by Scott Muniz | Feb 17, 2021 | Security, Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
The North Korean government has used multiple versions of AppleJeus since the malware was initially discovered in 2018. This section outlines seven of the versions below. The MARs listed above provide further technical details of these versions. Initially, HIDDEN COBRA actors used websites that appeared to host legitimate cryptocurrency trading platforms to infect victims with AppleJeus; however, these actors are now also using other initial infection vectors, such as phishing, social networking, and social engineering techniques, to get users to download the malware.
Targeted Nations
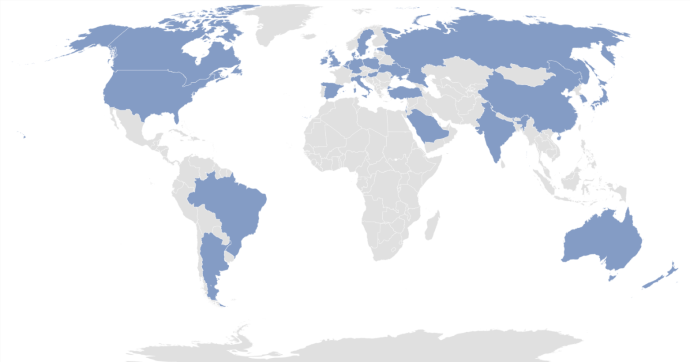
HIDDEN COBRA actors have targeted institutions with AppleJeus malware in several sectors, including energy, finance, government, industry, technology, and telecommunications. Since January 2020, the threat actors have targeted these sectors in the following countries: Argentina, Australia, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, China, Denmark, Estonia, Germany, Hong Kong, Hungary, India, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Poland, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Slovenia, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Turkey, the United Kingdom, Ukraine, and the United States (figure 1).

Figure 1: Countries targeted with AppleJeus by HIDDEN COBRA threat actors since 2020
AppleJeus Versions Note
The version numbers used for headings in this document correspond to the order the AppleJeus campaigns were identified in open source or through other investigative means. These versions may or may not be in the correct order to develop or deploy the AppleJeus campaigns.
AppleJeus Version 1: Celas Trade Pro
Introduction and Infrastructure
In August 2018, open-source reporting disclosed information about a trojanized version of a legitimate cryptocurrency trading application on an undisclosed victim’s computer. The malicious program, known as Celas Trade Pro, was a modified version of the benign Q.T. Bitcoin Trader application. This incident led to the victim company being infected with a Remote Administration Tool (RAT) known as FALLCHILL, which was attributed to North Korea (HIDDEN COBRA) by the U.S. Government. FALLCHILL is a fully functional RAT with multiple commands that the adversary can issue from a command and control (C2) server to infected systems via various proxies. FALLCHILL typically infects a system as a file dropped by other HIDDEN COBRA malware (Develop Capabilities: Malware [T1587.001]). Because of this, additional HIDDEN COBRA malware may be present on systems compromised with FALLCHILL.[4]
Further research revealed that a phishing email from a Celas LLC company (Phishing: Spearphishing Link [T1566.002]) recommended the trojanized cryptocurrency trading application to victims. The email provided a link to the Celas’ website, celasllc[.]com (Acquire Infrastructure: Domain [T1583.001]), where the victim could download a Windows or macOS version of the trojanized application.
The celasllc[.]com domain resolved to the following Internet Protocol (IP) addresses from May 29, 2018, to January 23, 2021.
45.199.63[.]220107.187.66[.]103145.249.106[.]19175.29.32[.]160185.142.236[.]213185.181.104[.]82198.251.83[.]27208.91.197[.]46209.99.64[.]18
The celasllc[.]com domain had a valid Sectigo (previously known as Comodo) Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate (Obtain Capabilities: Digital Certificates [T1588.004]). The SSL certificate was “Domain Control Validated,” a weak security verification level that does not require validation of the owner’s identity or the actual business’s existence.
Celas Trade Pro Application Analysis
Windows Program
The Windows version of the malicious Celas Trade Pro application is an MSI Installer (.msi). The MSI Installer installation package comprises a software component and an application programming interface (API) that Microsoft uses for the installation, maintenance, and removal of software. The installer looks legitimate and is signed by a valid Sectigo certificate that was purchased by the same user as the SSL certificate for celasllc[.]com (Obtain Capabilities: Code Signing Certificates [T1588.003]). The MSI Installer asks the victim for administrative privileges to run (User Execution: Malicious File [T1204.002]).
Once permission is granted, the threat actor is able to run the program with elevated privileges (Abuse Elevation Control Mechanism [T1548]) and MSI executes the following actions.
- Installs
CelasTradePro.exe in folder C:Program Files (x86)CelasTradePro
- Installs
Updater.exe in folder C:Program Files (x86)CelasTradePro
- Runs
Updater.exe with the CheckUpdate parameters
The CelasTradePro.exe program asks for the user’s exchange and loads a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency trading platform—very similar to the benign Q.T. Bitcoin Trader—that exhibits no signs of malicious activity.
The Updater.exe program has the same program icon as CelasTradePro.exe. When run, it checks for the CheckUpdate parameter, collects the victim’s host information (System Owner/User Discovery [T1033]), encrypts the collected information with a hardcoded XOR encryption, and sends information to a C2 website (Exfiltration Over C2 Channel [T1041]).
macOS X Program
The macOS version of the malicious application is a DMG Installer that has a disk image format that Apple commonly uses to distribute software over the internet. The installer looks legitimate and has a valid digital signature from Sectigo (Obtain Capabilities: Digital Certificates [T1588.004]). It has very similar functionality to the Windows version. The installer executes the following actions.
- Installs
CelasTradePro in folder /Applications/CelasTradePro.app/Contents/MacOS/
- Installs
Updater in folder /Applications/CelasTradePro.app/Contents/MacOS
- Executes a
postinstall script
- Moves
.com.celastradepro.plist to folder LaunchDaemons
- Runs
Updater with the CheckUpdate parameter
CelasTradePro asks for the user’s exchange and loads a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency trading platform—very similar to the benign Q.T. Bitcoin Trader—that exhibits no signs of malicious activity.
Updater checks for the CheckUpdate parameter and, when found, it collects the victim’s host information (System Owner/User Discovery [T1033]), encrypts the collected information with a hardcoded XOR key before exfiltration, and sends the encrypted information to a C2 website (Exfiltration Over C2 Channel [T1041]). This process helps the adversary obtain persistence on a victim’s network.
The postinstall script is a sequence of instructions that runs after successfully installing an application (Command and Scripting Interpreter: AppleScript [T1059.002]). This script moves property list (plist) file .com.celastradepro.plist from the installer package to the LaunchDaemons folder (Scheduled Task/Job: Launchd [T1053.004]). The leading “.” makes it unlisted in the Finder app or default Terminal directory listing (Hide Artifacts: Hidden Files and Directories [T1564.001]). Once in the folder, this property list (plist) file will launch the Updater program with the CheckUpdate parameter on system load as Root for every user. Because the LaunchDaemon will not run automatically after the plist file is moved, the postinstall script launches the Updater program with the CheckUpdate parameter and runs it in the background (Create or Modify System Process: Launch Daemon [T1543.004]).
Payload
After a cybersecurity company published a report detailing the above programs and their malicious extras, the website was no longer accessible. Since this site was the C2 server, the payload cannot be confirmed. The cybersecurity company that published the report states the payload was an encrypted and obfuscated binary (Obfuscated Files or Information [T1027]), which eventually drops FALLCHILL onto the machine and installs it as a service (Create or Modify System Process: Windows Service [T1543.003]). FALLCHILL malware uses an RC4 encryption algorithm with a 16-byte key to protect its communications (Encrypted Channel: Symmetric Cryptography [T1573.001]). The key employed in these versions has also been used in a previous version of FALLCHILL.[5][6]
For more details on AppleJeus Version 1: Celas Trade Pro, see MAR-10322463-1.v1.
AppleJeus Version 2: JMT Trading
Introduction and Infrastructure
In October 2019, a cybersecurity company identified a new version of the AppleJeus malware—JMT Trading—thanks to its many similarities to the original AppleJeus malware. Again, the malware was in the form of a cryptocurrency trading application, which a legitimate-looking company, called JMT Trading, marketed and distributed on their website, jmttrading[.]org (Acquire Infrastructure: Domain [T1583.001]). This website contained a “Download from GitHub” button, which linked to JMT Trading’s GitHub page (Acquire Infrastructure: Web Services [T1583.006]), where Windows and macOS X versions of the JMT Trader application were available for download (Develop Capabilities: Malware [T1587.001]). The GitHub page also included .zip and tar.gz files containing the source code.
The jmttrading[.]org domain resolved to the following IP addresses from October 15, 2016, to January 22, 2021.
45.33.2[.]7945.33.23[.]18345.56.79[.]2345.79.19[.]19696.126.123[.]244146.112.61[.]107184.168.221[.]40184.168.221[.]57198.187.29[.]20198.54.117[.]197198.54.117[.]198198.54.117[.]199198.54.117[.]200198.58.118[.]167
The jmttrading[.]org domain had a valid Sectigo SSL certificate (Obtain Capabilities: Digital Certificates [T1588.004]). The SSL certificate was “Domain Control Validated,” a weak security verification level that does not require validation of the owner’s identity or the actual business’s existence. The current SSL certificate was issued by Let’s Encrypt.
JMT Trading Application Analysis
Windows Program
The Windows version of the malicious cryptocurrency application is an MSI Installer. The installer looks legitimate and has a valid digital signature from Sectigo (Obtain Capabilities: Digital Certificates [T1588.004]). The signature was signed with a code signing certificate purchased by the same user as the SSL certificate for jmttrading[.]org (Obtain Capabilities: Code Signing Certificates [T1588.003]). The MSI Installer asks the victim for administrative privileges to run (User Execution: Malicious File [T1204.002]).
Once permission is granted, the MSI executes the following actions.
- Installs
JMTTrader.exe in folder C:Program Files (x86)JMTTrader
- Installs
CrashReporter.exe in folder C:Users<username>AppDataRoamingJMTTrader
- Runs
CrashReporter.exe with the Maintain parameter
The JMTTrader.exe program asks for the user’s exchange and loads a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency trading platform—very similar to CelasTradePro.exe and the benign Q.T. Bitcoin Trader—that exhibits no signs of malicious activity.
The program CrashReporter.exe is heavily obfuscated with the ADVObfuscation library, renamed “snowman” (Obfuscated Files or Information [T1027]). When run, it checks for the Maintain parameter and collects the victim’s host information (System Owner/User Discovery [T1033]), encrypts the collected information with a hardcoded XOR key before exfiltration, and sends the encrypted information to a C2 website (Exfiltration Over C2 Channel [T1041]). The program also creates a scheduled SYSTEM task, named JMTCrashReporter, which runs CrashReporter.exe with the Maintain parameter at any user’s login (Scheduled Task/Job: Scheduled Task [T1053.005]).
macOS X Program
The macOS version of the malicious application is a DMG Installer. The installer looks legitimate and has very similar functionality to the Windows version, but it does not have a digital certificate and will warn the user of that before installation. The installer executes the following actions.
- Installs
JMTTrader in folder /Applications/JMTTrader.app/Contents/MacOS/
- Installs
.CrashReporter in folder /Applications/JMTTrader.app/Contents/Resources/
- Note: the leading “.” makes it unlisted in the Finder app or default Terminal directory listing.
- Executes a
postinstall script
- Moves
.com.jmttrading.plist to folder LaunchDaemons
- Changes the file permissions on the
plist
- Runs
CrashReporter with the Maintain parameter
- Moves
.CrashReporter to folder /Library/JMTTrader/CrashReporter
- Makes
.CrashReporter executable
The JMTTrader program asks for the user’s exchange and loads a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency trading platform—very similar to CelasTradePro and the benign Q.T. Bitcoin Trader—that exhibits no signs of malicious activity.
The CrashReporter program checks for the Maintain parameter and is not obfuscated. This lack of obfuscation makes it easier to determine the program’s functionality in detail. When it finds the Maintain parameter, it collects the victim’s host information (System Owner/User Discovery [T1033]), encrypts the collected information with a hardcoded XOR key before exfiltration, and sends the encrypted information to a C2 website (Exfiltration Over C2 Channel [T1041]).
The postinstall script has similar functionality to the one used by CelasTradePro, but it has a few additional features (Command and Scripting Interpreter: AppleScript [T1059.002]). It moves the property list (plist) file .com.jmttrading.plist from the Installer package to the LaunchDaemons folder (Scheduled Task/Job: Launchd [T1053.004]), but also changes the file permissions on the plist file. Once in the folder, this property list (plist) file will launch the CrashReporter program with the Maintain parameter on system load as Root for every user. Also, the postinstall script moves the .CrashReporter program to a new location /Library/JMTTrader/CrashReporter and makes it executable. Because the LaunchDaemon will not run automatically after the plist file is moved, the postinstall script launches CrashReporter with the Maintain parameter and runs it in the background (Create or Modify System Process: Launch Daemon [T1543.004]).
