
by Contributed | Jan 7, 2022 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
What’s New??
Since our last update in September 2021, we have published new training content to support the features and functionality added to Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps during the previous quarter. The new materials are included in our Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps | December 2021 blog post. If you previously completed the Defender for Cloud Apps Ninja Training and want to view only updated content, we have highlighted and linked to the new material for your convenience.
Legend:
Module (ordered by Competency Level)
|
What’s new
|
Microsoft Cloud Apps for Security – Fundamental Level:
Module 2. Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps Introduction
|
|
Microsoft Cloud Apps for Security – Fundamental Level:
Module 3. Initial Setting
|
|
Microsoft Cloud Apps for Security – Intermediate Level:
Module 3. Information Protection and Real-Time Control
|
|
Microsoft Cloud Apps for Security – Intermediate Level:
Module 4. Threat Detection
|
|
by Contributed | Jan 6, 2022 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
In this episode of Data Exposed, Anna Hoffman and Lior Kamrat discuss why should you care about Azure Arc-enabled data services connectivity options and which one is the best for your organization.
Resources:
Demystifying Azure Arc-enabled data services: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7Z6WZgaupIk
Connectivity modes and requirements: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-arc/data/connectivity
Azure Arc-enabled data services: https://azurearcjumpstart.io/azure_arc_jumpstart/azure_arc_data/
by Scott Muniz | Jan 5, 2022 | Security, Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
Google has released Chrome version 97.0.4692.71 for Windows, Mac, and Linux. This version addresses vulnerabilities that an attacker could exploit to take control of an affected system.
CISA encourages users and administrators to review the Chrome Release Note and apply the necessary updates as soon as possible.
by Scott Muniz | Jan 5, 2022 | Security, Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
VMware has released a security advisory to address a vulnerability in Workstation, Fusion, and ESXi. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability to take control of an affected system.
CISA encourages users and administrators to review VMware Security Advisory VMSA-2022-0001 and apply the necessary updates and workarounds.
by Contributed | Jan 5, 2022 | Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
We are excited to announce the preview release of auto-failover groups for Azure SQL Hyperscale tier. This preview release includes support for forced and planned failover for Azure SQL Hyperscale databases that use active geo-replication and auto-failover groups. Some key benefits of auto-failover groups include:
- Simplified management of a group of geo-replicated databases including ability to failover the entire group of databases.
- Ability for application to maintain the same read/write and read-only endpoints after failover.
- Recovery during loss of an entire region through geo-failover which can be initiated manually or through an automatic failover policy.
- Readable online secondaries that can be used for read-only workloads by connecting with read-only listener endpoints which remain unchanged during geo-failovers.
Hyperscale service tier supports 100 TB of database size, rapid scale (out and up) and nearly instantaneous database backups, removing the limits traditionally seen in cloud databases.
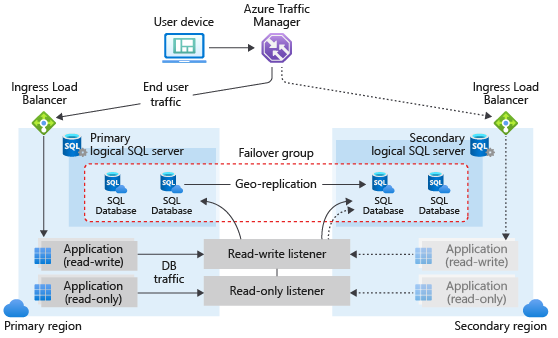
How auto-failover groups work for Hyperscale
Auto-failover groups are created between servers in 2 regions. The groups can include all or some databases in the servers. If a Hyperscale database is selected to be part of the failover group, then this database will failover with the rest of the failover group unit. The following diagram illustrates a typical configuration of a geo-redundant cloud application using multiple databases and auto-failover group.

