to unchecked arithmetic resulting in a heap-based buffer overflow that causes memory corruption. An attacker can convince a user to open a video to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21835
MISC |
gpac_project — advanced_content_library
|
An exploitable integer overflow vulnerability exists within the MPEG-4 decoding functionality of the GPAC Project on Advanced Content library v1.0.1. A specially crafted MPEG-4 input can cause an integer overflow when processing an atom using the ‘ssix’ FOURCC code, due to unchecked arithmetic resulting in a heap-based buffer overflow that causes memory corruption. An attacker can convince a user to open a video to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21842
MISC |
huawei — cloudengine
|
There is a denial of service vulnerability in some huawei products. In specific scenarios, due to the improper handling of the packets, an attacker may craft the specific packet. Successful exploit may cause some services abnormal. Affected product versions include:CloudEngine 12800 V200R005C00SPC800, CloudEngine 5800 V200R005C00SPC800, CloudEngine 6800 V200R005C00SPC800, CloudEngine 7800 V200R005C00SPC800. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22328
MISC |
huawei — multiple_products
|
There is a denial of service vulnerability in Huawei products. A module cannot deal with specific messages due to validating inputs insufficiently. Attackers can exploit this vulnerability by sending specific messages to affected module. This can cause denial of service. Affected product versions include: S12700 V200R013C00SPC500, V200R019C00SPC500; S5700 V200R013C00SPC500, V200R019C00SPC500; S6700 V200R013C00SPC500, V200R019C00SPC500; S7700 V200R013C00SPC500, V200R019C00SPC500. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-22357
MISC |
ibm — aix
|
IBM AIX 7.1, 7.2, and VIOS 3.1 could allow a local user to exploit a vulnerability in the AIX kernel to cause a denial of service. IBM X-Force ID: 201106. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29727
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — aix
|
IBM AIX 7.1, 7.2, and VIOS 3.1 could allow a non-privileged local user to exploit a vulnerability in the kernel to gain root privileges. IBM X-Force ID: 203977. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29801
CONFIRM
XF |
ibm — aix
|
IBM AIX 7.1, 7.2, and VIOS 3.1 could allow a non-privileged local user to exploit a vulnerability in the AIX kernel to cause a denial of service. IBM X-Force ID: 206086. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29862
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — api_connect
|
IBM API Connect 5.0.0.0 through 5.0.8.11 could alllow a remote user to obtain sensitive information or conduct denial of serivce attacks due to open ports. IBM X-Force ID: 201018. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29715
XF
CONFIRM |
ibm — api_connect
|
IBM API Connect 5.0.0.0 through 5.0.8.11 could allow a user to potentially inject code due to unsanitized user input. IBM X-Force ID: 202774. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29772
CONFIRM
XF |
ibm — mximo_asset_management
|
IBM Maximo Asset Management 7.6.0 and 7.6.1 is vulnerable to cross-site scripting. This vulnerability allows users to embed arbitrary JavaScript code in the Web UI thus altering the intended functionality potentially leading to credentials disclosure within a trusted session. IBM X-Force ID: 201694. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29744
XF
CONFIRM |
iec104 — iec104
|
A segmentation violation in the Iec104_Deal_I function of IEC104 v1.0 allows attackers to cause a denial of service (DOS). |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18730
MISC |
iec104 — iec104
|
A segmentation violation in the Iec104_Deal_FirmUpdate function of IEC104 v1.0 allows attackers to cause a denial of service (DOS). |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18731
MISC |
istio — istio
|
Istio is an open source platform for providing a uniform way to integrate microservices, manage traffic flow across microservices, enforce policies and aggregate telemetry data. According to [RFC 4343](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc4343), Istio authorization policy should compare the hostname in the HTTP Host header in a case insensitive way, but currently the comparison is case sensitive. The proxy will route the request hostname in a case-insensitive way which means the authorization policy could be bypassed. As an example, the user may have an authorization policy that rejects request with hostname “httpbin.foo” for some source IPs, but the attacker can bypass this by sending the request with hostname “Httpbin.Foo”. Patches are available in Istio 1.11.1, Istio 1.10.4 and Istio 1.9.8. As a work around a Lua filter may be written to normalize Host header before the authorization check. This is similar to the Path normalization presented in the [Security Best Practices](https://istio.io/latest/docs/ops/best-practices/security/#case-normalization) guide. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39155
MISC
CONFIRM |
istio — istio
|
Istio is an open source platform for providing a uniform way to integrate microservices, manage traffic flow across microservices, enforce policies and aggregate telemetry data. Istio 1.11.0, 1.10.3 and below, and 1.9.7 and below contain a remotely exploitable vulnerability where an HTTP request with `#fragment` in the path may bypass Istio’s URI path based authorization policies. Patches are available in Istio 1.11.1, Istio 1.10.4 and Istio 1.9.8. As a work around a Lua filter may be written to normalize the path. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39156
MISC
CONFIRM |
joomla! — joomla!
|
An issue was discovered in Joomla! 4.0.0. The media manager does not correctly check the user’s permissions before executing a file deletion command. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-26040
MISC |
joplin — joplin
|
The package joplin before 2.3.2 are vulnerable to Cross-site Request Forgery (CSRF) due to missing CSRF checks in various forms. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-23431
MISC
MISC |
jupyter — nbgitpuller
|
nbgitpuller is a Jupyter server extension to sync a git repository one-way to a local path. Due to unsanitized input, visiting maliciously crafted links could result in arbitrary code execution in the user environment. This has been resolved in version 0.10.2 and all users are advised to upgrade. No work around exist for users who can not upgrade. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39160
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
| knot_resolver — knot_resolver |
Knot Resolver before 5.3.2 is prone to an assertion failure, triggerable by a remote attacker in an edge case (NSEC3 with too many iterations used for a positive wildcard proof). |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40083
MISC |
lg — n1t1_10124_devices
|
Network Attached Storage on LG N1T1*** 10124 devices allows an unauthenticated attacker to gain root access via OS command injection in the en/ajp/plugins/access.ssh/checkInstall.php destServer parameter. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-38306
MISC
MISC
MISC |
libav — libav
|
In Libav 12.3, there is a heap-based buffer over-read in vc1_decode_p_mb_intfi in vc1_block.c that allows an attacker to cause denial-of-service via a crafted file. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18778
MISC |
libav — libav
|
In Libav 12.3, there is a heap-based buffer over-read in vc1_decode_b_mb_intfi in vc1_block.c that allows an attacker to cause denial-of-service via a crafted file. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18775
MISC |
libav — libav
|
In Libav 12.3, there is a segmentation fault in vc1_decode_b_mb_intfr in vc1_block.c that allows an attacker to cause denial-of-service via a crafted file. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18776
MISC |
mender — enterprise
|
The useradm service 1.14.0 (in Northern.tech Mender Enterprise 2.7.x before 2.7.1) and 1.13.0 (in Northern.tech Mender Enterprise 2.6.x before 2.6.1) allows users to access the system with their JWT token after logout, because of missing invalidation (if the JWT verification cache is enabled). |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-35342
MISC
MISC |
mezzanine — mezzanine
|
Cross Site Scripting (XSS) in Mezzanine v4.3.1 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via the ‘Description’ field of the component ‘admin/blog/blogpost/add/’. This issue is different than CVE-2018-16632. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-19002
MISC |
| microsoft — edge |
Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-36929
MISC |
microsoft — edge
|
Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-36931. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-36928
MISC |
microsoft — edge
|
Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2021-36928. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-36931
MISC |
miniftpd — miniftpd
|
A Buffer Overflow vulnerabilty exists in Miniftpd 1.0 in the do_mkd function in the ftpproto.c file, which could let a remote malicious user cause a Denial of Service. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39602
MISC |
misskey — misskey
|
Misskey is a decentralized microblogging platform. In versions of Misskey prior to 12.51.0, malicious actors can use the web client built-in dialog to display a malicious string, leading to cross-site scripting (XSS). XSS could compromise the API request token. This issue has been fixed in version 12.51.0. There are no known workarounds aside from upgrading. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39169
CONFIRM
MISC |
mit — kerberos
|
The Key Distribution Center (KDC) in MIT Kerberos 5 (aka krb5) before 1.18.5 and 1.19.x before 1.19.3 has a NULL pointer dereference in kdc/do_tgs_req.c via a FAST inner body that lacks a server field. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37750
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM
FEDORA |
mootools — mootools
|
This affects all versions of package mootools. This is due to the ability to pass untrusted input to Object.merge() |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-23432
MISC |
| movable_type — movable_type |
Cross-site scripting vulnerability in Setting screen of Server Sync of Movable Type (Movable Type Advanced 7 r.4903 and earlier (Movable Type Advanced 7 Series) and Movable Type Premium Advanced 1.44 and earlier) allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary script or HTML via unspecified vectors. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20812
MISC
MISC |
| movable_type — movable_type |
Cross-site scripting vulnerability in Website Management screen of Movable Type (Movable Type 7 r.4903 and earlier (Movable Type 7 Series), Movable Type 6.8.0 and earlier (Movable Type 6 Series), Movable Type Advanced 7 r.4903 and earlier (Movable Type Advanced 7 Series), Movable Type Premium 1.44 and earlier, and Movable Type Premium Advanced 1.44 and earlier) allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary script or HTML via unspecified vectors. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20810