Payload
Soon after the cybersecurity company tweeted about JMT Trader on October 11, 2019, the files on GitHub were updated to clean, non-malicious installers. Then on October 13, 2019, a different cybersecurity company published an article detailing the macOS X JMT Trader, and soon after, the C2 beastgoc[.]com website went offline. There is not a confirmed sample of the payload to analyze at this point.
For more details on AppleJeus Version 2: JMT Trading, see MAR-10322463-2.v1.
AppleJeus Version 3: Union Crypto
Introduction and Infrastructure
In December 2019, another version of the AppleJeus malware was identified on Twitter by a cybersecurity company based on many similarities to the original AppleJeus malware. Again, the malware was in the form of a cryptocurrency trading application, which was marketed and distributed by a legitimate-looking company, called Union Crypto, on their website, unioncrypto[.]vip (Acquire Infrastructure: Domain [T1583.001]). Although this website is no longer available, a cybersecurity researcher discovered a download link, https://www.unioncrypto[.]vip/download/W6c2dq8By7luMhCmya2v97YeN, recorded on VirusTotal for the macOS X version of UnionCryptoTrader. In contrast, open-source reporting stated that the Windows version might have been downloaded via instant messaging service Telegram, as it was found in a “Telegram Downloads” folder on an unnamed victim.[7]
The unioncrypto[.]vip domain resolved to the following IP addresses from June 5, 2019, to July 15, 2020.
104.168.167[.]16198.54.117[.]197198.54.117[.]198198.54.117[.]199198.54.117[.]200
The domain unioncrypto[.]vip had a valid Sectigo SSL certificate (Obtain Capabilities: Digital Certificates [T1588.004]). The SSL certificate was “Domain Control Validated,” a weak security verification level that does not require validation of the owner’s identity or the actual business’s existence.
Union Crypto Trader Application Analysis
Windows Program
The Windows version of the malicious cryptocurrency application is a Windows executable (.exe) (User Execution: Malicious File [T1204.002]), which acts as an installer that extracts a temporary MSI Installer.
The Windows program executes the following actions.
- Extracts
UnionCryptoTrader.msi to folder C:Users<username>AppDataLocalTemp{82E4B719-90F74BD1-9CF1-56CD777E0C42}
- Runs
UnionCryptoUpdater.msi
- Installs
UnionCryptoTrader.exe in folder C:Program FilesUnionCryptoTrader
- Installs
UnionCryptoUpdater.exe in folder C:Users<username>AppDataLocalUnionCryptoTrader
- Deletes
UnionCryptoUpdater.msi
- Runs
UnionCryptoUpdater.exe
The program UnionCryptoTrader.exe loads a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency arbitrage application—defined as “the simultaneous buying and selling of securities, currency, or commodities in different markets or in derivative forms to take advantage of differing prices for the same asset”—which exhibits no signs of malicious activity. This application is very similar to another cryptocurrency arbitrage application known as Blackbird Bitcoin Arbitrage.[8]
The program UnionCryptoUpdater.exe first installs itself as a service (Create or Modify System Process: Windows Service [T1543.003]), which will automatically start when any user logs on (Boot or Logon Autostart Execution [T1547]). The service is installed with a description stating it “Automatically installs updates for Union Crypto Trader.” When launched, it collects the victim’s host information (System Owner/User Discovery [T1033]), combines the information in a string that is MD5 hashed and stored in the auth_signature variable before exfiltration, and sends it to a C2 website (Exfiltration Over C2 Channel [T1041]).
macOS X Program
The macOS version of the malicious application is a DMG Installer. The installer looks legitimate and has very similar functionality to the Windows version, but it does not have a digital certificate and will warn the user of that before installation. The installer executes the following actions.
- Installs
UnionCryptoTrader in folder /Applications/UnionCryptoTrader.app/Contents/MacOS/
- Installs
.unioncryptoupdater in folder /Applications/UnionCryptoTrader.app/Contents/Resources/
- Note: the leading “.” makes it unlisted in the Finder app or default Terminal directory listing
- Executes a
postinstall script
- Moves
.vip.unioncrypto.plist to folder LaunchDaemons
- Changes the file permissions on the
plist to Root
- Runs
unioncryptoupdater
- Moves
.unioncryptoupdater to folder /Library/UnionCrypto/unioncryptoupdater
- Makes
.unioncryptoupdater executable
The UnionCryptoTrader program loads a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency arbitrage application, which exhibits no signs of malicious activity. The application is very similar to another cryptocurrency arbitrage application known as Blackbird Bitcoin Arbitrage.
The .unioncryptoupdater program is signed ad-hoc, meaning it is not signed with a valid code-signing identity. When launched, it collects the victim’s host information (System Owner/User Discovery [T1033]), combines the information in a string that is MD5 hashed and stored in the auth_signature variable before exfiltration, and sends it to a C2 website (Exfiltration Over C2 Channel [T1041]).
The postinstall script has similar functionality to the one used by JMT Trading (Command and Scripting Interpreter: AppleScript [T1059.002]). It moves the property list (plist) file .vip.unioncrypto.plist from the Installer package to the LaunchDaemons folder (Scheduled Task/Job: Launchd [T1053.004]), but also changes the file permissions on the plist file to Root. Once in the folder, this property list (plist) file will launch the .unioncryptoupdater on system load as Root for every user. The postinstall script moves the .unioncryptoupdater program to a new location /Library/UnionCrypto/unioncryptoupdater and makes it executable. Because the LaunchDaemon will not run automatically after the plist file is moved, the postinstall script launches .unioncryptoupdater and runs it in the background (Create or Modify System Process: Launch Daemon [T1543.004]).
Payload
The payload for the Windows malware is a Windows Dynamic-Link-Library. UnionCryptoUpdater.exe does not immediately download the stage 2 malware but instead downloads it after a time specified by the C2 server. This delay could be implemented to prevent researchers from directly obtaining the stage 2 malware.
The macOS X malware’s payload could not be downloaded, as the C2 server is no longer accessible. Additionally, none of the open-source reporting for this sample contained copies of the macOS X payload. The macOS X payload is likely similar in functionality to the Windows stage 2 detailed above.
For more details on AppleJeus Version 3: Union Crypto, see MAR-10322463-3.v1.
Commonalities between Celas Trade Pro, JMT Trading, and Union Crypto
Hardcoded Values
In each AppleJeus version, there are hardcoded values used for encryption or to create a signature when combined with the time (table 1).
Table 1: AppleJeus hardcoded values and uses
| AppleJeus Version |
Value |
Use |
| 1: Celas Trade Pro |
Moz&Wie;#t/6T!2y |
XOR encryption to send data |
| 1: Celas Trade Pro |
W29ab@ad%Df324V$Yd |
RC4 decryption |
| 2: JMT Trader Windows |
X,%`PMk–Jj8s+6=15:20:11 |
XOR encryption to send data |
| 2: JMT Trader OSX |
X,%`PMk–Jj8s+6=x02 |
XOR encryption to send data |
| 3: Union Crypto Trader |
12GWAPCT1F0I1S14 |
Combined with time for signature |
The Union Crypto Trader and Celas LLC (XOR) values are 16 bytes in length. For JMT Trader, the first 16 bytes of the Windows and macOS X values are identical, and the additional bytes are in a time format for the Windows sample. The structure of a 16-byte value combined with the time is also used in Union Crypto Trader to create the auth_signature.
As mentioned, FALLCHILL was reported as the final payload for Celas Trade Pro. All FALLCHILL samples use 16-byte hardcoded RC4 keys for sending data, similar to the 16-byte keys in the AppleJeus samples.
Open-Source Cryptocurrency Applications
All three AppleJeus samples are bundled with modified copies of legitimate cryptocurrency applications and can be used as originally designed to trade cryptocurrency. Both Celas LLC and JMT Trader modified the same cryptocurrency application, Q.T. Bitcoin Trader; Union Crypto Trader modified the Blackbird Bitcoin Arbitrage application.
Postinstall Scripts, Property List Files, and LaunchDaemons
The macOS X samples of all three AppleJeus versions contain postinstall scripts with similar logic. The Celas LLC postinstall script only moves the plist file to a new location and launches Updater with the CheckUpdate parameter in the background. The JMT Trader and Union Crypto Trader also perform these actions and have identical functionality. The additional actions performed by both postinstall scripts are to change the file permissions on the plist, make a new directory in the /Library folder, move CrashReporter or UnionCryptoUpdater to the newly created folder, and make them executable.
The plist files for all three AppleJeus files have identical functionality. They only differ in the files’ names and one default comment that was not removed from the Celas LLC plist. As the logic and functionality of the postinstall scripts and plist files are almost identical, the LaunchDaemons created also function the same.
They will all launch the secondary executable as Root on system load for every user.
AppleJeus Version 4: Kupay Wallet
Introduction and Infrastructure
On March 13, 2020, a new version of the AppleJeus malware was identified. The malware was marketed and distributed by a legitimate-looking company, called Kupay Wallet, on their website kupaywallet[.]com (Acquire Infrastructure: Domain [T1583.001]).
The domain www.kupaywallet[.]com resolved to IP address 104.200.67[.]96 from March 20, 2020, to January 16, 2021. CrownCloud US, LLC controlled the IP address (autonomous system number [ASN] 8100), and is located in New York, NY.
The domain www.kupaywallet[.]com had a valid Sectigo SSL certificate (Obtain Capabilities: Digital Certificates [T1588.004]). The SSL certificate was “Domain Control Validated,” a weak security verification level that does not require validation of the owner’s identity or the actual business’s existence.
Kupay Wallet Application Analysis
Windows Program
The Windows version of the malicious cryptocurrency application is an MSI Installer. The MSI executes the following actions.
- Installs
Kupay.exe in folder C:Program Files (x86)Kupay
- Installs
KupayUpgrade.exe in folder C:Users<username>AppDataRoamingKupaySupport
- Runs
KupayUpgrade.exe
The program Kupay.exe loads a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency wallet platform, which exhibits no signs of malicious activity and is very similar to an open-source platform known as Copay, distributed by Atlanta-based company BitPay.
The program KupayUpgrade.exe first installs itself as a service (Create or Modify System Process: Windows Service [T1543.003]), which will automatically start when any user logs on (Boot or Logon Autostart Execution [T1547]). The service is installed with a description stating it is an “Automatic Kupay Upgrade.” When launched, it collects the victim’s host information (System Owner/User Discovery [T1033]), combines the information in strings before exfiltration, and sends it to a C2 website (Exfiltration Over C2 Channel [T1041]).
macOS X Program
The macOS version of the malicious application is a DMG Installer. The installer looks legitimate and has very similar functionality to the Windows version, but it does not have a digital certificate and will warn the user of that before installation. The installer executes the following actions.
- Installs
Kupay in folder /Applications/Kupay.app/Contents/MacOS/
- Installs
kupay_upgrade in folder /Applications/Kupay.app/Contents/MacOS/
- Executes a
postinstall script
- Creates
KupayDaemon folder in /Library/Application Support folder
- Moves
kupay_upgrade to the new folder
- Moves
com.kupay.pkg.wallet.plist to folder /Library/LaunchDaemons/
- Runs the command
launchctl load to load the plist without a restart
- Runs
kupay_upgrade in the background
Kupay is likely a copy of an open-source cryptocurrency wallet application, loads a legitimate-looking wallet program (fully functional), and its functionality is identical to the Windows Kupay.exe program.
The kupay_upgrade program calls its function CheckUpdate (which contains most of the logic functionality of the malware) and sends a POST to the C2 server with a connection named “Kupay Wallet 9.0.1 (Check Update Osx)” (Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols [T1071.001]). If the C2 server returns a file, it is decoded and written to the victim’s folder /private/tmp/kupay_update with permissions set by the command chmod 700 (only the user can read, write, and execute) (Command and Scripting Interpreter [T1059]). Stage 2 is then launched, and the malware, kupay_upgrade, returns to sleeping and checking in with the C2 server at predetermined intervals (Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols [T1071.001]).
The postinstall script has similar functionality to other AppleJeus scripts (Command and Scripting Interpreter: AppleScript [T1059.002]). It creates the KupayDaemon folder in /Library/Application Support folder and then moves kupay_upgrade to the new folder. It moves the property list (plist) file com.kupay.pkg.wallet.plist from the Installer package to the /Library/LaunchDaemons/ folder (Scheduled Task/Job: Launchd [T1053.004]). The script runs the command launchctl load to load the plist without a restart (Command and Scripting Interpreter [T1059]). But, since the LaunchDaemon will not run automatically after the plist file is moved, the postinstall script launches kupay_upgrade and runs it in the background (Create or Modify System Process: Launch Daemon [T1543.004]).
Payload
The Windows malware’s payload could not be downloaded since the C2 server is no longer accessible. Additionally, none of the open-source reporting for this sample contained copies of the payload. The Windows payload is likely similar in functionality to the macOS X stage 2 detailed below.
