by Scott Muniz | Nov 21, 2022 | Security, Technology
This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
| aiphone — gt-dmb-n_firmware |
Aiphone GT-DMB-N 3-in-1 Video Entrance Station with NFC Reader 1.0.3 does not mitigate against repeated failed access attempts, which allows an attacker to gain administrative privileges. |
2022-11-14 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-40903
MISC
MISC |
| amazon — opensearch |
OpenSearch is a community-driven, open source fork of Elasticsearch and Kibana. There is an issue with the implementation of fine-grained access control rules (document-level security, field-level security and field masking) where they are not correctly applied to the indices that back data streams potentially leading to incorrect access authorization. OpenSearch 1.3.7 and 2.4.0 contain a fix for this issue. Users are advised to update. There are no known workarounds for this issue. |
2022-11-15 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-41918
MISC
CONFIRM |
| amazon — opensearch_notifications |
OpenSearch Notifications is a notifications plugin for OpenSearch that enables other plugins to send notifications via Email, Slack, Amazon Chime, Custom web-hook etc channels. A potential SSRF issue in OpenSearch Notifications Plugin 2.2.0 and below could allow an existing privileged user to enumerate listening services or interact with configured resources via HTTP requests exceeding the Notification plugin’s intended scope. OpenSearch 2.2.1+ contains the fix for this issue. There are currently no recommended workarounds. |
2022-11-11 |
8.7 |
CVE-2022-41906
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
| apache — airflow |
A vulnerability in Example Dags of Apache Airflow allows an attacker with UI access who can trigger DAGs, to execute arbitrary commands via manually provided run_id parameter. This issue affects Apache Airflow Apache Airflow versions prior to 2.4.0. |
2022-11-14 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-40127
MISC
MISC
MLIST |
| apache — airflow |
A vulnerability in UI of Apache Airflow allows an attacker to view unmasked secrets in rendered template values for tasks which were not executed (for example when they were depending on past and previous instances of the task failed). This issue affects Apache Airflow prior to 2.3.1. |
2022-11-14 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-27949
MISC
MISC
MLIST |
| apache — archiva |
If anonymous read enabled, it’s possible to read the database file directly without logging in. |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-40308
CONFIRM
MLIST |
| apache — sshd |
Class org.apache.sshd.server.keyprovider.SimpleGeneratorHostKeyProvider in Apache MINA SSHD <= 2.9.1 uses Java deserialization to load a serialized java.security.PrivateKey. The class is one of several implementations that an implementor using Apache MINA SSHD can choose for loading the host keys of an SSH server. |
2022-11-16 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-45047
CONFIRM |
| archesproject — arches |
Arches is a web platform for creating, managing, & visualizing geospatial data. Versions prior to 6.1.2, 6.2.1, and 7.1.2 are vulnerable to SQL Injection. With a carefully crafted web request, it’s possible to execute certain unwanted sql statements against the database. This issue is fixed in version 7.12, 6.2.1, and 6.1.2. Users are recommended to upgrade as soon as possible. There are no workarounds. |
2022-11-11 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-41892
CONFIRM |
| atlassian — bitbucket |
There is a command injection vulnerability using environment variables in Bitbucket Server and Data Center. An attacker with permission to control their username can exploit this issue to execute arbitrary code on the system. This vulnerability can be unauthenticated if the Bitbucket Server and Data Center instance has enabled “Allow public signup”. |
2022-11-17 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-43781
MISC
MISC |
| atlassian — confluence_data_center |
The Netic User Export add-on before 1.3.5 for Atlassian Confluence has the functionality to generate a list of users in the application, and export it. During export, the HTTP request has a fileName parameter that accepts any file on the system (e.g., an SSH private key) to be downloaded. |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-42977
MISC |
| atlassian — confluence_data_center |
In the Netic User Export add-on before 1.3.5 for Atlassian Confluence, authorization is mishandled. An unauthenticated attacker could access files on the remote system. |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-42978
MISC |
| atlassian — crowd |
Affected versions of Atlassian Crowd allow an attacker to authenticate as the crowd application via security misconfiguration and subsequent ability to call privileged endpoints in Crowd’s REST API under the {{usermanagement}} path. This vulnerability can only be exploited by IPs specified under the crowd application allowlist in the Remote Addresses configuration, which is {{none}} by default. The affected versions are all versions 3.x.x, versions 4.x.x before version 4.4.4, and versions 5.x.x before 5.0.3 |
2022-11-17 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-43782
MISC |
| automattic — crowdsignal_dashboard |
Auth. (contributor+) Privilege Escalation vulnerability in Crowdsignal Dashboard plugin <= 3.0.9 on WordPress. |
2022-11-17 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-45069
CONFIRM |
| automotive_shop_management_system_project — automotive_shop_management_system |
Automotive Shop Management System v1.0 is vulnerable to SQL via /asms/classes/Master.php?f=delete_mechanic. |
2022-11-18 |
7.2 |
CVE-2022-44378
MISC |
| automotive_shop_management_system_project — automotive_shop_management_system |
Automotive Shop Management System v1.0 is vulnerable to SQL Injection via /asms/classes/Master.php?f=delete_service. |
2022-11-18 |
7.2 |
CVE-2022-44379
MISC |
| automotive_shop_management_system_project — automotive_shop_management_system |
Automotive Shop Management System v1.0 is vulnerable to SQL Injection via /asms/classes/Master.php?f=delete_transaction. |
2022-11-17 |
7.2 |
CVE-2022-44402
MISC |