MISC
MISC |
| movable_type — movable_type |
Cross-site scripting vulnerability in List of Assets screen of Movable Type (Movable Type 7 r.4903 and earlier (Movable Type 7 Series), Movable Type 6.8.0 and earlier (Movable Type 6 Series), Movable Type Advanced 7 r.4903 and earlier (Movable Type Advanced 7 Series), Movable Type Premium 1.44 and earlier, and Movable Type Premium Advanced 1.44 and earlier) allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary script or HTML via unspecified vectors. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20811
MISC
MISC |
| movable_type — movable_type |
Cross-site scripting vulnerability in Edit screen of Content Data of Movable Type (Movable Type 7 r.4903 and earlier (Movable Type 7 Series) and Movable Type Advanced 7 r.4903 and earlier (Movable Type Advanced 7 Series)) allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary script or HTML via unspecified vectors. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20813
MISC
MISC |
movable_type — movable_type
|
Cross-site scripting vulnerability in Setting screen of ContentType Information Widget Plugin of Movable Type (Movable Type 7 r.4903 and earlier (Movable Type 7 Series), Movable Type Advanced 7 r.4903 and earlier (Movable Type Advanced 7 Series), and Movable Type Premium 1.44 and earlier) allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary script or HTML via unspecified vectors. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20814
MISC
MISC |
movable_type — movable_type
|
Cross-site scripting vulnerability in Edit Boilerplate screen of Movable Type (Movable Type 7 r.4903 and earlier (Movable Type 7 Series), Movable Type 6.8.0 and earlier (Movable Type 6 Series), Movable Type Advanced 7 r.4903 and earlier (Movable Type Advanced 7 Series), Movable Type Premium 1.44 and earlier, and Movable Type Premium Advanced 1.44 and earlier) allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary script or HTML via unspecified vectors. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20815
MISC
MISC |
movable_type — movable_type
|
Cross-site scripting vulnerability in Search screen of Movable Type (Movable Type 7 r.4903 and earlier (Movable Type 7 Series), Movable Type 6.8.0 and earlier (Movable Type 6 Series), Movable Type Advanced 7 r.4903 and earlier (Movable Type Advanced 7 Series), Movable Type Premium 1.44 and earlier, and Movable Type Premium Advanced 1.44 and earlier) allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary script or HTML via unspecified vectors. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20808
MISC
MISC |
movable_type — movable_type
|
Cross-site scripting vulnerability in Create screens of Entry, Page, and Content Type of Movable Type (Movable Type 7 r.4903 and earlier (Movable Type 7 Series), Movable Type 6.8.0 and earlier (Movable Type 6 Series), Movable Type Advanced 7 r.4903 and earlier (Movable Type Advanced 7 Series), Movable Type Premium 1.44 and earlier, and Movable Type Premium Advanced 1.44 and earlier) allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary script or HTML via unspecified vectors. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20809
MISC
MISC |
mz_automation — gmbh_lib60870
|
A denial of service vulnerability exists in the ASDU message processing functionality of MZ Automation GmbH lib60870.NET 2.2.0. A specially crafted network request can lead to loss of communications. An attacker can send an unauthenticated message to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-21778
MISC |
nascent — remkon_device_manager
|
In NASCENT RemKon Device Manager 4.0.0.0, a Directory Traversal vulnerability in a log-reading function in maintenance/readLog.php allows an attacker to read any file via a specialized URL. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-38612
MISC
MISC |
nascent — remkon_device_manager
|
A command-injection vulnerability in the Image Upload function of the NASCENT RemKon Device Manager 4.0.0.0 allows attackers to execute arbitrary commands, as root, via shell metacharacters in the filename parameter to assets/index.php. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-38611
MISC
MISC |
nascent — remkon_device_manager
|
The assets/index.php Image Upload feature of the NASCENT RemKon Device Manager 4.0.0.0 allows attackers to upload any code to the target system and achieve remote code execution. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-38613
MISC
MISC |
netwide_assembler — netwide_assembler
|
Buffer Overflow in Netwide Assembler (NASM) v2.15.xx allows attackers to cause a denial of service via ‘crc64i’ in the component ‘nasmlib/crc64’. This issue is different than CVE-2019-7147. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18974
MISC |
ngiflib — ngiflib
|
ngiflib 0.4 has a heap overflow in GetByteStr() at ngiflib.c:108 in NGIFLIB_NO_FILE mode, GetByteStr() copy memory buffer without checking the boundary. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-36530
MISC |
ngiflib — ngiflib
|
ngiflib 0.4 has a heap overflow in GetByte() at ngiflib.c:70 in NGIFLIB_NO_FILE mode, GetByte() reads memory buffer without checking the boundary. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-36531
MISC |
nvcaffe — nvcaffe
|
NVCaffe’s python required dependencies list used to contain `gfortran`version prior to 0.17.4, entry which does not exist in the repository pypi.org. An attacker could potentially have posted malicious files to pypi.org causing a user to install it within NVCaffe. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39158
CONFIRM |
object-path — object-path
|
This affects the package object-path before 0.11.6. A type confusion vulnerability can lead to a bypass of CVE-2020-15256 when the path components used in the path parameter are arrays. In particular, the condition currentPath === ‘__proto__’ returns false if currentPath is [‘__proto__’]. This is because the === operator returns always false when the type of the operands is different. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-23434
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
octobercms — octobercms
|
octobercms in a CMS platform based on the Laravel PHP Framework. In affected versions of the october/system package an attacker can request an account password reset and then gain access to the account using a specially crafted request. The issue has been patched in Build 472 and v1.1.5. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32648
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
octobercms — octobercms
|
octobercms in a CMS platform based on the Laravel PHP Framework. In affected versions of the october/system package an attacker can exploit this vulnerability to bypass authentication and takeover of and user account on an October CMS server. The vulnerability is exploitable by unauthenticated users via a specially crafted request. This only affects frontend users and the attacker must obtain a Laravel secret key for cookie encryption and signing in order to exploit this vulnerability. The issue has been patched in Build 472 and v1.1.5. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-29487
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
ok-file-formats — ok-file-formats
|
ok-file-formats through 2021-04-29 has a heap-based buffer overflow in the ok_csv_circular_buffer_read function in ok_csv.c. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32263
MISC |
ok-file-formats — ok-file-formats
|
Heap-based Buffer Overflow vulnerability exists in ok-file-formats 1 via the ok_jpg_generate_huffman_table function in ok_jpg.c. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28233
MISC |
opc_foundation — local_discovery_server
|
In OPC Foundation Local Discovery Server (LDS) before 1.04.402.463, remote attackers can cause a denial of service (DoS) by sending carefully crafted messages that lead to Access of a Memory Location After the End of a Buffer. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40142
MISC
MISC |
openexr — ucompress
|
There’s a flaw in OpenEXR’s rleUncompress functionality in versions prior to 3.0.5. An attacker who is able to submit a crafted file to an application linked with OpenEXR could cause an out-of-bounds read. The greatest risk from this flaw is to application availability. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3605
MISC |
openmage — magento_lts
|
OpenMage Magento LTS is an alternative to the Magento CE official releases. Prior to versions 19.4.15 and 20.0.11, layout XML enabled admin users to execute arbitrary commands via block methods. The latest OpenMage Versions up from v19.4.15 and v20.0.11 have this Issue patched. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32758
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
openmage — magento_lts
|
OpenMage magento-lts is an alternative to the Magento CE official releases. Due to missing sanitation in data flow in versions prior to 19.4.15 and 20.0.13, it was possible for admin users to upload arbitrary executable files to the server. OpenMage versions 19.4.15 and 20.0.13 have a patch for this Issue. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32759
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
| openssl — openssl |
ASN.1 strings are represented internally within OpenSSL as an ASN1_STRING structure which contains a buffer holding the string data and a field holding the buffer length. This contrasts with normal C strings which are repesented as a buffer for the string data which is terminated with a NUL (0) byte. Although not a strict requirement, ASN.1 strings that are parsed using OpenSSL’s own “d2i” functions (and other similar parsing functions) as well as any string whose value has been set with the ASN1_STRING_set() function will additionally NUL terminate the byte array in the ASN1_STRING structure. However, it is possible for applications to directly construct valid ASN1_STRING structures which do not NUL terminate the byte array by directly setting the “data” and “length” fields in the ASN1_STRING array. This can also happen by using the ASN1_STRING_set0() function. Numerous OpenSSL functions that print ASN.1 data have been found to assume that the ASN1_STRING byte array will be NUL terminated, even though this is not guaranteed for strings that have been directly constructed. Where an application requests an ASN.1 structure to be printed, and where that ASN.1 structure contains ASN1_STRINGs that have been directly constructed by the application without NUL terminating the “data” field, then a read buffer overrun can occur. The same thing can also occur during name constraints processing of certificates (for example if a certificate has been directly constructed by the application instead of loading it via the OpenSSL parsing functions, and the certificate contains non NUL terminated ASN1_STRING structures). It can also occur in the X509_get1_email(), X509_REQ_get1_email() and X509_get1_ocsp() functions. If a malicious actor can cause an application to directly construct an ASN1_STRING and then process it through one of the affected OpenSSL functions then this issue could be hit. This might result in a crash (causing a Denial of Service attack). It could also result in the disclosure of private memory contents (such as private keys, or sensitive plaintext). Fixed in OpenSSL 1.1.1l (Affected 1.1.1-1.1.1k). Fixed in OpenSSL 1.0.2za (Affected 1.0.2-1.0.2y). |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3712