The stage 2 payload for the macOS X malware was decoded and analyzed. The stage 2 malware has a variety of functionalities. Most importantly, it checks in with a C2 and, after connecting to the C2, can send or receive a payload, read and write files, execute commands via the terminal, etc.
For more details on AppleJeus Version 4: Kupay Wallet, see MAR-10322463-4.v1.
AppleJeus Version 5: CoinGoTrade
Introduction and Infrastructure
In early 2020, another version of the AppleJeus malware was identified. This time the malware was marketed and distributed by a legitimate-looking company called CoinGoTrade on their website coingotrade[.]com (Acquire Infrastructure: Domain [T1583.001]).
The domain CoinGoTrade[.]com resolved to IP address 198.54.114[.]175 from February 28, 2020, to January 23, 2021. The IP address is controlled by NameCheap Inc. (ASN 22612) and is located in Atlanta, GA. This IP address is in the same ASN for Dorusio[.]com and Ants2Whale[.]com.
The domain CoinGoTrade[.]com had a valid Sectigo SSL certificate (Obtain Capabilities: Digital Certificates [T1588.004]). The SSL certificate was “Domain Control Validated,” a weak security verification level that does not require validation of the owner’s identity or the actual business’s existence.
CoinGoTrade Application Analysis
Windows Program
The Windows version of the malicious application is an MSI Installer. The installer appears to be legitimate and will execute the following actions.
- Installs
CoinGoTrade.exe in folder C:Program Files (x86)CoinGoTrade
- Installs
CoinGoTradeUpdate.exe in folder C:Users<username>AppDataRoamingCoinGoTradeSupport
- Runs
CoinGoTradeUpdate.exe
CoinGoTrade.exe loads a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency wallet platform with no signs of malicious activity and is a copy of an open-source cryptocurrency application.
CoinGoTradeUpdate.exe first installs itself as a service (Create or Modify System Process: Windows Service [T1543.003]), which will automatically start when any user logs on (Boot or Logon Autostart Execution [T1547]). The service is installed with a description stating it is an “Automatic CoinGoTrade Upgrade.” When launched, it collects the victim’s host information (System Owner/User Discovery [T1033]), combines the information in strings before exfiltration, and sends it to a C2 website (Exfiltration Over C2 Channel [T1041]).
macOS X Program
The macOS version of the malicious application is a DMG Installer. The installer looks legitimate and has very similar functionality to the Windows version, but it does not have a digital certificate and will warn the user of that before installation. The installer executes the following actions.
- Installs
CoinGoTrade in folder /Applications/CoinGoTrade.app/Contents/MacOS/
- Installs
CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon in folder /Applications/CoinGoTrade.app/Contents/MacOS/
- Executes a
postinstall script
- Creates
CoinGoTradeService folder in /Library/Application Support folder
- Moves
CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon to the new folder
- Moves
com.coingotrade.pkg.product.plist to folder /Library/LaunchDaemons/
- Runs
CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon in the background
The CoinGoTrade program is likely a copy of an open-source cryptocurrency wallet application and loads a legitimate-looking, fully functional wallet program).
The CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon program calls its function CheckUpdate (which contains most of the logic functionality of the malware) and sends a POST to the C2 server with a connection named “CoinGoTrade 1.0 (Check Update Osx)” (Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols [T1071.001]). If the C2 server returns a file, it is decoded and written to the victim’s folder /private/tmp/updatecoingotrade with permissions set by the command chmod 700 (only the user can read, write, and execute) (Command and Scripting Interpreter [T1059]). Stage 2 is then launched, and the malware, CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon, returns to sleeping and checking in with the C2 server at predetermined intervals (Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols [T1071.001]).
The postinstall script has similar functionality to the other scripts (Command and Scripting Interpreter: AppleScript [T1059.002]) and installs CoinGoTrade and CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon in folder /Applications/CoinGoTrade.app/Contents/MacOS/. It moves the property list (plist) file com.coingotrade.pkg.product.plist to the /Library/LaunchDaemons/ folder (Scheduled Task/Job: Launchd [T1053.004]). Because the LaunchDaemon will not run automatically after the plist file is moved, the postinstall script launches CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon and runs it in the background (Create or Modify System Process: Launch Daemon [T1543.004]).
Payload
The Windows malware’s payload could not be downloaded because the C2 server is no longer accessible. Additionally, none of the open-source reporting for this sample contained copies of the payload. The Windows payload is likely similar in functionality to the macOS X stage 2 detailed below.
The stage 2 payload for the macOS X malware was no longer available from the specified download URL. Still, a file was submitted to VirusTotal by the same user on the same date as the macOS X CoinGoTradeUpgradeDaemon. These clues suggest that the submitted file may be related to the macOS X version of the malware and the downloaded payload.
The file prtspool is a 64-bit Mach-O executable with a large variety of features that have all been confirmed as functionality. The file has three C2 URLs hardcoded into the file and communicates to these with HTTP POST multipart-form data boundary string. Like other HIDDEN COBRA malware, prtspool uses format strings to store data collected about the system and sends it to the C2s.
For more details on AppleJeus Version 5: CoinGoTrade, see MAR-10322463-5.v1.
AppleJeus Version 6: Dorusio
Introduction and Infrastructure
In March 2020, an additional version of the AppleJeus malware was identified. This time the malware was marketed and distributed by a legitimate-looking company called Dorusio on their website, dorusio[.]com (Acquire Infrastructure: Domain [T1583.001]). Researchers collected samples for Windows and macOS X versions of the Dorusio Wallet (Develop Capabilities: Malware [T1587.001]). As of at least early 2020, the actual download links result in 404 errors. The download page has release notes with version revisions claiming to start with version 1.0.0, released on April 15, 2019.
The domain dorusio[.]com resolved to IP address 198.54.115[.]51 from March 30, 2020 to January 23, 2021. The IP address is controlled by NameCheap Inc. (ASN 22612) and is located in Atlanta, GA. This IP address is in the same ASN for CoinGoTrade[.]com and Ants2Whale[.]com.
The domain dorusio[.]com had a valid Sectigo SSL certificate (Obtain Capabilities: Digital Certificates [T1588.004]). The SSL certificate was “Domain Control Validated,” a weak security verification level that does not require validation of the owner’s identity or the actual business’s existence.
Dorusio Application Analysis
Windows Program
The Windows version of the malicious application is an MSI Installer. The installer appears to be legitimate and will install the following two programs.
- Installs
Dorusio.exe in folder C:Program Files (x86)Dorusio
- Installs
DorusioUpgrade.exe in folder C:Users<username>AppDataRoamingDorusioSupport
- Runs
DorusioUpgrade.exe
The program, Dorusio.exe, loads a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency wallet platform with no signs of malicious activity and is a copy of an open-source cryptocurrency application.
The program DorusioUpgrade.exe first installs itself as a service (Create or Modify System Process: Windows Service [T1543.003]), which will automatically start when any user logs on (Boot or Logon Autostart Execution [T1547]). The service is installed with a description stating it “Automatic Dorusio Upgrade.” When launched, it collects the victim’s host information (System Owner/User Discovery [T1033]), combines the information in strings before exfiltration, and sends it to a C2 website (Exfiltration Over C2 Channel [T1041]).
macOS X Program
The macOS version of the malicious application is a DMG Installer. The installer looks legitimate and has very similar functionality to the Windows version, but it does not have a digital certificate and will warn the user of that before installation. The installer executes the following actions.
- Installs
Dorusio in folder /Applications/Dorusio.app/Contents/MacOS/
- Installs
Dorusio_upgrade in folder /Applications/Dorusio.app/Contents/MacOS/
- Executes a
postinstall script
- Creates
DorusioDaemon folder in /Library/Application Support folder
- Moves
Dorusio_upgrade to the new folder
- Moves
com.dorusio.pkg.wallet.plist to folder /Library/LaunchDaemons/
- Runs
Dorusio_upgrade in the background
The Dorusio program is likely a copy of an open-source cryptocurrency wallet application and loads a legitimate-looking wallet program (fully functional). Aside from the Dorusio logo and two new services, the wallet appears to be the same as the Kupay Wallet. This application seems to be a modification of the open-source cryptocurrency wallet Copay distributed by Atlanta-based company BitPay.
The Dorusio_upgrade program calls its function CheckUpdate (which contains most of the logic functionality of the malware) and sends a POST to the C2 server with a connection named “Dorusio Wallet 2.1.0 (Check Update Osx)” (Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols [T1071.001]). If the C2 server returns a file, it is decoded and written to the victim’s folder /private/tmp/Dorusio_update with permissions set by the command chmod 700 (only the user can read, write, and execute) (Command and Scripting Interpreter [T1059]). Stage 2 is then launched, and the malware, Dorusio_upgrade, returns to sleeping and checking in with the C2 server at predetermined intervals (Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols [T1071.001]).
The postinstall script has similar functionality to other AppleJeus scripts (Command and Scripting Interpreter: AppleScript [T1059.002]). It creates the DorusioDaemon folder in /Library/Application Support folder and then moves Dorusio_upgrade to the new folder. It moves the property list (plist) file com.dorusio.pkg.wallet.plist from the Installer package to the /Library/LaunchDaemons/ folder (Scheduled Task/Job: Launchd [T1053.004]). Because the LaunchDaemon will not run automatically after the plist file is moved, the postinstall script launches Dorusio_upgrade and runs it in the background (Create or Modify System Process: Launch Daemon [T1543.004]).
Payload
Neither the payload for the Windows nor macOS X malware could be downloaded; the C2 server is no longer accessible. The payloads are likely similar in functionality to the macOS X stage 2 from CoinGoTrade and Kupay Wallet, or the Windows stage 2 from Union Crypto.
For more details on AppleJeus Version 6: Dorusio, see MAR-10322463-6.v1.
AppleJeus 4, 5, and 6 Installation Conflictions
If a user attempts to install the Kupay Wallet, CoinGoTrade, and Dorusio applications on the same system, they will encounter installation conflicts.
If Kupay Wallet is already installed on a system and the user tries to install CoinGoTrade or Dorusio:
- Pop-up windows appear, stating a more recent version of the program is already installed.
If CoinGoTrade is already installed on a system and the user attempts to install Kupay Wallet:
Kupay.exe will be installed in the C:Program Files (x86)CoinGoTrade folder.- All
CoinGoTrade files will be deleted.
- The folders and files contained in the
C:Users<username>AppDataRoamingCoinGoTradeSupport will remain installed.
KupayUpgrade.exe is installed in the new folder C:Users<username>AppDataRoamingKupaySupport.
If Dorusio is already installed on a system and the user attempts to install Kupay Wallet:
Kupay.exe will be installed in the C:Program Files (x86)Dorusio folder.- All
Dorusio.exe files will be deleted.
- The folders and files contained in
C:Users<username>AppDataRoamingDorusioSupport will remain installed.
KupayUpgrade.exe is installed in the new folder C:Users<username>AppDataRoamingKupaySupport.
AppleJeus Version 7: Ants2Whale
Introduction and Infrastructure
In late 2020, a new version of AppleJeus was identified called “Ants2Whale.” The site for this version of AppleJeus is ants2whale[.]com (Acquire Infrastructure: Domain [T1583.001]). The website shows a legitimate-looking cryptocurrency company and application. The website contains multiple spelling and grammar mistakes indicating the creator may not have English as a first language. The website states that to download Ants2Whale, a user must contact the administrator, as their product is a “premium package” (Develop Capabilities: Malware [T1587.001]).
The domain ants2whale[.]com resolved to IP address 198.54.114[.]237 from September 23, 2020, to January 22, 2021. The IP address is controlled by NameCheap, Inc. (ASN 22612) and is located in Atlanta, GA. This IP address is in the same ASN for CoinGoTrade[.]com and Dorusio[.]com.
The domain ants2whale[.]com had a valid Sectigo SSL certificate (Obtain Capabilities: Digital Certificates [T1588.004]). The SSL certificate was “Domain Control Validated,” a weak security verification level that does not require validation of the owner’s identity or the actual business’s existence.
Ants2Whale Application Analysis
Windows Program
As of late 2020, the Windows program was not available on VirusTotal. It is likely very similar to the macOS X version detailed below.
macOS X Program
The macOS version of the malicious application is a DMG Installer. The installer looks legitimate and has very similar functionality to the Windows version, but it does not have a digital certificate and will warn the user of that before installation. The installer executes the following actions.
- Installs
Ants2Whale in folder /Applications/Ants2whale.app/Contents/MacOS/Ants2whale
- Installs
Ants2WhaleHelper in folder /Library/Application Support/Ants2WhaleSupport/
- Executes a
postinstall script
- Moves
com.Ants2whale.pkg.wallet.plist to folder /Library/LaunchDaemons/
- Runs
Ants2WhaleHelper in the background
The Ants2Whale and Ants2WhaleHelper programs and the postinstall script function almost identically to previous versions of AppleJeus and will not be discussed in depth in this advisory.
For more details on AppleJeus Version 7: Ants2Whale, see MAR-10322463-7.v1.