Available regions
Auto-failover groups for Hyperscale will be supported in all regions where Azure SQL Hyperscale is supported.
Quick start
a. Create an Auto-failover group using Portal.
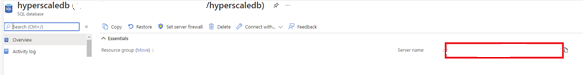
- Failover groups can be configured at the server level. Select the name of the server under Server name to open the settings for the server.
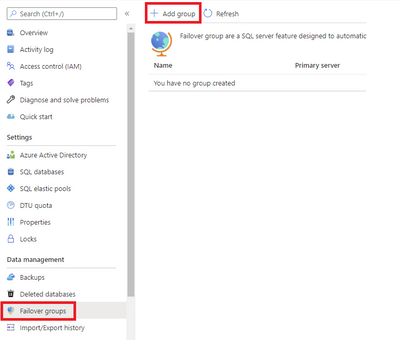
- Select Failover groups under the Settings pane, and then select Add group to create a new failover group.
- On the Failover Group page, enter or select your desired values for your failover group.
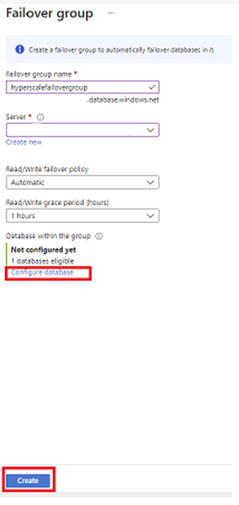
- Add your Hyperscale database to the failover group then select Create.
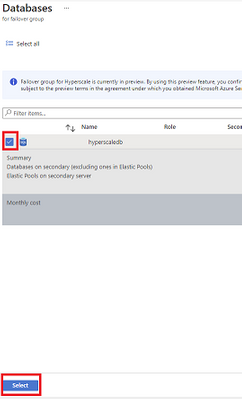
b. Create an Auto-failover group using PowerShell.
c. Create an Auto-failover group using CLI.
d. Create an Auto-failover group using REST API.
Geo-failover examples
Example 1: Planned failover for an auto-failover group
a. Execute a failover of an auto-failover group in Portal.
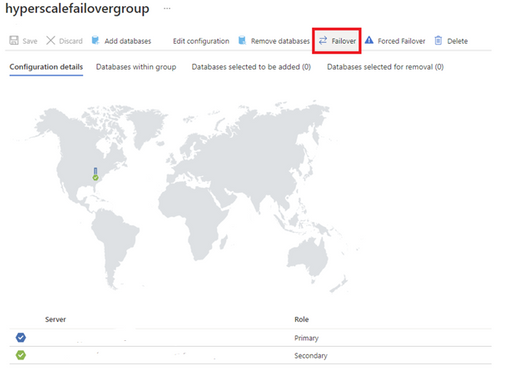
1. Select your failover group.
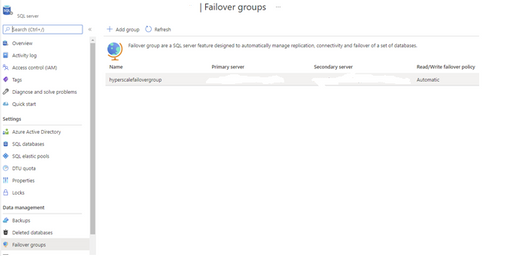
2. Select Failover to initiate failover for your auto-failover group. Once failover is completed you should see that your primary and secondary servers have swapped roles.
b. Execute a failover of an auto-failover group using Switch-AzSqlDatabaseFailoverGroup in PowerShell.
c. Execute a failover of an auto-failover group using az sql failover-group set-primary in CLI.
d. Execute a failover of an auto-failover group using REST API.
Example 2: Forced failover with active geo-replication
a. Execute a failover using Portal.
1. Select the Replicas tab. In the list of geo replicas click the ellipsis for the secondary you would like to become the new primary. Then select Forced failover.
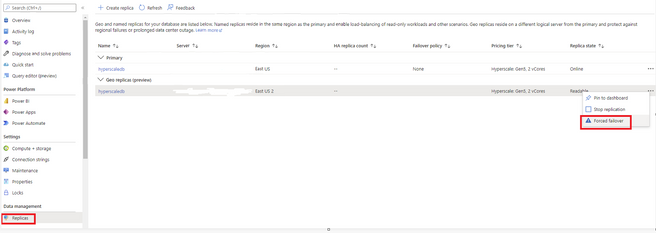
2. You should now see that the primary and secondary have swapped roles.
b. Execute a failover using Set-AzSqlDatabaseSecondary in PowerShell with the -AllowDataLoss parameter specified.
c. Execute a failover using az sql db replica set-primary in CLI with the –allow-data-loss parameter specified.
d. Execute a failover using REST API.
Learn more
https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/azure-sql/database/auto-failover-group-overview
https://aka.ms/activegeoreplication
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/service-tier-hyperscale

 Product videos
Product videos  Webcast recordings
Webcast recordings Tech Community
Tech Community Docs on Microsoft
Docs on Microsoft Blogs on Microsoft
Blogs on Microsoft GitHub
GitHub Interactive guides
Interactive guides


Recent Comments