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
DEBIAN
MLIST
MLIST
MLIST
CONFIRM |
openssl — openssl
|
In order to decrypt SM2 encrypted data an application is expected to call the API function EVP_PKEY_decrypt(). Typically an application will call this function twice. The first time, on entry, the “out” parameter can be NULL and, on exit, the “outlen” parameter is populated with the buffer size required to hold the decrypted plaintext. The application can then allocate a sufficiently sized buffer and call EVP_PKEY_decrypt() again, but this time passing a non-NULL value for the “out” parameter. A bug in the implementation of the SM2 decryption code means that the calculation of the buffer size required to hold the plaintext returned by the first call to EVP_PKEY_decrypt() can be smaller than the actual size required by the second call. This can lead to a buffer overflow when EVP_PKEY_decrypt() is called by the application a second time with a buffer that is too small. A malicious attacker who is able present SM2 content for decryption to an application could cause attacker chosen data to overflow the buffer by up to a maximum of 62 bytes altering the contents of other data held after the buffer, possibly changing application behaviour or causing the application to crash. The location of the buffer is application dependent but is typically heap allocated. Fixed in OpenSSL 1.1.1l (Affected 1.1.1-1.1.1k). |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3711
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
DEBIAN
MLIST
MLIST
MLIST
CONFIRM |
openzepplin — openzepplin
|
OpenZepplin is a library for smart contract development. In affected versions a vulnerability in TimelockController allowed an actor with the executor role to escalate privileges. Further details about the vulnerability will be disclosed at a later date. As a workaround revoke the executor role from accounts not strictly under the team’s control. We recommend revoking all executors that are not also proposers. When applying this mitigation, ensure there is at least one proposer and executor remaining. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39168
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
openzepplin — openzepplin
|
OpenZepplin is a library for smart contract development. In affected versions a vulnerability in TimelockController allowed an actor with the executor role to escalate privileges. Further details about the vulnerability will be disclosed at a later date. As a workaround revoke the executor role from accounts not strictly under the team’s control. We recommend revoking all executors that are not also proposers. When applying this mitigation, ensure there is at least one proposer and executor remaining. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39167
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
pac-resolver — pac-resolver
|
This affects the package pac-resolver before 5.0.0. This can occur when used with untrusted input, due to unsafe PAC file handling. **NOTE:** The fix for this vulnerability is applied in the node-degenerator library, a dependency written by the same maintainer. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-23406
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
passport-saml — passport-saml
|
Passport-SAML is a SAML 2.0 authentication provider for Passport, the Node.js authentication library. Prior to version 3.1.0, a malicious SAML payload can require transforms that consume significant system resources to process, thereby resulting in reduced or denied service. This would be an effective way to perform a denial-of-service attack. This has been resolved in version 3.1.0. The resolution is to limit the number of allowable transforms to 2. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39171
CONFIRM
MISC |
philips — healthcare_tasy_electronic_medical_record
|
Philips Healthcare Tasy Electronic Medical Record (EMR) 3.06 allows SQL injection via the CorCad_F2/executaConsultaEspecifico IE_CORPO_ASSIST or CD_USUARIO_CONVENIO parameter. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39376
MISC |
philips — healthcare_tasy_electronic_medical_record
|
Philips Healthcare Tasy Electronic Medical Record (EMR) 3.06 allows SQL injection via the WAdvancedFilter/getDimensionItemsByCode FilterValue parameter. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39375
MISC
MISC |
plib — plib
|
In Plib through 1.85, there is an integer overflow vulnerability that could result in arbitrary code execution. The vulnerability is found in ssgLoadTGA() function in src/ssg/ssgLoadTGA.cxx file. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-38714
MISC |
podofo — podofo
|
Stack-based Buffer Overflow in PoDoFo v0.9.6 allows attackers to cause a denial of service via the component ‘src/base/PdfDictionary.cpp:65’. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18971
MISC |
podofo — podofo
|
Exposure of Sensitive Information to an Unauthorized Actor in PoDoFo v0.9.6 allows attackers to obtain sensitive information via ‘IsNextToken’ in the component ‘src/base/PdfToenizer.cpp’. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18972
MISC |
ponzu — ponzu
|
A cross site request forgery (CSRF) vulnerability in the configure.html component of Ponzu 0.11.0 allows attackers to change user and administrator credentials, and add or delete administrator accounts. |
2021-08-20 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-24130
MISC |
| popojicms — popojicms |
Directory Traversal vulnerability exists in PopojiCMS 2.0.1 via the id parameter in admin.php. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-19547
MISC |
popojicms — popojicms
|
Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF) vulnerability exist in PopojiCMS 2.0.1 in po-admin/route.php?mod=user&act=multidelete. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28070
MISC |
popojicms — popojicms
|
Cross Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability exists in PopojiCMS 2.0.1 in admin.php?mod=menumanager——— edit menu. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18065
MISC |
prestashop — smartdatasoft_smartblog
|
Multiple SQL injection vulnerabilities in SmartDataSoft SmartBlog for PrestaShop before 4.06 allow a remote unauthenticated attacker to execute arbitrary SQL commands via the day, month, or year parameter to the controllers/front/archive.php archive controller, or the id_category parameter to the controllers/front/category.php category controller. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37538
MISC
MISC |
| primekey — ejbca |
An issue was discovered in PrimeKey EJBCA before 7.6.0. CMP RA Mode can be configured to use a known client certificate to authenticate enrolling clients. The same RA client certificate is used for revocation requests as well. While enrollment enforces multi tenancy constraints (by verifying that the client certificate has access to the CA and Profiles being enrolled against), this check was not performed when authenticating revocation operations, allowing a known tenant to revoke a certificate belonging to another tenant. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40088
MISC |
| primekey — ejbca |
An issue was discovered in PrimeKey EJBCA before 7.6.0. The General Purpose Custom Publisher, which is normally run to invoke a local script upon a publishing operation, was still able to run if the System Configuration setting Enable External Script Access was disabled. With this setting disabled it’s not possible to create new such publishers, but existing publishers would continue to run. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40089
MISC |
primekey — ejbca
|
An issue was discovered in PrimeKey EJBCA before 7.6.0. As part of the configuration of the aliases for SCEP, CMP, EST, and Auto-enrollment, the enrollment secret was reflected on a page (that can only be viewed by an administrator). While hidden from direct view, checking the page source would reveal the secret. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40086
MISC |
primekey — ejbca
|
An issue was discovered in PrimeKey EJBCA before 7.6.0. When audit logging changes to the alias configurations of various protocols that use an enrollment secret, any modifications to the secret were logged in cleartext in the audit log (that can only be viewed by an administrator). This affects use of any of the following protocols: SCEP, CMP, or EST. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40087
MISC |
qemu — qemu
|
An out-of-bounds write flaw was found in the UAS (USB Attached SCSI) device emulation of QEMU in versions prior to 6.2.0-rc0. The device uses the guest supplied stream number unchecked, which can lead to out-of-bounds access to the UASDevice->data3 and UASDevice->status3 fields. A malicious guest user could use this flaw to crash QEMU or potentially achieve code execution with the privileges of the QEMU process on the host. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3713
MISC |
| raspap — raspap |
raspap-webgui in RaspAP 2.6.6 allows attackers to execute commands as root because of the insecure sudoers permissions. The www-data account can execute /etc/raspap/hostapd/enablelog.sh as root with no password; however, the www-data account can also overwrite /etc/raspap/hostapd/enablelog.sh with any executable content. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-38557
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| raspap — raspap |
includes/configure_client.php in RaspAP 2.6.6 allows attackers to execute commands via command injection. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-38556
MISC
MISC
MISC |
recaptcha_solver — recaptcha_solver
|
An XSS issue was discovered in ReCaptcha Solver 5.7. A response from Anti-Captcha.com, RuCaptcha.com, 2captcha.com, DEATHbyCAPTCHA.com, ImageTyperz.com, or BestCaptchaSolver.com in setCaptchaCode() is inserted into the DOM as HTML, resulting in full control over the user’s browser by these servers. |
2021-08-22 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39362
MISC |
simiki — simiki
|
Command Injection in Simiki v1.6.2.1 and prior allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary system commands via line 64 of the component ‘simiki/blob/master/simiki/config.py’. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-19001
MISC |
simiki — simiki
|
Cross Site Scripting (XSS) in Simiki v1.6.2.1 and prior allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via line 54 of the component ‘simiki/blob/master/simiki/generators.py’. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-19000
MISC |
solarwinds — web_help_desk
|
Access Restriction Bypass via referrer spoof was discovered in SolarWinds Web Help Desk 12.7.2. An attacker can access the “Web Help Desk Getting Started Wizard”, especially the admin account creationpage, from a non-privileged IP address network range or loopback address by intercepting the HTTP request and changing the referrer from the public IP address to the loopback. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-32076