ATT&CK Profile
Figure 2 and table 2 provide summaries of the MITRE ATT&CK techniques observed.
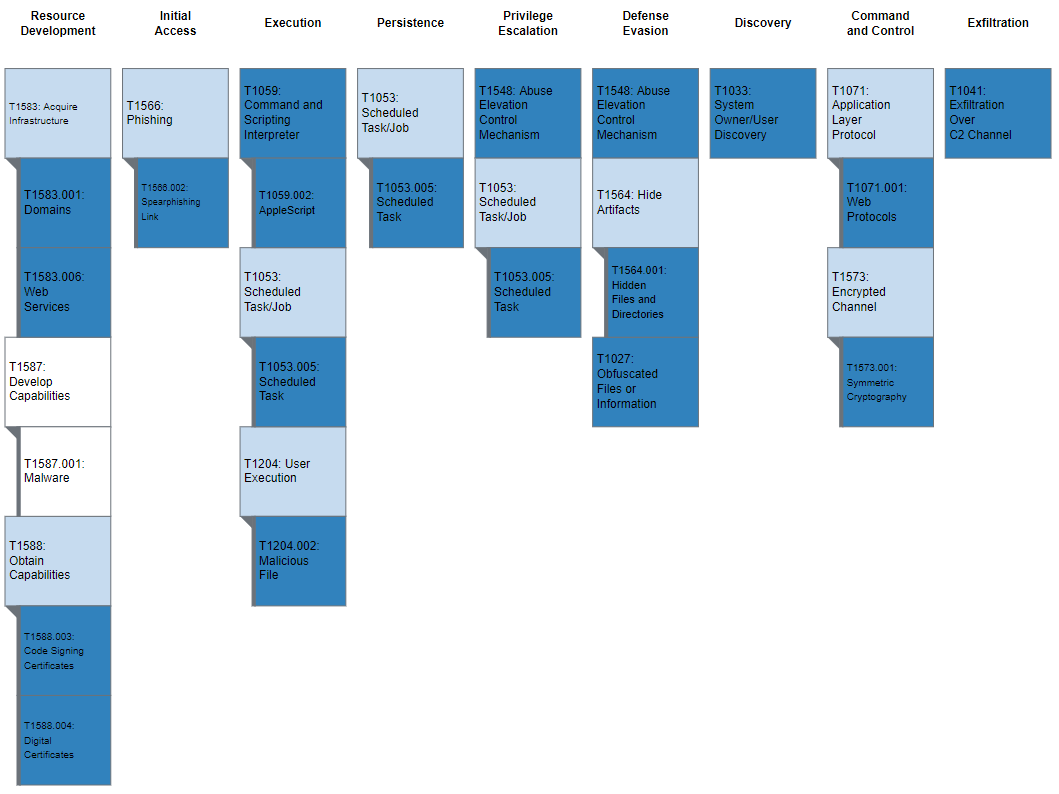
Figure 2: MITRE ATT&CK enterprise techniques used by AppleJeus
Table 2: MITRE ATT&CK techniques observed
by Scott Muniz | Feb 15, 2021 | Security, Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
| 1password — scim_bridge |
1Password SCIM Bridge before 1.6.2 mishandles validation of authenticated requests for log files, leading to disclosure of a TLS private key. |
2021-02-08 |
4 |
CVE-2021-26905
MISC
CONFIRM |
| adminer — adminer |
Adminer through 4.7.8 allows XSS via the history parameter to the default URI. |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-35572
MISC
MISC |
| adobe — acrobat |
Acrobat Reader DC versions versions 2020.013.20074 (and earlier), 2020.001.30018 (and earlier) and 2017.011.30188 (and earlier) are affected by a heap-based buffer overflow vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-02-11 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21017
MISC |
| adobe — acrobat |
Acrobat Reader DC versions versions 2020.013.20074 (and earlier), 2020.001.30018 (and earlier) and 2017.011.30188 (and earlier) are affected by a Use After Free vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-02-11 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21028
MISC |
| adobe — acrobat |
Acrobat Reader DC versions versions 2020.013.20074 (and earlier), 2020.001.30018 (and earlier) and 2017.011.30188 (and earlier) are affected by a Use After Free vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-02-11 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21033
MISC |
| adobe — acrobat |
Acrobat Reader DC versions versions 2020.013.20074 (and earlier), 2020.001.30018 (and earlier) and 2017.011.30188 (and earlier) are affected by a Use After Free vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-02-11 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21035
MISC |
| adobe — acrobat |
Acrobat Reader DC versions versions 2020.013.20074 (and earlier), 2020.001.30018 (and earlier) and 2017.011.30188 (and earlier) are affected by an Integer Overflow vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-02-11 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21036
MISC |
| adobe — acrobat |
Acrobat Reader DC versions versions 2020.013.20074 (and earlier), 2020.001.30018 (and earlier) and 2017.011.30188 (and earlier) are affected by a Path Traversal vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-02-11 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21037
MISC |
| adobe — acrobat |
Acrobat Reader DC versions versions 2020.013.20074 (and earlier), 2020.001.30018 (and earlier) and 2017.011.30188 (and earlier) are affected by an Out-of-bounds Write vulnerability when parsing a crafted jpeg file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-02-11 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21038
MISC |
| adobe — acrobat |
Acrobat Reader DC versions versions 2020.013.20074 (and earlier), 2020.001.30018 (and earlier) and 2017.011.30188 (and earlier) are affected by a Use After Free vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-02-11 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21039
MISC |
| adobe — acrobat |
Acrobat Reader DC versions versions 2020.013.20074 (and earlier), 2020.001.30018 (and earlier) and 2017.011.30188 (and earlier) are affected by a Use After Free vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-02-11 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21040
MISC |
| adobe — acrobat |
Acrobat Reader DC versions versions 2020.013.20074 (and earlier), 2020.001.30018 (and earlier) and 2017.011.30188 (and earlier) are affected by a use-after-free vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-02-11 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21041
MISC |
| adobe — acrobat |
Acrobat Reader DC versions versions 2020.013.20074 (and earlier), 2020.001.30018 (and earlier) and 2017.011.30188 (and earlier) are affected by a Use After Free vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-02-11 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21021
MISC |
| adobe — acrobat |
Acrobat Reader DC versions versions 2020.013.20074 (and earlier), 2020.001.30018 (and earlier) and 2017.011.30188 (and earlier) are affected by an Out-of-bounds Read vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to locally elevate privileges in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-02-11 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-21034
MISC |
| adobe — acrobat |
Acrobat Pro DC versions versions 2020.013.20074 (and earlier), 2020.001.30018 (and earlier) and 2017.011.30188 (and earlier) are affected by a Use-after-free vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted PDF file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to disclose sensitive information in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-02-11 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-21061
MISC |
| adobe — acrobat |
Adobe Acrobat Pro DC versions 2020.013.20074 (and earlier), 2020.001.30018 (and earlier) and 2017.011.30188 (and earlier) are affected by an improper input validation vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to disclose sensitive information in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-02-11 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-21060
MISC |
| adobe — acrobat |
Acrobat Reader DC versions versions 2020.013.20074 (and earlier), 2020.001.30018 (and earlier) and 2017.011.30188 (and earlier) are affected by a null pointer dereference vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted PDF file. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to achieve denial of service in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-02-11 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-21057
MISC |
| adobe — acrobat |
Acrobat Reader DC versions versions 2020.013.20074 (and earlier), 2020.001.30018 (and earlier) and 2017.011.30188 (and earlier) are affected by an memory corruption vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to cause an application denial-of-service. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-02-11 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-21046
MISC |
| adobe — acrobat |
Acrobat Reader DC versions versions 2020.013.20074 (and earlier), 2020.001.30018 (and earlier) and 2017.011.30188 (and earlier) are affected by an Out-of-bounds Read vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to locally escalate privileges in the context of the current user. Exploitation of this issue requires user interaction in that a victim must open a malicious file. |
2021-02-11 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-21042
MISC |
| advantech — iview |
Advantech iView versions prior to v5.7.03.6112 are vulnerable to directory traversal, which may allow an attacker to read sensitive files. |
2021-02-11 |
5 |
CVE-2021-22656
MISC
MISC |
| advantech — iview |
Advantech iView versions prior to v5.7.03.6112 are vulnerable to a SQL injection, which may allow an unauthorized attacker to disclose information. |
2021-02-11 |
5 |
CVE-2021-22654
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| apache — activemq |
An instance of a cross-site scripting vulnerability was identified to be present in the web based administration console on the message.jsp page of Apache ActiveMQ versions 5.15.12 through 5.16.0. |
2021-02-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-13947
MISC
MLIST
MLIST
MLIST |
| apostrophecms — sanitize-html |
Apostrophe Technologies sanitize-html before 2.3.1 does not properly handle internationalized domain name (IDN) which could allow an attacker to bypass hostname whitelist validation set by the “allowedIframeHostnames” option. |
2021-02-08 |
5 |
CVE-2021-26539
MISC
MISC |
| apostrophecms — sanitize-html |
Apostrophe Technologies sanitize-html before 2.3.2 does not properly validate the hostnames set by the “allowedIframeHostnames” option when the “allowIframeRelativeUrls” is set to true, which allows attackers to bypass hostname whitelist for iframe element, related using an src value that starts with “/example.com”. |
2021-02-08 |
5 |
CVE-2021-26540
MISC
MISC |
| b2evolution — b2evolution |
Open redirect vulnerability in b2evolution CMS version prior to 6.11.6 allows an attacker to perform malicious open redirects to an attacker controlled resource via redirect_to parameter in email_passthrough.php. |
2021-02-09 |
5.8 |
CVE-2020-22840
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| b2evolution — b2evolution_cms |
Reflected cross-site scripting vulnerability (XSS) in the evoadm.php file in b2evolution cms version 6.11.6-stable allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary webscript or HTML code via the tab3 parameter. |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-22839
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| carrierwave_project — carrierwave |
CarrierWave is an open-source RubyGem which provides a simple and flexible way to upload files from Ruby applications. In CarrierWave before versions 1.3.2 and 2.1.1 the download feature has an SSRF vulnerability, allowing attacks to provide DNS entries or IP addresses that are intended for internal use and gather information about the Intranet infrastructure of the platform. This is fixed in versions 1.3.2 and 2.1.1. |
2021-02-08 |
4 |
CVE-2021-21288
MISC
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
| cesanta — mongoose |
The mg_http_serve_file function in Cesanta Mongoose HTTP server 7.0 is vulnerable to remote OOB write attack via connection request after exhausting memory pool. |
2021-02-08 |
6.4 |
CVE-2021-26528
MISC |
| cesanta — mongoose |
The mg_tls_init function in Cesanta Mongoose HTTPS server 7.0 and 6.7-6.18 (compiled with mbedTLS support) is vulnerable to remote OOB write attack via connection request after exhausting memory pool. |
2021-02-08 |
6.4 |
CVE-2021-26529
MISC |
| cesanta — mongoose |
The mg_tls_init function in Cesanta Mongoose HTTPS server 7.0 (compiled with OpenSSL support) is vulnerable to remote OOB write attack via connection request after exhausting memory pool. |
2021-02-08 |
6.4 |
CVE-2021-26530
MISC |
| chainsafe — ethermint |
Cosmos Network Ethermint <= v0.4.0 is affected by cache lifecycle inconsistency in the EVM module. Due to the inconsistency between the Storage caching cycle and the Tx processing cycle, Storage changes caused by a failed transaction are improperly reserved in memory. Although the bad storage cache data will be discarded at EndBlock, it is still valid in the current block, which enables many possible attacks such as an “arbitrary mint token”. |
2021-02-08 |
5 |
CVE-2021-25837
MISC |
| chainsafe — ethermint |
Cosmos Network Ethermint <= v0.4.0 is affected by a cross-chain transaction replay vulnerability in the EVM module. Since ethermint uses the same chainIDEpoch and signature schemes with ethereum for compatibility, a verified signature in ethereum is still valid in ethermint with the same msg content and chainIDEpoch, which enables “cross-chain transaction replay” attack. |
2021-02-08 |
5 |
CVE-2021-25835
MISC
MISC |
| chainsafe — ethermint |
Cosmos Network Ethermint <= v0.4.0 is affected by a transaction replay vulnerability in the EVM module. If the victim sends a very large nonce transaction, the attacker can replay the transaction through the application. |
2021-02-08 |
5 |
CVE-2021-25834
MISC |
| chainsafe — ethermint |
Cosmos Network Ethermint <= v0.4.0 is affected by cache lifecycle inconsistency in the EVM module. The bytecode set in a FAILED transaction wrongfully remains in memory(stateObject.code) and is further written to persistent store at the Endblock stage, which may be utilized to build honeypot contracts. |
2021-02-08 |
5 |
CVE-2021-25836
MISC |
| cryptography_project — cryptography |
In the cryptography package before 3.3.2 for Python, certain sequences of update calls to symmetrically encrypt multi-GB values could result in an integer overflow and buffer overflow, as demonstrated by the Fernet class. |
2021-02-07 |
6.4 |
CVE-2020-36242
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
MISC
FEDORA |
| dell — emc_powerscale_onefs |
Dell EMC PowerScale OneFS versions 8.2.0 – 9.1.0 contain a privilege escalation vulnerability. A non-admin user with either ISI_PRIV_LOGIN_CONSOLE or ISI_PRIV_LOGIN_SSH may potentially exploit this vulnerability to read arbitrary data, tamper with system software or deny service to users. Note: no non-admin users or roles have these privileges by default. |
2021-02-09 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-26192
MISC |
| dell — emc_powerscale_onefs |
Dell EMC PowerScale OneFS versions 8.1.2 – 9.1.0 contain an issue where the OneFS SMB directory auto-create may erroneously create a directory for a user. A remote unauthenticated attacker may take advantage of this issue to slow down the system. |
2021-02-09 |
5 |
CVE-2020-26195
MISC |
| dell — emc_powerscale_onefs |
Dell EMC PowerScale OneFS versions 8.1.2 and 8.2.2 contain an Incorrect Permission Assignment for a Critical Resource vulnerability. This may allow a non-admin user with either ISI_PRIV_LOGIN_CONSOLE or ISI_PRIV_LOGIN_SSH privileges to exploit the vulnerability, leading to compromised cryptographic operations. Note: no non-admin users or roles have these privileges by default. |
2021-02-09 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-26194
MISC |
| dell — emc_powerscale_onefs |
Dell EMC PowerScale OneFS versions 8.1.0 – 9.1.0 contain a privilege escalation vulnerability. A user with ISI_PRIV_JOB_ENGINE may use the PermissionRepair job to grant themselves the highest level of RBAC privileges thus being able to read arbitrary data, tamper with system software or deny service to users. |
2021-02-09 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-26191
MISC |
| elecom — wrc-300febk-a_firmware |
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) vulnerability in ELECOM WRC-300FEBK-A allows remote attackers to hijack the authentication of administrators and execute an arbitrary request via unspecified vector. As a result, the device settings may be altered and/or telnet daemon may be started. |
2021-02-12 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-20646
MISC
MISC |
| elecom — wrc-300febk-a_firmware |
Cross-site scripting vulnerability in ELECOM WRC-300FEBK-A allows remote authenticated attackers to inject arbitrary script via unspecified vectors. |
2021-02-12 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-20645
MISC
MISC |
| elecom — wrc-300febk-s_firmware |
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) vulnerability in ELECOM WRC-300FEBK-S allows remote attackers to hijack the authentication of administrators and execute an arbitrary request via unspecified vector. As a result, the device settings may be altered and/or telnet daemon may be started. |
2021-02-12 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-20647
MISC
MISC |
| elecom — wrc-300febk-s_firmware |
ELECOM WRC-300FEBK-S contains an improper certificate validation vulnerability. Via a man-in-the-middle attack, an attacker may alter the communication response. As a result, an arbitrary OS command may be executed on the affected device. |
2021-02-12 |
5.8 |
CVE-2021-20649
MISC
MISC |
| electriccoin — zcashd |
In Electric Coin Company Zcashd before 2.1.1-1, the time offset between messages could be leveraged to obtain sensitive information about the relationship between a suspected victim’s address and an IP address, aka a timing side channel. |
2021-02-05 |
5 |
CVE-2020-8807
MISC |
| electriccoin — zcashd |