MISC |
sony — audio_usb_driver
|
Untrusted search path vulnerability in the installer of Sony Audio USB Driver V1.10 and prior and the installer of HAP Music Transfer Ver.1.3.0 and prior allows an attacker to gain privileges and execute arbitrary code via a Trojan horse DLL in an unspecified directory. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-20793
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
spring-boot-admin — spring-boot-admin
|
A stored cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability via ResourceController.java in spring-boot-admin as of 20190710 allows attackers to execute arbitrary web scripts or HTML. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-19704
MISC |
sqlite — sqlite
|
** DISPUTED ** A segmentation fault can occur in the sqlite3.exe command-line component of SQLite 3.36.0 via the idxGetTableInfo function when there is a crafted SQL query. NOTE: the vendor disputes the relevance of this report because a sqlite3.exe user already has full privileges (e.g., is intentionally allowed to execute commands). This report does NOT imply any problem in the SQLite library. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-36690
MISC |
startserver — startserver
|
All versions of package startserver are vulnerable to Directory Traversal due to missing sanitization. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-23430
MISC
MISC |
tcpreplay — tcpreplay
|
Buffer Overflow in Tcpreplay v4.3.2 allows attackers to cause a Denial of Service via the ‘do_checksum’ function in ‘checksum.c’. It can be triggered by sending a crafted pcap file to the ‘tcpreplay-edit’ binary. This issue is different than CVE-2019-8381. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18976
MISC |
thinkphp-zcms — thinkphp-zcms
|
thinkphp-zcms as of 20190715 allows SQL injection via index.php?m=home&c=message&a=add. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-19705
MISC |
transpile — transpile
|
All versions of package transpile are vulnerable to Denial of Service (DoS) due to a lack of input sanitization or whitelisting, coupled with improper exception handling in the .to() function. |
2021-08-24 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-23429
MISC
MISC |
| ubuntu — ubuntu |
IOMMU page mapping issues on x86 T[his CNA information record relates to multiple CVEs; the text explains which aspects/vulnerabilities correspond to which CVE.] Both AMD and Intel allow ACPI tables to specify regions of memory which should be left untranslated, which typically means these addresses should pass the translation phase unaltered. While these are typically device specific ACPI properties, they can also be specified to apply to a range of devices, or even all devices. On all systems with such regions Xen failed to prevent guests from undoing/replacing such mappings (CVE-2021-28694). On AMD systems, where a discontinuous range is specified by firmware, the supposedly-excluded middle range will also be identity-mapped (CVE-2021-28695). Further, on AMD systems, upon de-assigment of a physical device from a guest, the identity mappings would be left in place, allowing a guest continued access to ranges of memory which it shouldn’t have access to anymore (CVE-2021-28696). |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28696
MISC |
ubuntu — ubuntu
|
IOMMU page mapping issues on x86 T[his CNA information record relates to multiple CVEs; the text explains which aspects/vulnerabilities correspond to which CVE.] Both AMD and Intel allow ACPI tables to specify regions of memory which should be left untranslated, which typically means these addresses should pass the translation phase unaltered. While these are typically device specific ACPI properties, they can also be specified to apply to a range of devices, or even all devices. On all systems with such regions Xen failed to prevent guests from undoing/replacing such mappings (CVE-2021-28694). On AMD systems, where a discontinuous range is specified by firmware, the supposedly-excluded middle range will also be identity-mapped (CVE-2021-28695). Further, on AMD systems, upon de-assigment of a physical device from a guest, the identity mappings would be left in place, allowing a guest continued access to ranges of memory which it shouldn’t have access to anymore (CVE-2021-28696). |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28695
MISC |
ubuntu — ubuntu
|
IOMMU page mapping issues on x86 T[his CNA information record relates to multiple CVEs; the text explains which aspects/vulnerabilities correspond to which CVE.] Both AMD and Intel allow ACPI tables to specify regions of memory which should be left untranslated, which typically means these addresses should pass the translation phase unaltered. While these are typically device specific ACPI properties, they can also be specified to apply to a range of devices, or even all devices. On all systems with such regions Xen failed to prevent guests from undoing/replacing such mappings (CVE-2021-28694). On AMD systems, where a discontinuous range is specified by firmware, the supposedly-excluded middle range will also be identity-mapped (CVE-2021-28695). Further, on AMD systems, upon de-assigment of a physical device from a guest, the identity mappings would be left in place, allowing a guest continued access to ranges of memory which it shouldn’t have access to anymore (CVE-2021-28696). |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28694
MISC |
umbraco — forms
|
A security issue in Umbraco Forms 4.0.0 to and including 8.7.5 could lead to a remote code execution attack and/or arbitrary file deletion. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-37334
MISC
MISC |
unsquash — squashfs-tools
|
Squashfs-Tools in unsquash-1.c in Squashfs-Tools 4.5 stores the filename in the directory entry; this is then used by unsquashfs to create the new file during the unsquash. The filename is not validated for traversal outside of the destination directory, and thus allows writing to locations outside of the destination. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-40153
MISC
MISC
MISC |
vaadin — vaadin
|
Improper check in CheckboxGroup in com.vaadin:vaadin-checkbox-flow versions 1.2.0 prior to 2.0.0 (Vaadin 12.0.0 prior to 14.0.0), 2.0.0 prior to 3.0.0 (Vaadin 14.0.0 prior to 14.5.0), 3.0.0 through 4.0.1 (Vaadin 15.0.0 through 17.0.11), 14.5.0 through 14.6.7 (Vaadin 14.5.0 through 14.6.7), and 18.0.0 through 20.0.5 (Vaadin 18.0.0 through 20.0.5) allows attackers to modify the value of a disabled Checkbox inside enabled CheckboxGroup component via unspecified vectors. |
2021-08-25 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-33605
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
vizio — multiple_products
|
Several high privileged APIs on the Vizio P65-F1 6.0.31.4-2 and E50x-E1 10.0.31.4-2 Smart TVs do not enforce access controls, allowing an unauthenticated threat actor to access privileged functionality, leading to OS command execution. The specific attack methodology is a file upload. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-27944
MISC
MISC |
wms — wms
|
The GET parameter “id” in WMS v1.0 is passed without filtering, which allows attackers to perform SQL injection. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18106
MISC |
wordpress — wordpress
|
The update functionality in the rslider_page uses an rs_id POST parameter which is not validated, sanitised or escaped before being inserted in sql query, therefore leading to SQL injection for users having Administrator role. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24557
MISC
MISC |
wordpress — wordpress
|
The WP SMS WordPress plugin before 5.4.13 does not sanitise the “wp_group_name” parameter before outputting it back in the “Groups” page, leading to an Authenticated Stored Cross-Site Scripting issue |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24561
CONFIRM
MISC |
wordpress — wordpress
|
The Giveaway WordPress plugin through 1.2.2 is vulnerable to an SQL Injection issue which allows an administrative user to execute arbitrary SQL commands via the $post_id on the options.php page. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-24497
MISC |
xen_security — xen_security
|
grant table v2 status pages may remain accessible after de-allocation Guest get permitted access to certain Xen-owned pages of memory. The majority of such pages remain allocated / associated with a guest for its entire lifetime. Grant table v2 status pages, however, get de-allocated when a guest switched (back) from v2 to v1. The freeing of such pages requires that the hypervisor know where in the guest these pages were mapped. The hypervisor tracks only one use within guest space, but racing requests from the guest to insert mappings of these pages may result in any of them to become mapped in multiple locations. Upon switching back from v2 to v1, the guest would then retain access to a page that was freed and perhaps re-used for other purposes. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28697
MISC |
xen_security — xen_security
|
xen/arm: No memory limit for dom0less domUs The dom0less feature allows an administrator to create multiple unprivileged domains directly from Xen. Unfortunately, the memory limit from them is not set. This allow a domain to allocate memory beyond what an administrator originally configured. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28700
MISC |
xen_security — xen_security
|
long running loops in grant table handling In order to properly monitor resource use, Xen maintains information on the grant mappings a domain may create to map grants offered by other domains. In the process of carrying out certain actions, Xen would iterate over all such entries, including ones which aren’t in use anymore and some which may have been created but never used. If the number of entries for a given domain is large enough, this iterating of the entire table may tie up a CPU for too long, starving other domains or causing issues in the hypervisor itself. Note that a domain may map its own grants, i.e. there is no need for multiple domains to be involved here. A pair of “cooperating” guests may, however, cause the effects to be more severe. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28698
MISC |
xen_security — xen_security
|
inadequate grant-v2 status frames array bounds check The v2 grant table interface separates grant attributes from grant status. That is, when operating in this mode, a guest has two tables. As a result, guests also need to be able to retrieve the addresses that the new status tracking table can be accessed through. For 32-bit guests on x86, translation of requests has to occur because the interface structure layouts commonly differ between 32- and 64-bit. The translation of the request to obtain the frame numbers of the grant status table involves translating the resulting array of frame numbers. Since the space used to carry out the translation is limited, the translation layer tells the core function the capacity of the array within translation space. Unfortunately the core function then only enforces array bounds to be below 8 times the specified value, and would write past the available space if enough frame numbers needed storing. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-28699