Electric Coin Company Zcashd before 2.1.1-1 allows attackers to trigger consensus failure and double spending. A valid chain could be incorrectly rejected because timestamp requirements on block headers were not properly enforced. |
2021-02-05 |
5 |
CVE-2020-8806
MISC |
| emlog — emlog |
emlog v5.3.1 has full path disclosure vulnerability in t/index.php, which allows an attacker to see the path to the webroot/file. |
2021-02-08 |
5 |
CVE-2021-3293
MISC
MISC |
| epikur — epikur |
An issue was discovered in Epikur before 20.1.1. A Glassfish 4.1 server with a default configuration is running on TCP port 4848. No password is required to access it with the administrator account. |
2021-02-05 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-10537
MISC |
| ezxml_project — ezxml |
The ezxml_toxml function in ezxml 0.8.6 and earlier is vulnerable to OOB write when opening XML file after exhausting the memory pool. |
2021-02-08 |
5.8 |
CVE-2021-26220
MISC |
| ezxml_project — ezxml |
The ezxml_new function in ezXML 0.8.6 and earlier is vulnerable to OOB write when opening XML file after exhausting the memory pool. |
2021-02-08 |
5.8 |
CVE-2021-26221
MISC |
| ezxml_project — ezxml |
The ezxml_new function in ezXML 0.8.6 and earlier is vulnerable to OOB write when opening XML file after exhausting the memory pool. |
2021-02-08 |
5.8 |
CVE-2021-26222
MISC |
| fedoraproject — fedora |
A flaw was found in the default configuration of dnsmasq, as shipped with Fedora versions prior to 31 and in all versions Red Hat Enterprise Linux, where it listens on any interface and accepts queries from addresses outside of its local subnet. In particular, the option `local-service` is not enabled. Running dnsmasq in this manner may inadvertently make it an open resolver accessible from any address on the internet. This flaw allows an attacker to conduct a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) against other systems. |
2021-02-06 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-14312
MISC |
| fiberhome — an5506-04-fa_firmware |
An issue was discovered on FiberHome AN5506-04-FA devices with firmware RP2631. There is a gepon password for the gepon account. |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2021-27169
MISC |
| fiberhome — hg6245d_firmware |
An issue was discovered on FiberHome HG6245D devices through RP2613. By default, there are no firewall rules for IPv6 connectivity, exposing the internal management interfaces to the Internet. |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2021-27170
MISC |
| fiberhome — hg6245d_firmware |
An issue was discovered on FiberHome HG6245D devices through RP2613. A hardcoded GEPON password for root is defined inside /etc/init.d/system-config.sh. |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2021-27172
MISC |
| fiberhome — hg6245d_firmware |
An issue was discovered on FiberHome HG6245D devices through RP2613. There is a telnet?enable=0&key=calculated(BR0_MAC) backdoor API, without authentication, provided by the HTTP server. This will remove firewall rules and allow an attacker to reach the telnet server (used for the CLI). |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2021-27173
MISC |
| fiberhome — hg6245d_firmware |
An issue was discovered on FiberHome HG6245D devices through RP2613. There is a password of four hexadecimal characters for the admin account. These characters are generated in init_3bb_password in libci_adaptation_layer.so. |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2021-27167
MISC |
| fiberhome — hg6245d_firmware |
An issue was discovered on FiberHome HG6245D devices through RP2613. There is a 6GFJdY4aAuUKJjdtSn7d password for the rdsadmin account. |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2021-27168
MISC |
| fiberhome — hg6245d_firmware |
An issue was discovered on FiberHome HG6245D devices through RP2613. wifictl_5g.cfg has cleartext passwords and 0644 permissions. |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2021-27176
MISC |
| fiberhome — hg6245d_firmware |
An issue was discovered on FiberHome HG6245D devices through RP2613. The password for the enable command is gpon. |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2021-27166
MISC |
| fiberhome — hg6245d_firmware |
An issue was discovered on FiberHome HG6245D devices through RP2613. The telnet daemon on port 23/tcp can be abused with the gpon/gpon credentials. |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2021-27165
MISC |
| fiberhome — hg6245d_firmware |
An issue was discovered on FiberHome HG6245D devices through RP2613. The web daemon contains the hardcoded f~i!b@e#r$h%o^m*esuperadmin / s(f)u_h+g|u credentials for an ISP. |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2021-27144
MISC |
| fiberhome — hg6245d_firmware |
An issue was discovered on FiberHome HG6245D devices through RP2613. The web daemon contains the hardcoded user / user1234 credentials for an ISP. |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2021-27143
MISC |
| fiberhome — hg6245d_firmware |
An issue was discovered on FiberHome HG6245D devices through RP2613. The web management is done over HTTPS, using a hardcoded private key that has 0777 permissions. |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2021-27142
MISC |
| fiberhome — hg6245d_firmware |
An issue was discovered on FiberHome HG6245D devices through RP2613. Credentials in /fhconf/umconfig.txt are obfuscated via XOR with the hardcoded *j7a(L#yZ98sSd5HfSgGjMj8;Ss;d)(*&^#@$a2s0i3g key. (The webs binary has details on how XOR is used.) |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2021-27141
MISC |
| fiberhome — hg6245d_firmware |
An issue was discovered on FiberHome HG6245D devices through RP2613. It is possible to find passwords and authentication cookies stored in cleartext in the web.log HTTP logs. |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2021-27140
MISC |
| fiberhome — hg6245d_firmware |
An issue was discovered on FiberHome HG6245D devices through RP2613. It is possible to extract information from the device without authentication by disabling JavaScript and visiting /info.asp. |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2021-27139
MISC |
| fiberhome — hg6245d_firmware |
An issue was discovered on FiberHome HG6245D devices through RP2613. wifictl_2g.cfg has cleartext passwords and 0644 permissions. |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2021-27175
MISC |
| fiberhome — hg6245d_firmware |
An issue was discovered on FiberHome HG6245D devices through RP2613. wifi_custom.cfg has cleartext passwords and 0644 permissions. |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2021-27174
MISC |
| fiberhome — hg6245d_firmware |
An issue was discovered on FiberHome HG6245D devices through RP2613. It is possible to crash the telnet daemon by sending a certain 0a 65 6e 61 62 6c 65 0a 02 0a 1a 0a string. |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2021-27179
MISC |
| fiberhome — hg6245d_firmware |
An issue was discovered on FiberHome HG6245D devices through RP2613. Some passwords are stored in cleartext in nvram. |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2021-27178
MISC |
| flowpaper — pdf2json |
Buffer overflow in pdf2json 0.69 allows local users to execute arbitrary code by converting a crafted PDF file. |
2021-02-05 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-18750
CONFIRM
MISC |
| fortinet — fortiweb |
An improper neutralization of input during web page generation in FortiWeb GUI interface 6.3.0 through 6.3.7 and version before 6.2.4 may allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to perform a reflected cross site scripting attack (XSS) by injecting malicious payload in different vulnerable API end-points. |
2021-02-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-22122
CONFIRM |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_reader |
In Foxit Reader 10.1.0.37527, a specially crafted PDF document can trigger reuse of previously free memory which can lead to arbitrary code execution. An attacker needs to trick the user to open the malicious file to trigger this vulnerability. If the browser plugin extension is enabled, visiting a malicious site can also trigger the vulnerability. |
2021-02-10 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-13548
MISC |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_studio_photo |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Studio Photo 3.6.6.922. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of NEF files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a write past the end of an allocated structure. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-11192. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-17419
MISC
MISC |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_studio_photo |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Studio Photo 3.6.6.922. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the processing of NEF files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated structure. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-11334. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-17427
MISC
MISC |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_studio_photo |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Studio Photo 3.6.6.922. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of CR2 files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a memory corruption condition. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-11230. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-17426
MISC
MISC |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_studio_photo |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Studio Photo 3.6.6.922. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the parsing of EPS files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a write past the end of an allocated structure. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-11259. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-17425
MISC
MISC |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_studio_photo |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Studio Photo 3.6.6.922. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the parsing of EZI files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a write past the end of an allocated structure. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-11247. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-17424
MISC
MISC |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_studio_photo |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Studio Photo 3.6.6.922. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of ARW files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of the length of user-supplied data prior to copying it to a heap-based buffer. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-11196. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-17423
MISC
MISC |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_studio_photo |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Studio Photo 3.6.6.922. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the parsing of NEF files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a write past the end of an allocated structure. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-11488. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-27857
MISC
MISC |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_studio_photo |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Studio Photo 3.6.6.922. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the parsing of CR2 files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated structure. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-11434. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-27856
MISC
MISC |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_studio_photo |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Studio Photo 3.6.6.922. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the parsing of SR2 files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated structure. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-11433. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-27855
MISC
MISC |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_studio_photo |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Studio Photo 3.6.6.922. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the parsing of CMP files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated structure. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-11432. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-17436
MISC
MISC |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_studio_photo |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Studio Photo 3.6.6.922. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of EZIX files. A crafted id in a channel element can trigger a write past the end of an allocated buffer. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-11197. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-17418
MISC
MISC |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_studio_photo |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Studio Photo 3.6.6.922. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the parsing of CR2 files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a write past the end of an allocated structure. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-11332. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-17430
MISC
MISC |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_studio_photo |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Studio Photo 3.6.6.922. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of CMP files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated structure. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-11337. |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-17429
MISC
MISC |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_studio_photo |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Studio Photo 3.6.6.922. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of NEF files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a write past the end of an allocated structure. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-11194. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-17421
MISC
MISC |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_studio_photo |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected installations of Foxit Studio Photo 3.6.6.922. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the parsing of CR2 files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a write past the end of an allocated structure. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-11333. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-17431
MISC
MISC |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_studio_photo |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Studio Photo 3.6.6.922. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the parsing of CR2 files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated structure. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-11358. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-17435
MISC
MISC |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_studio_photo |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Studio Photo 3.6.6.922. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of CMP files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated structure. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-11336. |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-17428
MISC