MISC |
| xstream — xstream |
XStream is a simple library to serialize objects to XML and back again. In affected versions this vulnerability may allow a remote attacker to load and execute arbitrary code from a remote host only by manipulating the processed input stream. No user is affected, who followed the recommendation to setup XStream’s security framework with a whitelist limited to the minimal required types. XStream 1.4.18 uses no longer a blacklist by default, since it cannot be secured for general purpose. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39154
CONFIRM
MISC |
| xstream — xstream |
XStream is a simple library to serialize objects to XML and back again. In affected versions this vulnerability may allow a remote attacker to load and execute arbitrary code from a remote host only by manipulating the processed input stream, if using the version out of the box with Java runtime version 14 to 8 or with JavaFX installed. No user is affected, who followed the recommendation to setup XStream’s security framework with a whitelist limited to the minimal required types. XStream 1.4.18 uses no longer a blacklist by default, since it cannot be secured for general purpose. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39153
MISC
CONFIRM |
xstream — xstream
|
XStream is a simple library to serialize objects to XML and back again. In affected versions this vulnerability may allow a remote attacker to load and execute arbitrary code from a remote host only by manipulating the processed input stream. No user is affected, who followed the recommendation to setup XStream’s security framework with a whitelist limited to the minimal required types. XStream 1.4.18 uses no longer a blacklist by default, since it cannot be secured for general purpose. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39147
CONFIRM
MISC |
xstream — xstream
|
XStream is a simple library to serialize objects to XML and back again. In affected versions this vulnerability may allow a remote attacker to allocate 100% CPU time on the target system depending on CPU type or parallel execution of such a payload resulting in a denial of service only by manipulating the processed input stream. No user is affected, who followed the recommendation to setup XStream’s security framework with a whitelist limited to the minimal required types. XStream 1.4.18 uses no longer a blacklist by default, since it cannot be secured for general purpose. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39140
MISC
CONFIRM |
xstream — xstream
|
XStream is a simple library to serialize objects to XML and back again. In affected versions this vulnerability may allow a remote attacker to request data from internal resources that are not publicly available only by manipulating the processed input stream with a Java runtime version 14 to 8. No user is affected, who followed the recommendation to setup XStream’s security framework with a whitelist limited to the minimal required types. If you rely on XStream’s default blacklist of the [Security Framework](https://x-stream.github.io/security.html#framework), you will have to use at least version 1.4.18. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39150
MISC
CONFIRM |
xstream — xstream
|
XStream is a simple library to serialize objects to XML and back again. In affected versions this vulnerability may allow a remote attacker to load and execute arbitrary code from a remote host only by manipulating the processed input stream. No user is affected, who followed the recommendation to setup XStream’s security framework with a whitelist limited to the minimal required types. XStream 1.4.18 uses no longer a blacklist by default, since it cannot be secured for general purpose. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39148
CONFIRM
MISC |
xstream — xstream
|
XStream is a simple library to serialize objects to XML and back again. In affected versions this vulnerability may allow a remote attacker to load and execute arbitrary code from a remote host only by manipulating the processed input stream. No user is affected, who followed the recommendation to setup XStream’s security framework with a whitelist limited to the minimal required types. XStream 1.4.18 uses no longer a blacklist by default, since it cannot be secured for general purpose. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39149
MISC
CONFIRM |
xstream — xstream
|
XStream is a simple library to serialize objects to XML and back again. In affected versions this vulnerability may allow a remote attacker to load and execute arbitrary code from a remote host only by manipulating the processed input stream. No user is affected, who followed the recommendation to setup XStream’s security framework with a whitelist limited to the minimal required types. XStream 1.4.18 uses no longer a blacklist by default, since it cannot be secured for general purpose. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39151
CONFIRM
MISC |
xstream — xstream
|
XStream is a simple library to serialize objects to XML and back again. In affected versions this vulnerability may allow a remote attacker to request data from internal resources that are not publicly available only by manipulating the processed input stream with a Java runtime version 14 to 8. No user is affected, who followed the recommendation to setup XStream’s security framework with a whitelist limited to the minimal required types. If you rely on XStream’s default blacklist of the [Security Framework](https://x-stream.github.io/security.html#framework), you will have to use at least version 1.4.18. |
2021-08-23 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-39152
MISC
CONFIRM |
youdiancms — youdiancms
|
A lack of filtering for searched keywords in the search bar of YouDianCMS 8.0 allows attackers to perform SQL injection. |
2021-08-27 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-18116
MISC |
yourls — yourls
|
yourls is vulnerable to Improper Restriction of Rendered UI Layers or Frames |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2021-3734
MISC
CONFIRM |
zzcms — zzc,s
|
A remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability in template_user.php of ZZCMS version 2018 allows attackers to execute arbitrary PHP code via the “ml” and “title” parameters. |
2021-08-26 |
not yet calculated |
CVE-2020-19822
MISC |
by Contributed | Aug 29, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Get started with DevOps Guest post by Charlie Johnstone, Curriculum & Quality Leader for Computing, Film & TV at New College Lanarkshire: Microsoft Learn for Educator Ambassador
What is DevOps
DevOps enables better communications between developers, operations, quality and security professionals in an organisation, it is not software or hardware and not just a methodology, it is so much more! What it does is bring together the people in your teams (both developers and ops people), products and processes to deliver value to your end users.
This blog will focus on some of the tools and services used within Azure DevOps to build test and deploy your projects wherever you want to deploy, whether it be on prem or in the cloud.
This blog will be delivered in multiple parts, in this part, following a short primer, I will discuss part of the planning process using Azure Boards
 Plan:
Plan:
In the plan phase, the DevOps teams will specify and detail what the application will do. They may use tools like Kanban boards and Scrum for this planning.
Develop:
This is fairly obvious, this is mainly focused on coding, testing and reviewing. Automation is important here using automated testing and continuous integration (CI). In Azure, this would be done in a Dev/Test environment
Deliver:
In this phase, the application is deployed to a production environment, including the application’s infrastructure requirements. At this stage, the applications should be made available to customers, and should be scalable.
Operate:
Once in the production environment, the applications need monitoring to ensure high availability, if issues are found then maintenance and troubleshooting are necessary.
Each of these phases relies on each other and, to some degree, involves each of the aforementioned roles.
DevOps Practices
Continuous Integration (CI) & Continuous Delivery (CD)
Continuous Integration allows developers to merge code updates into the main code branch. Every time new code is committed, automated testing takes place to ensure stability of the main branch with bugs identified prior to merging.
Continuous Delivery automatically deploys new versions of your applications into your production environment.
Used together as CI/CD, you will benefit from automation all the way from committing new code to its deployment in your production environment, this allows incremental changes in code to be quickly and safely deployed.
Tools for CI/CD include Azure Pipelines and GitHub Actions.
Version Control
Version control systems basically track the history of changes to a project’s code. In an environment where where multiple developers are collaborating on a project, version control is vital. Tools like Git provide for development teams to collaborate on projects in writing code. Version control systems allow for code changes happening in the same files, dealing with conflicts and rolling back to previous states where necessary.
Azure Boards
This is where you can begin to manage your projects by creating your work items. Azure Boards has native support for Kanban and Scrum as well as reporting tools and customisable dashboards, and is fully scalable.
We are going to use Basic process for this walkthrough, other available process types are Agile, Scrum and CMMI.
To begin your project, go to https://dev.azure.com/ and sign in. The first task you need to do is optionally to create a new organization.
After selecting “Continue”, you will have the opportunity to name your organisation and choose the region where you want your project hosted.
Following this step we will create our new project, for the purposes of this article, I’ve named it “BBlog2 Project”, made it private, selected Git for version control and chosen to use Basic process for work items.
The next step is to create the “Boards” you will be using
It is worth a look at the screens on the welcome dialog. Once you have done this you will see a screen similar to that below.
This is where we will define our work items. I have created some simple items for demonstration purposes. Having created these items, the next screen will show how simple it is to change the status of an item.
Once your project is properly underway, it is very easy to change a work item’s state from To Do, to Doing and finally to Done. This gives you a simple visual view of where your work items are. The next 2 screens show all my work items created both in the Boards and Work Items tabs, but there’s still work to be done here, as you’ll see, all items are currently unassigned and no schedules have been created.
For the next screen I have set the dates for the project, using the default “Sprint 1” Iteration name.
Having done some tasks slightly out of order, my next task was to create my team, I would have been better doing this earlier. To do this, I returned to “Project Settings” (bottom left of screen) and selected the “Teams” page below.
At this stage I was the only team member of the only team
At this stage it’s a simple process to add team members by selecting “Add” on the right of the screen and searching your Azure AD for your desired team members.
On completion of this process you should see a fully populated team as below, names and emails blurred for privacy reasons
At this point if we return to our Boards tab, and select a work item, you will see (highlighted) that the items are still unassigned, clicking this area will allow you to assign this task to a member of your team.
The final screen below shows that all the Work Items have now been assigned. The team members will then start to work on the items and change the state form To Do, to Doing. When a task is completed, it can then be updated to Done.
This is a very straightforward tool to use, and I have only really touched the surface of it, as a getting started guide, the next item in this series will be on Pipelines.
My main source for this post has been an excellent new resource https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/modules/get-started-with-devops/. For more useful information on Azure DevOps services, another great resource is https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/get-started/?view=azure-devops.
The reason for the focus on Azure Boards is that my team is embarking on a new journey, we are beginning to teach DevOps to our first year students. Microsoft has provided great resources which are assisting us in this endeavour.
For students and faculty, Microsoft offers $100 of Azure credit per year on validation of your status as a student or educator, just follow the link here for Microsoft Azure for Student
This is far from the only DevOps resource offered by Microsoft. For a some more introductory information for educators wishing to become involved with DevOps, a great quick read is https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/education-hub/azure-dev-tools-teaching/about-program. This provides an introduction on how to get your students started with Azure and gives you and your students the opportunity to claim your free $100 in order study Azure; download a wealth of free software; get free licences for Azure DevOps and get started with how computing works now and in the future.
My team has only been working with Azure since the beginning of the 2021, initially focusing on the Fundamentals courses AZ-900 (Azure Fundamentals) and AI-900 (Azure AI Fundamentals)
We are adding DP-900 (Azure Data Fundamentals) and SC-900 (Security, Compliance, and Identity Fundamentals) to the courses we offer to our first year students.
Our second and third-year students are being given the opportunity to move to role based certifications through a pilot programme for AZ-104 (Microsoft Azure Administrator) to make their employment prospects much greater.
Our experience of these courses to date has been great, the students have been very engaged with many taking multiple courses. Our industry contacts have also taken notice with one large organisation offering our students a month’s placement in order to develop a talent stream.
My recommendations for how to approach the fundamentals courses is possibly slightly unusual. Though at this stage I think the most important courses for students to study are AZ-900 to learn about cloud computing in general and the tools and services within Azure; and DP-900 because data drives everything! I would start the students journey with AI-900, this is a great introduction to artificial intelligence services and tools in Azure, which like the other fundamentals courses, contains excellent labs for students to complete and does not require coding skills. The reason I recommend starting with AI-900 is that it provides a great “hook”, students love this course and on completion want more. This has made our job of engaging the students in the, arguably, more difficult courses quite straightforward.
If you don’t feel ready to teach complete courses or have a cohort for whom it wouldn’t be appropriate, Microsoft is happy for you to use their materials in a piecemeal manner, just pick out the parts you need. My team are going to do this with local schools, our plan is to give in introduction to all the fundamentals courses already mentioned over 10 hours.
To get fully involved and access additional great resources, sign up either as an individual educator or as an institution to the Microsoft Learn Educator Programme.
Education needs to move away from just developing software for PC and on-prem environments and embrace the cloud, services such as Azure is not the future, it is NOW! It’s time to get on board or risk your graduates being irrelevant to the modern workplace.
by Contributed | Aug 28, 2021 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Background
The field of Artificial Intelligence is being applied to more and more application areas, such as self-driving cars, natural language processing, visual recognition, fraud detection and many more.
A subset of artificial intelligence is Deep learning (DL), which is used to develop some of the more sophisticated training model, using deep neural networks (DNN) trying to mimic the human brain. Today, some of the largest DL training models can be used to do very complex and creative tasks like write poetry, write code, and understand the context of text/speech.

These large DL models are possible because of advancements in DL algorithms (DeepSpeed )), which maximize the efficiency of GPU memory management. Traditionally, DL models were very parallel floating-point intensive and so performed well on GPU’s, the newer more memory efficient algorithms made it possible to run much larger DL models but at the expense of significantly more inter-node communication operations, specifically, allreduce and alltoall collective operations.
Modern DL training jobs require large Clusters of multi-GPUs with high floating-point performance connected with high bandwidth, low latency networks. The Azure NDv4 VM series is designed specifically for these types of workloads. ND96asr_v4 has 8 A100 GPU’s connected via NVlink3, each A100 has access to 200 Gbps HDR InfiniBand, a total of 1.6 Tbps internode communication is possible.
We will be focusing on HPC+AI Clusters built with the ND96asr_v4 virtual machine type and providing specific performance optimization recommendations to get the best performance.
Deep Learning hardware and software stack
The Deep learning hardware and software stack is much more complicated compared to traditional HPC. From the hardware perspective CPU and GPU performance is important, especially floating-point performance and the speed in which data is moved from CPU (host) to GPU (device) or GPU (device) to GPU (device). There are many popular Deep learning frameworks e.g. pytorch, tensorflow, Caffe and CNTK. NCCL is one of the popular collective communication library for Nvidia GPU’s and low-level mathematics operations is dependent on the CUDA tools and libraries. We will touch on many parts of this H/W and S/W stack in this post.
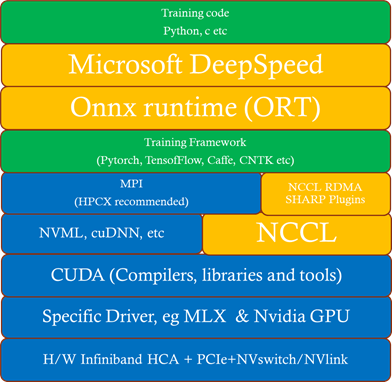
How to deploy an HPC+AI Cluster (using NDv4)
In this section we discuss some deployment options.
Which image to use
It’s recommended that you start with one of the Azure Marketplace images that support NDv4. The advantage of using one of these Marketplace images is the GPU driver, InfiniBand drivers, CUDA, NCCL and MPI libraries (including rdma_sharp_plugin) are pre-installed and should be fully functional after booting up the image.
- ubuntu-hpc 18.04 (microsoft-dsvm:ubuntu-hpc:1804:latest)
- Ubuntu is a popular DL linux OS and the most amount of testing on NDv4 was done with version 18.04.
- Ubuntu-hpc 20.04 (microsoft-dsvm:ubuntu-hpc:2004:latest)
- Popular image in DL community.
- CentOS-HPC 7.9 (OpenLogic:CentOS-HPC:7_9-gen2:latest)
- More popular in HPC, less popular in AI.
- NOTE: By default the NDv4 GPU NUMA topology is not correct, you need to apply this patch.
Another option, especially if you want to customize your image is to build your own custom image. The best place to start is the azhpc-images GitHub repository, which contains all the scripts used to build the HPC marketplace images.
You can then use packer or Azure Image builder to build the image and Azure Shared image gallery to store, use, share and distribute images.
Deployment options
In this section we will explore some options to deploy an HPC+AI NDv4 cluster.
- Nvidia Nephele
- Nephele is an open source GitHub repository, primary developers are Nvidia. It’s based on terraform and ansible. It also deploys a SLURM scheduler with container support, using enroot and pyxis.
- It’s a good and proven benchmark environment.
- AzureML
- Is the Azure preferred AI platform, it’s an Azure ML service. It can easily deploy as code a cluster using batch or AKS, upload your environment, create a container, and submit your job. You can monitor and review resulting using the Azure machine learning studio GUI.
- Maybe less control with specific tuning optimizations.
- Azure CycleCloud
- Is an Azure dynamic provisioning and VM autoscaling service that supports many traditional HPC schedulers like PBS, SLURM, LSF etc.
- By default, containers are not supported and if you would like to have SLURM supporting containers you would need to manually integrate enroot and pyxis with cycleCloud+SLURM.
- Currently, does not support Ubuntu 20.04.
- AzureHPC
- Is an open source framework that can combine many different build blocks to create complex and customized deployments in Azure.
- It’s designed as a flexible deployment environment for prototyping, testing, and benchmarking, it’s not designed for production.
- Does not support ubuntu (only CentOS).
- Azure HPC on-Demand Platform (az-hop)
- Is designed to be a complete E2E HPC as a service environment, its deployed using terraform and ansible and uses CycleCloud for its dynamic provisioning and autoscaling capabilities. It also supports OnDemand to provide a web interface to the HPC environment.
- Currently, only supports PBS and does not have any container support.
- Currently, supports CentOS-HPC based images (no Ubuntu).