MISC |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_studio_photo |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Studio Photo 3.6.6.922. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the parsing of CMP files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated structure. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-11356. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-17433
MISC
MISC |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_studio_photo |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Studio Photo 3.6.6.922. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the parsing of CR2 files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated structure. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-11335. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-17432
MISC
MISC |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_studio_photo |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Studio Photo 3.6.6.922. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the parsing of ARW files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated structure. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-11357. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-17434
MISC
MISC |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_studio_photo |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Studio Photo 3.6.6.922. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of EPS files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated structure. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-11195. |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-17422
MISC
MISC |
| foxitsoftware — foxit_studio_photo |
This vulnerability allows remote attackers to disclose sensitive information on affected installations of Foxit Studio Photo 3.6.6.922. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of NEF files. The issue results from the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a read past the end of an allocated structure. An attacker can leverage this in conjunction with other vulnerabilities to execute code in the context of the current process. Was ZDI-CAN-11193. |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-17420
MISC
MISC |
| fusioncharts — apexcharts |
The package apexcharts before 3.24.0 are vulnerable to Cross-site Scripting (XSS) via lack of sanitization of graph legend fields. |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-23327
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| genivia — gsoap |
A denial-of-service vulnerability exists in the WS-Security plugin functionality of Genivia gSOAP 2.8.107. A specially crafted SOAP request can lead to denial of service. An attacker can send an HTTP request to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2020-13578
MISC |
| genivia — gsoap |
A denial-of-service vulnerability exists in the WS-Security plugin functionality of Genivia gSOAP 2.8.107. A specially crafted SOAP request can lead to denial of service. An attacker can send an HTTP request to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2020-13577
MISC |
| genivia — gsoap |
A denial-of-service vulnerability exists in the WS-Addressing plugin functionality of Genivia gSOAP 2.8.107. A specially crafted SOAP request can lead to denial of service. An attacker can send an HTTP request to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2020-13575
MISC |
| genivia — gsoap |
A denial-of-service vulnerability exists in the WS-Security plugin functionality of Genivia gSOAP 2.8.107. A specially crafted SOAP request can lead to denial of service. An attacker can send an HTTP request to trigger this vulnerability. |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2020-13574
MISC |
| gitea — gitea |
Stack buffer overflow vulnerability in gitea 1.9.0 through 1.13.1 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (crash) via vectors related to a file path. |
2021-02-05 |
5 |
CVE-2021-3382
MISC |
| godotengine — godot_engine |
An integer overflow issue exists in Godot Engine up to v3.2 that can be triggered when loading specially crafted.TGA image files. The vulnerability exists in ImageLoaderTGA::load_image() function at line: const size_t buffer_size = (tga_header.image_width * tga_header.image_height) * pixel_size; The bug leads to Dynamic stack buffer overflow. Depending on the context of the application, attack vector can be local or remote, and can lead to code execution and/or system crash. |
2021-02-08 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-26825
MISC
MISC |
| godotengine — godot_engine |
A stack overflow issue exists in Godot Engine up to v3.2 and is caused by improper boundary checks when loading .TGA image files. Depending on the context of the application, attack vector can be local or remote, and can lead to code execution and/or system crash. |
2021-02-08 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-26826
MISC
MISC |
| google — android |
In onCreate of BluetoothPermissionActivity.java, there is a possible permissions bypass due to a tapjacking overlay that obscures the phonebook permissions dialog when a Bluetooth device is connecting. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with User execution privileges needed. User interaction is needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-8.1 Android-9 Android-10 Android-11Android ID: A-168504491 |
2021-02-10 |
6.9 |
CVE-2021-0333
MISC |
| google — android |
In SystemSettingsValidators, there is a possible permanent denial of service due to missing bounds checks on UI settings. This could lead to local denial of service with User execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-10 Android-11Android ID: A-156260178 |
2021-02-10 |
4.9 |
CVE-2021-0338
MISC |
| google — android |
In onCreate of NotificationAccessConfirmationActivity.java, there is a possible overlay attack due to an insecure default value. This could lead to local escalation of privilege and notification access with User execution privileges needed. User interaction is needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-9 Android-10 Android-11 Android-8.1Android ID: A-170731783 |
2021-02-10 |
6.9 |
CVE-2021-0331
MISC |
| google — android |
In process of C2SoftHevcDec.cpp, there is a possible out of bounds write due to a use after free. This could lead to remote information disclosure with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-11Android ID: A-160346309 |
2021-02-10 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-0335
MISC |
| google — android |
In onCreate of UninstallerActivity, there is a possible way to uninstall an all without informed user consent due to a tapjacking/overlay attack. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with User execution privileges needed. User interaction is needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-10 Android-11 Android-8.1 Android-9Android ID: A-171221302 |
2021-02-10 |
6.9 |
CVE-2021-0314
MISC |
| google — android |
In verifyHostName of OkHostnameVerifier.java, there is a possible way to accept a certificate for the wrong domain due to improperly used crypto. This could lead to remote information disclosure with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.Product: AndroidVersions: Android-8.1 Android-9 Android-10 Android-11Android ID: A-171980069 |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2021-0341
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Heap buffer overflow in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21128
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted Chrome Extension. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21127
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Insufficient data validation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21118
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Use after free in Media in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21119
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Use after free in WebSQL in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21120
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Use after free in Omnibox in Google Chrome on Linux prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21121
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21122
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Potential user after free in Speech Recognizer in Google Chrome on Android prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21124
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Inappropriate implementation in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted Chrome Extension. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21132
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted SCTP packet. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-16044
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Use after free in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a local attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted file. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21138
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Uninitialized use in USB in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a local attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via via a USB device. |
2021-02-09 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-21140
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Heap buffer overflow in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.150 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21148
MISC
MISC
FEDORA |
| google — chrome |
Use after free in Payments in Google Chrome on Mac prior to 88.0.4324.146 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21142
MISC
MISC
FEDORA |
| google — chrome |
Heap buffer overflow in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.146 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21143
MISC
MISC
FEDORA |
| google — chrome |
Use after free in Navigation in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.146 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21146
MISC
MISC
FEDORA |
| google — chrome |
Insufficient policy enforcement in File System API in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to bypass filesystem restrictions via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
5.8 |
CVE-2021-21125
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Heap buffer overflow in Tab Groups in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.146 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21144
MISC
MISC
FEDORA |
| google — chrome |
Use after free in Fonts in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.146 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-21145
MISC
MISC
FEDORA |
| google — chrome |
Insufficient policy enforcement in Cryptohome in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a local attacker to perform OS-level privilege escalation via a crafted file. |
2021-02-09 |
6.9 |
CVE-2021-21117
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Inappropriate implementation in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.146 allowed a local attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-21147
MISC
MISC
FEDORA |
| google — chrome |
Insufficient policy enforcement in File System API in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to bypass file extension policy via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-21141
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Inappropriate implementation in iframe sandbox in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-21139
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Inappropriate implementation in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from disk via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-21137
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Insufficient policy enforcement in WebView in Google Chrome on Android prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-21136
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Inappropriate implementation in Performance API in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-21135
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Incorrect security UI in Page Info in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-21134
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Insufficient policy enforcement in Downloads in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to download files to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-21133
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Insufficient policy enforcement in File System API in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to bypass filesystem restrictions via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-21131
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Insufficient policy enforcement in File System API in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to bypass filesystem restrictions via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-21130
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Insufficient policy enforcement in File System API in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to bypass filesystem restrictions via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-21129
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to bypass site isolation via a crafted Chrome Extension. |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-21126
MISC
MISC |
| google — chrome |
Insufficient data validation in File System API in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to bypass filesystem restrictions via a crafted HTML page. |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-21123
MISC
MISC |
| gradle — enterprise_test_distribution_agent |
A directory traversal issue was discovered in Gradle gradle-enterprise-test-distribution-agent before 1.3.2, test-distribution-gradle-plugin before 1.3.2, and gradle-enterprise-maven-extension before 1.8.2. A malicious actor (with certain credentials) can perform a registration step such that crafted TAR archives lead to extraction of files into arbitrary filesystem locations. |
2021-02-09 |
5.5 |
CVE-2021-26719
MISC |
| helm — helm |
Helm is open-source software which is essentially “The Kubernetes Package Manager”. Helm is a tool for managing Charts. Charts are packages of pre-configured Kubernetes resources. In Helm from version 3.0 and before version 3.5.2, there a few cases where data loaded from potentially untrusted sources was not properly sanitized. When a SemVer in the `version` field of a chart is invalid, in some cases Helm allows the string to be used “as is” without sanitizing. Helm fails to properly sanitized some fields present on Helm repository `index.yaml` files. Helm does not properly sanitized some fields in the `plugin.yaml` file for plugins In some cases, Helm does not properly sanitize the fields in the `Chart.yaml` file. By exploiting these attack vectors, core maintainers were able to send deceptive information to a terminal screen running the `helm` command, as well as obscure or alter information on the screen. In some cases, we could send codes that terminals used to execute higher-order logic, like clearing a terminal screen. Further, during evaluation, the Helm maintainers discovered a few other fields that were not properly sanitized when read out of repository index files. This fix remedies all such cases, and once again enforces SemVer2 policies on version fields. All users of the Helm 3 should upgrade to the fixed version 3.5.2 or later. Those who use Helm as a library should verify that they either sanitize this data on their own, or use the proper Helm API calls to sanitize the data. |
2021-02-05 |
4 |
CVE-2021-21303
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM |
| httplib2_project — httplib2 |
httplib2 is a comprehensive HTTP client library for Python. In httplib2 before version 0.19.0, a malicious server which responds with long series of “xa0” characters in the “www-authenticate” header may cause Denial of Service (CPU burn while parsing header) of the httplib2 client accessing said server. This is fixed in version 0.19.0 which contains a new implementation of auth headers parsing using the pyparsing library. |
2021-02-08 |
5 |
CVE-2021-21240
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
| huawei — ais-bw80h-00_firmware |
There is an insufficient integrity check vulnerability in Huawei Sound X Product. The system does not check certain software package’s integrity sufficiently. Successful exploit could allow an attacker to load a crafted software package to the device. Affected product versions include:AIS-BW80H-00 versions 9.0.3.1(H100SP13C00),9.0.3.1(H100SP18C00),9.0.3.1(H100SP3C00),9.0.3.1(H100SP9C00),9.0.3.2(H100SP1C00),9.0.3.2(H100SP2C00),9.0.3.2(H100SP5C00),9.0.3.2(H100SP8C00),9.0.3.3(H100SP1C00). |
2021-02-06 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-9118
CONFIRM |
| huawei — campusinsight |
Some Huawei products have an inconsistent interpretation of HTTP requests vulnerability. Attackers can exploit this vulnerability to cause information leak. Affected product versions include: CampusInsight versions V100R019C10; ManageOne versions 6.5.1.1, 6.5.1.SPC100, 6.5.1.SPC200, 6.5.1RC1, 6.5.1RC2, 8.0.RC2. Affected product versions include: Taurus-AL00A versions 10.0.0.1(C00E1R1P1). |
2021-02-06 |
5 |
CVE-2021-22293
CONFIRM |
| huawei — imaster_mae-m |
There is a local privilege escalation vulnerability in some Huawei products. A local, authenticated attacker could craft specific commands to exploit this vulnerability. Successful exploitation may cause the attacker to obtain a higher privilege. Affected product versions include: ManageOne versions 6.5.0,6.5.0.SPC100.B210,6.5.1.1.B010,6.5.1.1.B020,6.5.1.1.B030,6.5.1.1.B040,6.5.1.SPC100.B050,6.5.1.SPC101.B010,6.5.1.SPC101.B040,6.5.1.SPC200,6.5.1.SPC200.B010,6.5.1.SPC200.B030,6.5.1.SPC200.B040,6.5.1.SPC200.B050,6.5.1.SPC200.B060,6.5.1.SPC200.B070,6.5.1RC1.B060,6.5.1RC2.B020,6.5.1RC2.B030,6.5.1RC2.B040,6.5.1RC2.B050,6.5.1RC2.B060,6.5.1RC2.B070,6.5.1RC2.B080,6.5.1RC2.B090,6.5.RC2.B050,8.0.0,8.0.0-LCND81,8.0.0.SPC100,8.0.1,8.0.RC2,8.0.RC3,8.0.RC3.B041,8.0.RC3.SPC100; NFV_FusionSphere versions 6.5.1.SPC23,8.0.0.SPC12; SMC2.0 versions V600R019C00,V600R019C10; iMaster MAE-M versions MAE-TOOL(FusionSphereBasicTemplate_Euler_X86)V100R020C10SPC220. |
2021-02-06 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-22299
CONFIRM |
| huawei — manageone |
There is a logic vulnerability in Huawei Gauss100 OLTP Product. An attacker with certain permissions could perform specific SQL statement to exploit this vulnerability. Due to insufficient security design, successful exploit can cause service abnormal. Affected product versions include: ManageOne versions 6.5.1.1.B020, 6.5.1.1.B030, 6.5.1.1.B040, 6.5.1.SPC100.B050, 6.5.1.SPC101.B010, 6.5.1.SPC101.B040, 6.5.1.SPC200, 6.5.1.SPC200.B010, 6.5.1.SPC200.B030, 6.5.1.SPC200.B040, 6.5.1.SPC200.B050, 6.5.1.SPC200.B060, 6.5.1.SPC200.B070, 6.5.1RC1.B070, 6.5.1RC1.B080, 6.5.1RC2.B040, 6.5.1RC2.B050, 6.5.1RC2.B060, 6.5.1RC2.B070, 6.5.1RC2.B080, 6.5.1RC2.B090. |
2021-02-06 |
4 |
CVE-2021-22298
CONFIRM |
| huawei — manageone |
There has a CSV injection vulnerability in ManageOne 8.0.1. An attacker with common privilege may exploit this vulnerability through some operations to inject the CSV files. Due to insufficient input validation of some parameters, the attacker can exploit this vulnerability to inject CSV files to the target device. |
2021-02-06 |
4 |
CVE-2020-9205
CONFIRM |
| huawei — mate_30_firmware |
Mate 30 10.0.0.203(C00E201R7P2) have a buffer overflow vulnerability. After obtaining the root permission, an attacker can exploit the vulnerability to cause buffer overflow. |
2021-02-06 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-22301
CONFIRM |
| huawei — taurus-al00a_firmware |
There is a pointer double free vulnerability in Taurus-AL00A 10.0.0.1(C00E1R1P1). There is a lack of muti-thread protection when a function is called. Attackers can exploit this vulnerability by performing malicious operation to cause pointer double free. This may lead to module crash, compromising normal service. |
2021-02-06 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-22303
CONFIRM |
| ibm — cloud_pak_for_automation |
IBM Cloud Pak for Automation 20.0.3, 20.0.2-IF002 – Business Automation Application Designer Component stores potentially sensitive information in log files that could be obtained by an unauthorized user. IBM X-Force ID: 194966. |
2021-02-08 |
4 |
CVE-2021-20359
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — cloud_pak_for_automation |
IBM Cloud Pak for Automation 20.0.3, 20.0.2-IF002 stores potentially sensitive information in clear text in API connection log files. This information could be obtained by a user with permissions to read log files. IBM X-Force ID: 194965. |
2021-02-08 |
4 |
CVE-2021-20358
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — security_identity_governance_and_intelligence |
IBM Security Identity Governance and Intelligence 5.2.6 could disclose sensitive information to an unauthorized user using a specially crafted HTTP request. IBM X-Force ID: 189446. |
2021-02-09 |
6.4 |
CVE-2020-4795
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — security_identity_governance_and_intelligence |
IBM Security Identity Governance and Intelligence 5.2.6 does not invalidate session after logout which could allow a user to obtain sensitive information from another users’ session. IBM X-Force ID: 192912. |
2021-02-09 |
5 |
CVE-2020-4995
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — security_verify_information_queue |
IBM Security Verify Information Queue 1.0.6 and 1.0.7 could allow a user on the network to cause a denial of service due to an invalid cookie value that could prevent future logins. IBM X-Force ID: 196078. |
2021-02-11 |
5 |
CVE-2021-20404
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — security_verify_information_queue |
IBM Security Verify Information Queue 1.0.6 and 1.0.7 could allow a user to perform unauthorized activities due to improper encoding of output. IBM X-Force ID: 196183. |
2021-02-11 |
5 |
CVE-2021-20405
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — security_verify_information_queue |
IBM Security Verify Information Queue 1.0.6 and 1.0.7 discloses sensitive information in source code that could be used in further attacks against the system. IBM X-Force ID: 198185. |
2021-02-12 |
5 |
CVE-2021-20407
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — security_verify_information_queue |
IBM Security Verify Information Queue 1.0.6 and 1.0.7 could allow a remote attacker to obtain sensitive information, caused by the failure to properly enable HTTP Strict Transport Security. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability to obtain sensitive information using man in the middle techniques. IBM X-Force ID: 198188. |
2021-02-12 |
5 |
CVE-2021-20409
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — security_verify_information_queue |
IBM Security Verify Information Queue 1.0.6 and 1.0.7 is vulnerable to cross-site request forgery which could allow an attacker to execute malicious and unauthorized actions transmitted from a user that the website trusts. |
2021-02-11 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-20403
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — security_verify_information_queue |
IBM Security Verify Information Queue 1.0.6 and 1.0.7 uses weaker than expected cryptographic algorithms that could allow an attacker to decrypt highly sensitive information. IBM X-Force ID: 198184. |
2021-02-12 |
4 |
CVE-2021-20406
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — security_verify_information_queue |
IBM Security Verify Information Queue 1.0.6 and 1.0.7 could allow a remote attacker to obtain sensitive information when a detailed technical error message is returned in the browser. This information could be used in further attacks against the system. IBM X-Force ID: 196076. |
2021-02-11 |
4 |
CVE-2021-20402
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — security_verify_information_queue |
IBM Security Verify Information Queue 1.0.6 and 1.0.7 contains hard-coded credentials, such as a password or cryptographic key, which it uses for its own inbound authentication, outbound communication to external components, or encryption of internal data. IBM X-Force ID: 198192. |
2021-02-12 |
5 |
CVE-2021-20412
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — security_verify_information_queue |
IBM Security Verify Information Queue 1.0.6 and 1.0.7 could allow a user to impersonate another user on the system due to incorrectly updating the session identifier. IBM X-Force ID: 198191. |
2021-02-12 |
4.8 |
CVE-2021-20411
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — spectrum_protect_plus |
IBM Spectrum Protect Plus 10.1.0 through 10.1.7 could allow a remote user to inject arbitrary data iwhich could cause the serivce to crash due to excess resource consumption. IBM X-Force ID: 193659. |
2021-02-10 |
5 |
CVE-2020-5023
XF
CONFIRM |
| ibm — websphere_application_server |
IBM WebSphere Application Server 7.0, 8.0, 8.5, and 9.0 is vulnerable to an XML External Entity Injection (XXE) attack when processing XML data. A remote attacker could exploit this vulnerability to expose sensitive information or consume memory resources. IBM X-Force ID: 194882. |
2021-02-10 |
6.4 |
CVE-2021-20353
XF
CONFIRM
MISC |
| imagely — nextgen_gallery |
A Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) issue in the NextGEN Gallery plugin before 3.5.0 for WordPress allows File Upload. (It is possible to bypass CSRF protection by simply not including a nonce parameter.) |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-35943
MISC |
| imagely — nextgen_gallery |
A Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) issue in the NextGEN Gallery plugin before 3.5.0 for WordPress allows File Upload and Local File Inclusion via settings modification, leading to Remote Code Execution and XSS. (It is possible to bypass CSRF protection by simply not including a nonce parameter.) |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-35942
MISC |
| imagemagick — imagemagick |
A flaw was found in ImageMagick in MagickCore/gem.c. An attacker who submits a crafted file that is processed by ImageMagick could trigger undefined behavior in the form of math division by zero. This would most likely lead to an impact to application availability, but could potentially cause other problems related to undefined behavior. This flaw affects ImageMagick versions prior to 7.0.10-56. |
2021-02-06 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-20176
MISC |
| iobit — advanced_systemcare |
The AscRegistryFilter.sys kernel driver in IObit Advanced SystemCare 13.2 allows an unprivileged user to send an IOCTL to the device driver. If the user provides a NULL entry for the dwIoControlCode parameter, a kernel panic (aka BSOD) follows. The IOCTL codes can be found in the dispatch function: 0x8001E000, 0x8001E004, 0x8001E008, 0x8001E00C, 0x8001E010, 0x8001E014, 0x8001E020, 0x8001E024, 0x8001E040, 0x8001E044, and 0x8001E048. DosDevicesAscRegistryFilter and DeviceAscRegistryFilter are affected. |
2021-02-05 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-10234
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| jenzabar — jenzabar |
Jenzabar 9.2.x through 9.2.2 allows /ics?tool=search&query= XSS. |
2021-02-06 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-26723
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| librenms — librenms |
A second-order SQL injection issue in Widgets/TopDevicesController.php (aka the Top Devices dashboard widget) of LibreNMS before 21.1.0 allows remote authenticated attackers to execute arbitrary SQL commands via the sort_order parameter against the /ajax/form/widget-settings endpoint. |
2021-02-08 |
6.5 |
CVE-2020-35700
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
MISC |
| linkedin — oncall |
LinkedIn Oncall through 1.4.0 allows reflected XSS via /query because of mishandling of the “No results found for” message in the search bar. |
2021-02-05 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-26722
MISC |
| linux — linux_kernel |
A local privilege escalation was discovered in the Linux kernel before 5.10.13. Multiple race conditions in the AF_VSOCK implementation are caused by wrong locking in net/vmw_vsock/af_vsock.c. The race conditions were implicitly introduced in the commits that added VSOCK multi-transport support. |
2021-02-05 |
6.9 |
CVE-2021-26708
MLIST
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| marked_project — marked |
Marked is an open-source markdown parser and compiler (npm package “marked”). In marked from version 1.1.1 and before version 2.0.0, there is a Regular expression Denial of Service vulnerability. This vulnerability can affect anyone who runs user generated code through marked. This vulnerability is fixed in version 2.0.0. |
2021-02-08 |
5 |
CVE-2021-21306
MISC
MISC
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
| maxpcsecure — max_spyware_detector |
In Max Secure Max Spyware Detector 1.0.0.044, the driver file (MaxProc64.sys) allows local users to cause a denial of service (BSOD) or possibly have unspecified other impact because of not validating input values from IOCtl 0x2200019. (This also extends to the various other products from Max Secure that include MaxProc64.sys.) |
2021-02-05 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-12122
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| mcafee — endpoint_security |
A Null Pointer Dereference vulnerability in McAfee Endpoint Security (ENS) for Windows prior to 10.7.0 February 2021 Update allows a local administrator to cause Windows to crash via a specific system call which is not handled correctly. This varies by machine and had partial protection prior to this update. |
2021-02-10 |
4.9 |
CVE-2021-23883
CONFIRM |
| mcafee — total_protection |
Arbitrary Process Execution vulnerability in McAfee Total Protection (MTP) prior to 16.0.30 allows a local user to gain elevated privileges and execute arbitrary code bypassing MTP self-defense. |
2021-02-10 |
4.6 |
CVE-2021-23874
CONFIRM |
| microfocus — application_performance_management |
Cross Site Request Forgery vulnerability in Micro Focus Application Performance Management product, affecting versions 9.40, 9.50 and 9.51. The vulnerability could be exploited by attacker to trick the users into executing actions of the attacker’s choosing. |
2021-02-06 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-22500
CONFIRM |
| millewin — millewin |
Millennium Millewin (also known as “Cartella clinica”) 13.39.028, 13.39.28.3342, and 13.39.146.1 has insecure folder permissions allowing a malicious user for a local privilege escalation. |
2021-02-09 |
6.5 |
CVE-2021-3394
MISC
MISC |
| ms3d_project — ms3d |
An issue was discovered in the ms3d crate before 0.1.3 for Rust. It might allow attackers to obtain sensitive information from uninitialized memory locations via IoReader::read. |
2021-02-09 |
5 |
CVE-2021-26952
MISC |
| name_directory_project — name_directory |
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) vulnerability in Name Directory 1.17.4 and earlier allows remote attackers to hijack the authentication of administrators via unspecified vectors. |
2021-02-05 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-20652
MISC
MISC |
| nedi — nedi |
NeDi 1.9C allows an authenticated user to inject PHP code in the System Files function on the endpoint /System-Files.php via the txt HTTP POST parameter. This allows an attacker to obtain access to the operating system where NeDi is installed and to all application data. |