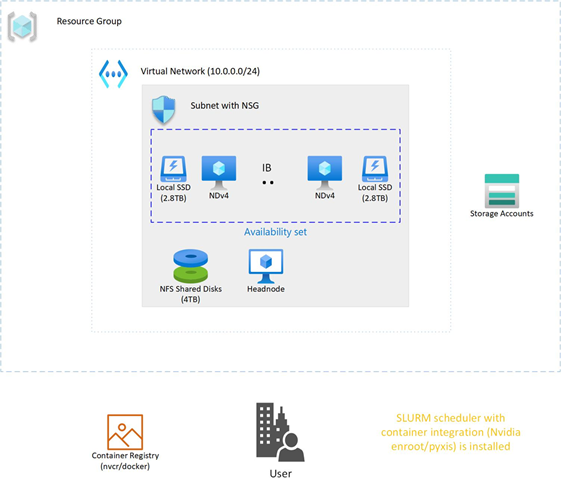
NDv4 tuning considerations
In this section we will look at a couple of areas that should be carefully considered to make sure your large DL training job is running optimally on NDv4.
GPU tuning
Here is the procedure to set the GPU’s to maximum clock rates and to then reset the GPU clock rate after your job is completed. The procedure for GPU id 0 is shown, need to do this procedure for all GPUs.
First get maximum graphics and memory clock frequencies
max_graphics_freq=$(nvidia-smi -i 0 –query-gpu=clocks.max.graphics –format=csv,noheader,nounits)
max_memory_freq=$( nvidia-smi -i 0 –query-gpu=clocks.max.mem –format=csv,noheader,nounits)
echo “max_graphics_freq=$max_graphics_freq MHz, max_memory_freq=$max_memory_freq MHz”
max_graphics_freq=1410 MHz, max_memory_freq=1215 MHz
Then set the GPUs to the maximum and memory clock frequencies.
sudo nvidia-smi -I 0 -ac $max_memory_freq, $max_graphics_freq
Applications clocks set to “(MEM 1215, SM 1410)” for GPU 00000001:00:00.0
All done.
Finally, when job is finished, reset the graphics and memory clock frequencies.
sudo nvidia-smi -i 0 -rgc
All done.
NCCL tuning
- It is recommended that you use NCCL version >= 2.9.9, especially at higher parallel scales.
- export LD_LIBRARY_PATH==/path/to/libnccl.so (or if necessary LD_PRELOAD=/path/to/libnccl.so)
- Use a specific topology file for ND96asr_v4 and set its location.
- You can get the ND96asr_v4 topology file here.
- export NCCL_TOPO_FILE=/path/to/topology.txt
- Using relaxed ordering for PCI operations is a key mechanism to get maximum performance when targeting memory attached to AMD 2nd Gen EPYC CPUs.
- export NCCL_IB_PCI_RELAXED_ORDERING=1
- export UCX_IB_PCI_RELAXED_ORDERING=on
- This is needed to make sure the correct topology is recognized.
- export CUDA_DEVICE_ORDER=PCI_BUS_ID
- Use eth0 (front-end network interface) to start up processes but use ib0 for processes to communicate.
- export NCCL_SOCKET_IFNAME=eth0
- It’s recommended to print NCCL debug information to verify that the correct environmental variables are set and correct plugins are used (e.g RDMA SHARP plugin).
- For Initial testing and verification, to check that parameters, environmental variables, and plugins are set correctly.
- Set to WARNING once you have confidence in your environment.
- export NCCL_DEBUG=WARNING
- Enable NCCL RDMA Sharp Plugin, has a big impact on performance and should always be enabled. There are a couple of ways to enable the plugin.
- source hpcx-init.sh && hpcx_load
- LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/path/to/plugin/{libnccl-net.so,libsharp*.so}:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH (or LD_PRELOAD)
- Note: SHARP is currently not enabled on ND96asr_v4.
- Check NCCL_DEBUG=INFO output to verify its loaded.
- x8a100-0000:60522:60522 [5] NCCL INFO Plugin Path : /opt/hpcx/nccl_rdma_sharp_plugin/lib/libnccl-net.so
- Lowering the message size threshold to determine if messages are broken up to use adaptive routing may improve the performance of smaller message sizes.
- export NCCL_IB_AR_THRESHOLD=0
- Also consider NCCL_TOPO=ring or tree (as experiment/debugging, but defaults are generally good)
MPI considerations
When MPI is used with NCCL, MPI is primarily used just to start-up the processes and NCCL is used for efficient collective communication.
You can start processes by explicitly executing mpirun or via a Scheduler MPI integration (e.g SLURM srun command.).
If you have flexibility on the choice of MPI library, then HPCX is the preferred MPI library due to its performance and features.
It is required to disable Mellanox hierarchical Collectives (HCOLL) when using MPI with NCCL.
mpirun –mca coll_hcoll_enable 0 or export OMPI_MCA_COLL_HCOLL_ENABLE=0
Process pinning optimizations
The first step is to determine what is the correct CPU (NUMA) to GPU topology. To see where the GPU’s are located, you can use
ltopo or nvidia-smi topo -m
to get this information or use the check application pinning tool (contained in the azurehpc Github repo (see experimental/check_app_pinning_tool)
./check_app_pinning.py
Virtual Machine (Standard_ND96asr_v4) Numa topology
NumaNode id Core ids GPU ids
============ ==================== ==========
0 [‘0-23′] [2, 3]
1 [’24-47′] [0, 1]
2 [’48-71′] [6, 7]
3 [’72-95’] [4, 5]
We can see that 2 GPU’s are located in each NUMA domain and that the GPU id order is not 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7, but 3,2,1,0,7,6,5,4. To make sure all GPU’s are used and running optimally we need to make sure that 2 processes are mapped correctly and running in each NUMA domain. There are several ways to force the correct gpu to cpu mapping. In SLURM we can map GPU ids 0,1 to NUMA 1,
GPU ids 2,3 to NUMA 0, GPU ids 4,5 to NUMA 3 and GPU ids 6,7 to NUMA 2 with the following explicit mapping using the SLURM srun command to launch processes.
srun –cpu-bind=mask_cpu:ffffff000000,ffffff000000,ffffff,ffffff,ffffff000000000000000000,ffffff000000000000000000,ffffff000000000000,ffffff00000000000
A similar gpu to cpu mapping is possible with HPCX MPI, setting the following environmental variable and mpirun arguments
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=2,3,0,1,6,7,4,5
–map-by ppr:2:numa (Add :pe=N, if running hybrid parallel (threads in addition to processes)
Then you can use the AzureHPC check_app_pinning.py tool as your job runs to verify if processes/threads are pinned optimally.
I/O tuning
Two aspects of I/O need to be addressed.
- Scratch Storage
- This type of storage needs to be fast (high throughput and low latency); the training job needs to read data, process the data and use this storage location as scratch space as the job runs.
- In an ideal case you would use the local SSD on each VM directly. The NDv4 has a local SSD already mounted at /mnt (2.8 TB), it also has 8 NVMe SSD devices, which when configured and mounted (see below), have ~7 TB capacity.
- If you need a shared filesystem for scratch, combining all NVMe SSD’s and creating a PFS system may be great option from a cost and performance perspective assuming it has sufficient capacity one way to do this is with BeeOND, if not there are other storage options to explore (IaaS Lustre PFS, Azure ClusterStor and Azure Netapp files).
- Checkpoint Storage
- Large DL training jobs can run for Weeks depending on how many VM’s are used, just like any HPC cluster you can have failures (e.g. InfiniBand, memory DIM, ECC error GPU memory etc). It’s critical to have a checkpointing strategy, know the checkpoint interval (e.g. when data is checkpointed), each time how much data is transferred and have a storage solution in place that can satisfy that capacity and performance requirements. If Blob Storage can meet the storage performance, it’s a great option.
How to set-up and configure the NDv4 local NVMe SSD’s
ND96asr_v4 virtual machine contains 8 NVMe SSD devices. You can combine the 8 devices into a striped raid 0 device, that can then be used to create an XFS (or ext4) filesystem and mounted. The script below can be run on all NDv4 VM’s with a parallel shell (e.g pdsh) to create a ~7TB local scratch space (/mnt_nvme).
The resulting local scratch space has a read and write I/O throughput of ~8 GB/s.
#!/bin/bash
mkdir /mnt/resource_nvme
mdadm --create /dev/md128 --level 0 --raid-devices 8 /dev/nvme0n1 /dev/nvme1n1 /dev/nvme2n1 /dev/nvme3n1 /dev/nvme4n1 /dev/nvme5n1 /dev/nvme6n1 /dev/nvme7n1
mkfs.xfs /dev/md128
mount /dev/md128 /mnt/resource_nvme
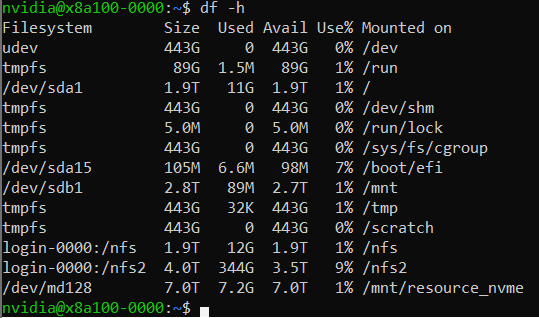
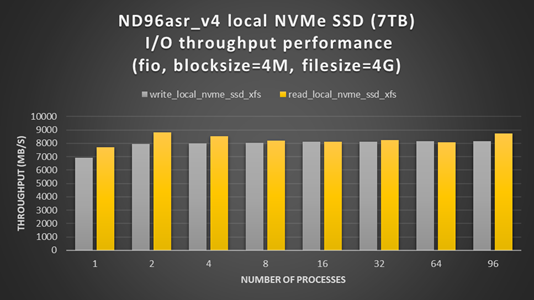
Restricting data transfer to BLOB storage using the azcopy tool
The process described here is specific to azcopy, but the same principals can be applied to any of the language specific SDK (e.g BLOB API via python).