2021-02-12 |
6.5 |
CVE-2021-26753
MISC |
| nedi — nedi |
NeDi 1.9C allows an authenticated user to perform a SQL Injection in the Monitoring History function on the endpoint /Monitoring-History.php via the det HTTP GET parameter. This allows an attacker to access all the data in the database and obtain access to the NeDi application. |
2021-02-12 |
4 |
CVE-2021-26751
MISC |
| nedi — nedi |
NeDi 1.9C allows an authenticated user to execute operating system commands in the Nodes Traffic function on the endpoint /Nodes-Traffic.php via the md or ag HTTP GET parameter. This allows an attacker to obtain access to the operating system where NeDi is installed and to all application data. |
2021-02-12 |
6.5 |
CVE-2021-26752
MISC |
| nopcommerce — nopcommerce |
In nopCommerce 4.30, a Reflected XSS issue in the Discount Coupon component allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML through the Filters/CheckDiscountCouponAttribute.cs discountcode parameter. |
2021-02-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-26916
MISC |
| octobercms — october |
An issue was discovered in October through build 471. It reactivates an old session ID (which had been invalid after a logout) once a new login occurs. NOTE: this violates the intended Auth/Manager.php authentication behavior but, admittedly, is only relevant if an old session ID is known to an attacker. |
2021-02-05 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-3311
CONFIRM
MISC |
| omron — cx-one |
The Omron CX-One Version 4.60 and prior is vulnerable to a stack-based buffer overflow, which may allow an attacker to remotely execute arbitrary code. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-27261
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| omron — cx-one |
The Omron CX-One Version 4.60 and prior may allow an attacker to supply a pointer to arbitrary memory locations, which may allow an attacker to remotely execute arbitrary code. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-27259
MISC
MISC |
| omron — cx-one |
This vulnerability allows local attackers to execute arbitrary code due to the lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, which can result in a type-confusion condition in the Omron CX-One Version 4.60 and prior devices. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-27257
MISC
MISC |
| opmantek — open-audit |
Opmantek Open-AudIT 4.0.1 is affected by cross-site scripting (XSS). When outputting SQL statements for debugging, a maliciously crafted query can trigger an XSS attack. This attack only succeeds if the user is already logged in to Open-AudIT before they click the malicious link. |
2021-02-05 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-3333
MISC |
| otrs — cis_in_customer_frontend |
Agents are able to see and link Config Items without permissions, which are defined in General Catalog. This issue affects: OTRS AG OTRSCIsInCustomerFrontend 7.0.x version 7.0.14 and prior versions. |
2021-02-08 |
4 |
CVE-2021-21436
CONFIRM |
| otrs — otrs |
Article Bcc fields and agent personal information are shown when customer prints the ticket (PDF) via external interface. This issue affects: OTRS AG OTRS 7.0.x version 7.0.23 and prior versions; 8.0.x version 8.0.10 and prior versions. |
2021-02-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-21435
CONFIRM |
| otrs — ticket_forms |
When dynamic templates are used (OTRSTicketForms), admin can use OTRS tags which are not masked properly and can reveal sensitive information. This issue affects: OTRS AG OTRSTicketForms 6.0.x version 6.0.40 and prior versions; 7.0.x version 7.0.29 and prior versions; 8.0.x version 8.0.3 and prior versions. |
2021-02-08 |
4 |
CVE-2020-1779
CONFIRM |
| phpshe — phpshe |
Multiple SQL Injection vulnerabilities in PHPSHE 1.7 in phpshe/admin.php via the (1) ad_id, (2) menu_id, and (3) cashout_id parameters, which could let a remote malicious user execute arbitrary code. |
2021-02-09 |
6.5 |
CVE-2020-18215
MISC
MISC |
| privateoctopus — picoquic |
picoquic (before 3rd of July 2020) allows attackers to cause a denial of service (infinite loop) via a crafted QUIC frame, related to the picoquic_decode_frames and picoquic_decode_stream_frame functions and epoch==3. |
2021-02-08 |
5 |
CVE-2020-24944
MISC |
| psyprax — psyprax |
An issue was discovered in Psyprax beforee 3.2.2. Passwords used to encrypt the data are stored in the database in an obfuscated format, which can be easily reverted. For example, the password AAAAAAAA is stored in the database as MMMMMMMM. |
2021-02-05 |
5 |
CVE-2020-10554
MISC |
| psyprax — psyprax |
An issue was discovered in Psyprax before 3.2.2. The Firebird database is accessible with the default user sysdba and password masterke after installation. This allows any user to access it and read and modify the contents, including passwords. Local database files can be accessed directly as well. |
2021-02-05 |
5.5 |
CVE-2020-10552
MISC |
| redwood — report2web |
A cross-site scripting (XSS) issue in the login panel in Redwood Report2Web 4.3.4.5 and 4.5.3 allows remote attackers to inject JavaScript via the signIn.do urll parameter. |
2021-02-05 |
4.3 |
CVE-2021-26710
MISC |
| redwood — report2web |
A frame-injection issue in the online help in Redwood Report2Web 4.3.4.5 allows remote attackers to render an external resource inside a frame via the help/Online_Help/NetHelp/default.htm turl parameter. |
2021-02-05 |
5 |
CVE-2021-26711
MISC |
| sdgc — pnpscada |
PNPSCADA 2.200816204020 allows cross-site scripting (XSS), which can execute arbitrary JavaScript in the victim’s browser. |
2021-02-10 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-24842
MISC |
| siemens — cscape |
Cscape (All versions prior to 9.90 SP3.5) lacks proper validation of user-supplied data when parsing project files. This could lead to an out-of-bounds read. An attacker could leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2021-22663
MISC |
| siemens — jt2go |
A vulnerability has been identified in JT2Go (All versions < V13.1.0.1), Teamcenter Visualization (All versions < V13.1.0.1). Affected applications lack proper validation of user-supplied data when parsing BMP files. This can result in a memory corruption condition. An attacker could leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. (ZDI-CAN-12018) |
2021-02-09 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-27000
MISC |
| siemens — jt2go |
A vulnerability has been identified in JT2Go (All versions < V13.1.0.1), Teamcenter Visualization (All versions < V13.1.0.1). Affected applications lack proper validation of user-supplied data when parsing of PAR files. This could result in a stack based buffer overflow. An attacker could leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. (ZDI-CAN-12041) |
2021-02-09 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-27001
MISC |
| siemens — jt2go |
A vulnerability has been identified in JT2Go (All versions < V13.1.0.1), Teamcenter Visualization (All versions < V13.1.0.1). Affected applications lack proper validation of user-supplied data when parsing TIFF files. This could lead to pointer dereferences of a value obtained from untrusted source. An attacker could leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. (ZDI-CAN-12158) |
2021-02-09 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-27003
MISC |
| siemens — jt2go |
A vulnerability has been identified in JT2Go (All versions < V13.1.0.1), Teamcenter Visualization (All versions < V13.1.0.1). Affected applications lack proper validation of user-supplied data when parsing of TGA files. This could result in an out of bounds write past the end of an allocated structure. An attacker could leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. (ZDI-CAN-12178) |
2021-02-09 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-27005
MISC |
| siemens — jt2go |
A vulnerability has been identified in JT2Go (All versions < V13.1.0.1), Teamcenter Visualization (All versions < V13.1.0.1). Affected applications lack proper validation of user-supplied data when parsing of PCT files. This could result in a memory corruption condition. An attacker could leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process. (ZDI-CAN-12182) |
2021-02-09 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-27006
MISC |
| siemens — nucleus_net |
A vulnerability has been identified in Nucleus NET (All versions < V5.2), Nucleus ReadyStart for ARM, MIPS, and PPC (All versions < V2012.12). Initial Sequence Numbers (ISNs) for TCP connections are derived from an insufficiently random source. As a result, the ISN of current and future TCP connections could be predictable. An attacker could hijack existing sessions or spoof future ones. |
2021-02-09 |
5 |
CVE-2020-28388
MISC |
| siemens — simaris_configuration |
A vulnerability has been identified in SIMARIS configuration (All versions). During installation to default target folder, incorrect permissions are configured for the application folder and subfolders which could allow an attacker to gain persistence or potentially escalate privileges should a user with elevated credentials log onto the machine. |
2021-02-09 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-28392
MISC |
| sthttpd_project — sthttpd |
An issue was discovered in sthttpd through 2.27.1. On systems where the strcpy function is implemented with memcpy, the de_dotdot function may cause a Denial-of-Service (daemon crash) due to overlapping memory ranges being passed to memcpy. This can triggered with an HTTP GET request for a crafted filename. NOTE: this is similar to CVE-2017-10671, but occurs in a different part of the de_dotdot function. |
2021-02-07 |
5 |
CVE-2021-26843
MISC |
| svakom — siime_eye_firmware |
An issue was discovered in Svakom Siime Eye 14.1.00000001.3.330.0.0.3.14. By sending a set_params.cgi?telnetd=1&save=1&reboot=1 request to the webserver, it is possible to enable the telnet interface on the device. The telnet interface can then be used to obtain access to the device with root privileges via a reecam4debug default password. This default telnet password is the same across all Siime Eye devices. In order for the attack to be exploited, an attacker must be physically close in order to connect to the device’s Wi-Fi access point. |
2021-02-08 |
4.6 |
CVE-2020-11915
MISC |
| symonics — libmysofa |
Incorrect handling of input data in verifyAttribute function in the libmysofa library 0.5 – 1.1 will lead to NULL pointer dereference and segmentation fault error in case of restrictive memory protection or near NULL pointer overwrite in case of no memory restrictions (e.g. in embedded environments). |
2021-02-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-36148
MISC |
| symonics — libmysofa |
Incorrect handling of input data in changeAttribute function in the libmysofa library 0.5 – 1.1 will lead to NULL pointer dereference and segmentation fault error in case of restrictive memory protection or near NULL pointer overwrite in case of no memory restrictions (e.g. in embedded environments). |
2021-02-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-36149
MISC |
| symonics — libmysofa |
Incorrect handling of input data in loudness function in the libmysofa library 0.5 – 1.1 will lead to heap buffer overflow and access to unallocated memory block. |
2021-02-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-36150
MISC |
| symonics — libmysofa |
Incorrect handling of input data in mysofa_resampler_reset_mem function in the libmysofa library 0.5 – 1.1 will lead to heap buffer overflow and overwriting large memory block. |
2021-02-08 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-36151
MISC |
| symonics — libmysofa |
Buffer overflow in readDataVar in hdf/dataobject.c in Symonics libmysofa 0.5 – 1.1 allows attackers to execute arbitrary code via a crafted SOFA. |
2021-02-08 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-36152
MISC |
| tenable — nessus_amazon_machine_image |
Nessus AMI versions 8.12.0 and earlier were found to either not validate, or incorrectly validate, a certificate which could allow an attacker to spoof a trusted entity by using a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack. |
2021-02-06 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-5812
MISC |
| tipsandtricks-hq — wp_security_&_firewall |
Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in admin/wp-security-blacklist-menu.php in the Tips and Tricks HQ All In One WP Security & Firewall (all-in-one-wp-security-and-firewall) plugin before 4.4.6 for WordPress. |
2021-02-10 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-29171
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
MISC |
| tufin — securetrack |
Multiple Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) vulnerabilities were present in Tufin SecureTrack, affecting all versions prior to R20-2 GA. |
2021-02-09 |
6.8 |
CVE-2020-13460
MISC |
| tufin — securetrack |
Tufin SecureTrack < R20-2 GA contains reflected + stored XSS (as in, the value is reflected back to the user, but is also stored within the DB and can be later triggered again by the same victim, or also later by different users). Both stored, and reflected payloads are triggerable by admin, so malicious non-authenticated user could get admin level access. Even malicious low-privileged user can inject XSS, which can be executed by admin, potentially elevating privileges and obtaining admin access. (issue 1 of 3) |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-13407
MISC |
| tufin — securetrack |
Tufin SecureTrack < R20-2 GA contains reflected + stored XSS (as in, the value is reflected back to the user, but is also stored within the DB and can be later triggered again by the same victim, or also later by different users). Both stored, and reflected payloads are triggerable by admin, so malicious non-authenticated user could get admin level access. Even malicious low-privileged user can inject XSS, which can be executed by admin, potentially elevating privileges and obtaining admin access. (issue 2 of 3) |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-13408
MISC |
| tufin — securetrack |
Tufin SecureTrack < R20-2 GA contains reflected + stored XSS (as in, the value is reflected back to the user, but is also stored within the DB and can be later triggered again by the same victim, or also later by different users). Both stored, and reflected payloads are triggerable by admin, so malicious non-authenticated user could get admin level access. Even malicious low-privileged user can inject XSS, which can be executed by admin, potentially elevating privileges and obtaining admin access. (issue 3 of 3) |
2021-02-09 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-13409
MISC |
| tufin — securetrack |
Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR) exists in Tufin SecureChange, affecting all versions prior to R20-2 GA. Fixed in version R20-2 GA. |
2021-02-09 |
5 |
CVE-2020-13462
MISC |
| typora — typora |
An issue was discovered in Typora 0.9.67. There is an XSS vulnerability that causes Remote Code Execution. |
2021-02-05 |
4.3 |
CVE-2020-18737
MISC |
| zohocorp — manageengine_applications_manager |
doFilter in com.adventnet.appmanager.filter.UriCollector in Zoho ManageEngine Applications Manager through 14930 allows an authenticated SQL Injection via the resourceid parameter to showresource.do. |
2021-02-05 |
6.5 |
CVE-2020-35765
MISC
CONFIRM
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| zulip — zulip_desktop |
Zulip Desktop before 5.0.0 allows attackers to perform recording via the webcam and microphone due to a missing permission request handler. |
2021-02-05 |
5 |
CVE-2020-10858
CONFIRM |







Recent Comments