In this example, lets assume that we have as single BLOB storage account with an ingress limit of 20 Gbps. At each checkpoint, 8 files (corresponding to each GPU) need to be copied to the BLOB storage account, each file will be transferred with its own azcopy. We choose that each azcopy can transfer data at a maximum transfer speed of 2300 Mbps (2300 x 8 = 18400 < 20000 Gpbs) to avoid throttling. The ND96asr_v4 has 96 vcores and so we choose that each azcopy can use 10 cores, so each instance of azcopy gets enough cores and other processes have some additional vcores.
export AZCOPY_CONCURRENCY_VALUE=10
azcopy cp ./file “blob_storage_acc_container” –caps-mbps 2300
DeepSpeed and Onnx Runtime (ORT)
The performance of large scale DL training models built with the pytorch framework can be significantly improved by utilizing DeepSpeed and/or Onnx runtime. It can be straight forward to enable DeepSpeed and Onnx runtime by importing a few extra modules and replacing a few lines of code with some wrapper functions. If using DeepSpeed and Onnx its best practice to apply Onnx first and then DeepSpeed.
HPC+AI NDv4 cluster health checks
Within Azure there is automated testing to help identify unhealthy VM’s. Our testing processes and procedures continue to improve, but still it is possible for an unhealthy VM to be not identified by our testing and to be deployed. Large DL training jobs typically require many VM’s collaborating and communicating with each other to complete the DL job. The more VM’s deployed the greater the change that one of them may be unhealthy, resulting in the DL job failing or underperforming. It is recommended that before starting a large scale DL training job to run some health checks on your cluster to verify it’s performing as expected.
Check GPU floating-point performance
Run high performance linpack (HPL) on each VM, its convenience to use the version contained in the Nvidia hpc-benchmarks container. (Note: This is a non-optimized version of HPL so the numbers reported are ~5-7% slower than the optimized container. It will give you good node to node variation numbers and identify a system that is having CPU, memory, or GPU issues).
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -t 00:20:00
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=8
#SBATCH -o logs/%x_%j.log
CONT='nvcr.io#nvidia/hpc-benchmarks:20.10-hpl'
MOUNT='/nfs2/hpl/dats/hpl-${SLURM_JOB_NUM_NODES}N.dat:/workspace/hpl-linux-x86_64/sample-dat/HPL-dgx-a100-${SLURM_JOB_NUM_NODES}N.dat'
echo "Running on hosts: $(echo $(scontrol show hostname))"
export NCCL_DEBUG=INFO
export OMPI_MCA_pml=ucx
export OMPI_MCA_btl=^openib,smcuda
CMD="hpl.sh --cpu-affinity 24-35:36-47:0-11:12-23:72-83:84-95:48-59:60-71 --cpu-cores-per-rank 8 --gpu-affinity 0:1:2:3:4:5:6:7 --mem-affinity 1:1:0:0:3:3:2:2 --ucx-affinity ibP257p0s0:ibP258p0s0:ibP259p0s0:ibP260p0s0:ibP261p0s0:ibP262p0s0:ibP263p0s0:ibP264p0s0 --dat /workspace/hpl-linux-x86_64/sample-dat/HPL-dgx-a100-${SLURM_JOB_NUM_NODES}N.dat"
srun --gpus-per-node=8 --container-image="${CONT}" --container-mounts="${MOUNT}" ${CMD}
You should see ~95 TFLOPs DP on ND96asr_v4 (which has 8 A100 GPU’s)
Check host to device and device to host transfer bandwidth
The CUDA bandwidthTest is a convenience way to verify that the host to gpu and gpu to host data bandwidth speeds are good. Below is an example testing gpu id = 0, you would run a similar test for the other 7 gpu_ids, paying close attention to what NUMA domains they are contained in.
numactl –cpunodebind=1 –membind=1 ./bandwidthTest –dtoh –htod –device=0
[CUDA Bandwidth Test] – Starting…
Running on…
Device 0: A100-SXM4-40GB
Quick Mode
Host to Device Bandwidth, 1 Device(s)
PINNED Memory Transfers
Transfer Size (Bytes) Bandwidth(GB/s)
32000000 26.1
Device to Host Bandwidth, 1 Device(s)
PINNED Memory Transfers
Transfer Size (Bytes) Bandwidth(GB/s)
32000000 25.0
Result = PASS
The expected host to device and device to host transfer speed is > 20 GB/s.
This health check and many more detailed tests to diagnose unhealthy VMs can be found in the azhpc-diagnostics Github repository.
Check the InfiniBand network and NCCL performance
Running a NCCL allreduce and/or alltoall benchmark at the scale you plan on running your deep learning training job is a great way to identify problems with the InfiniBand inter-node network or with NCCL performance.
Here is a SLURM script to run a NCCL alltoall benchmark (Note: using SLURM container integration with enroot+pyxis to use the Nvidia pytorch container.)
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -t 00:20:00
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=8
#SBATCH --gpus-per-node=8
#SBATCH -o logs/%x_%j.log
export UCX_IB_PCI_RELAXED_ORDERING=on
UCX_TLS=rc
NCCL_DEBUG=INFO
CUDA_DEVICE_ORDER=PCI_BUS_ID
NCCL_IB_PCI_RELAXED_ORDERING=1
NCCL_TOPO_FILE=/workspace/nccl/nccl-topology.txt
CONT="nvcr.io#nvidia/pytorch:21.05-py3"
MOUNT="/nfs2/nccl:/workspace/nccl_284,/nfs2/hpcx-v2.8.1-gcc-MLNX_OFED_LINUX-5.1-0.6.6.0-ubuntu18.04-x86_64:/opt/hpcx,/nfs2/nccl_2.10.3-1/nccl:/workspace/nccl"
export OMPI_MCA_pml=ucx
export OMPI_MCA_btl=^openib
export OMPI_MCA_COLL_HCOLL_ENABLE=0
srun --ntasks=$SLURM_JOB_NUM_NODES --container-image "${CONT}"
--container-name=nccl
--container-mounts="${MOUNT}"
--ntasks-per-node=1
bash -c "apt update && apt-get install -y infiniband-diags"
srun --gpus-per-node=8
--ntasks-per-node=8
--container-name=nccl
--container-mounts "${MOUNT}"
bash -c 'export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/opt/hpcx/nccl_rdma_sharp_plugin/lib:/opt/hpcx/sharp/lib:/workspace/nccl/build/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH && /workspace/nccl/nccl-tests/build/alltoall_perf -b8 -f 2 -g 1 -e 8G'
Then submit the above script on for example 4 ND96asr_v4 VM’s
sbatch -N 4 ./nccl.slrm
Similarly, for allreduce, just change the executable to be all_reduce_perf.
The following plots show NCCL allreduce and alltoall expect performance on ND96asr_v4.
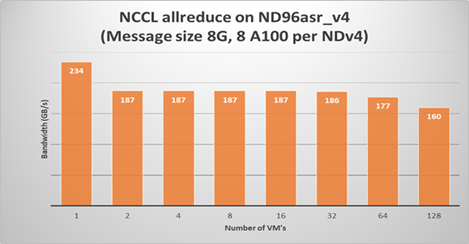
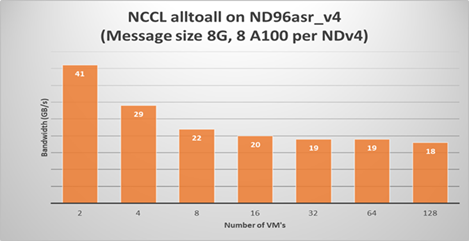
Summary
Large scale DL models are becoming very complex and sophisticated being applied to many application areas. The computational and network resources to train these large modern DL models can be quite substantial. The Azure NDv4 series is designed specifically for these large scale DL computational, network and I/O requirements.
Several key performance optimization tips and tricks are discussed to allow you to get the best possible performance running your large deep learning model on Azure NDv4 series.
Credits
To would like to acknowledge the significant contribution of my Colleagues at Microsoft to this post. Jithin Jose provided the NCCL scaling performance data and was the primary contributor to the NCCL, MPI an GPU tuning parameters, he also helped review this document. I would also like to thank Kanchan Mehrotra and Jon Shelley for reviewing this document and providing outstanding feedback.


























Recent Comments