| automotive_shop_management_system_project — automotive_shop_management_system |
Automotive Shop Management System v1.0 is vulnerable to SQL Injection via /asms/admin/?page=user/manage_user&id=. |
2022-11-17 |
7.2 |
CVE-2022-44403
MISC |
| automotive_shop_management_system_project — automotive_shop_management_system |
Automotive Shop Management System v1.0 is vulnerable to SQL Injection via /asms/admin/mechanics/manage_mechanic.php?id=. |
2022-11-18 |
7.2 |
CVE-2022-44413
MISC |
| automotive_shop_management_system_project — automotive_shop_management_system |
Automotive Shop Management System v1.0 is vulnerable to SQL Injection via /asms/admin/services/manage_service.php?id=. |
2022-11-18 |
7.2 |
CVE-2022-44414
MISC |
| automotive_shop_management_system_project — automotive_shop_management_system |
Automotive Shop Management System v1.0 is vulnerable to SQL Injection via /asms/admin/mechanics/view_mechanic.php?id=. |
2022-11-18 |
7.2 |
CVE-2022-44415
MISC |
| automotive_shop_management_system_project — automotive_shop_management_system |
Automotive Shop Management System v1.0 is vulnerable to SQL Injection via /asms/admin/?page=transactions/manage_transaction&id=. |
2022-11-18 |
7.2 |
CVE-2022-44820
MISC |
| axiosys — bento4 |
A vulnerability classified as critical was found in Axiomatic Bento4. Affected by this vulnerability is the function AP4_StdcFileByteStream::ReadPartial of the file Ap4StdCFileByteStream.cpp of the component mp4info. The manipulation leads to heap-based buffer overflow. The attack can be launched remotely. The exploit has been disclosed to the public and may be used. The identifier VDB-213553 was assigned to this vulnerability. |
2022-11-13 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-3974
N/A
N/A
N/A |
| backclick — backclick |
An issue was discovered in BACKCLICK Professional 5.9.63. User authentication for accessing the CORBA back-end services can be bypassed. |
2022-11-17 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-44001
MISC
MISC |
| backclick — backclick |
An issue was discovered in BACKCLICK Professional 5.9.63. Due to insufficient escaping of user-supplied input, the application is vulnerable to SQL injection at various locations. |
2022-11-16 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-44003
MISC
MISC |
| backclick — backclick |
An issue was discovered in BACKCLICK Professional 5.9.63. Due to insecure design or lack of authentication, unauthenticated attackers can complete the password-reset process for any account and set a new password. |
2022-11-16 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-44004
MISC
MISC |
| backclick — backclick |
An issue was discovered in BACKCLICK Professional 5.9.63. Due to improper validation or sanitization of upload filenames, an externally reachable, unauthenticated update function permits writing files outside the intended target location. Achieving remote code execution is possible, e.g., by uploading an executable file. |
2022-11-16 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-44006
MISC
MISC |
| badgermeter — moni |
In s::can moni::tools before version 4.2 an authenticated attacker could get full access to the database through SQL injection. This may result in loss of confidentiality, loss of integrity and DoS. |
2022-11-15 |
8.8 |
CVE-2020-12507
MISC |
| badgermeter — moni |
In s::can moni::tools in versions below 4.2 an unauthenticated attacker could get any file from the device by path traversal in the image-relocator module. |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2020-12508
MISC |
| bruhn-newtech — cbrn-analysis |
CBRN-Analysis before 22 has weak file permissions under Public Profile, leading to disclosure of file contents or privilege escalation. |
2022-11-12 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-45193
MISC |
| camp_project — camp |
patrickfuller camp up to and including commit bbd53a256ed70e79bd8758080936afbf6d738767 is vulnerable to Incorrect Access Control. Access to the password.txt file is not properly restricted as it is in the root directory served by StaticFileHandler and the Tornado rule to throw a 403 error when password.txt is accessed can be bypassed. Furthermore, it is not necessary to crack the password hash to authenticate with the application because the password hash is also used as the cookie secret, so an attacker can generate his own authentication cookie. |
2022-11-14 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-37109
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| canteen_management_system_project — canteen_management_system |
An arbitrary file upload vulnerability in the component /pages/save_user.php of Canteen Management System v1.0 allows attackers to execute arbitrary code via a crafted PHP file. |
2022-11-15 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-43265
MISC
MISC |
| canteen_management_system_project — canteen_management_system |
An arbitrary file upload vulnerability in the image upload function of Canteen Management System v1.0 allows attackers to execute arbitrary code via a crafted PHP file. |
2022-11-14 |
7.2 |
CVE-2022-43146
MISC
MISC |
| cisco — firepower_management_center |
A vulnerability in the processing of SSH connections of Cisco Firepower Management Center (FMC) and Cisco Firepower Threat Defense (FTD) Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to cause a denial of service (DoS) condition on an affected device. This vulnerability is due to improper error handling when an SSH session fails to be established. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a high rate of crafted SSH connections to the instance. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause resource exhaustion, resulting in a reboot on the affected device. |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-20854
MISC |
| clogica — seo_redirection |
Multiple Cross-Site Scripting (CSRF) vulnerabilities in SEO Redirection Plugin plugin <= 8.9 on WordPress. |
2022-11-18 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-40695
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| college_management_system_project — college_management_system |
College Management System v1.0 – SQL Injection (SQLi). By inserting SQL commands to the username and password fields in the login.php page. |
2022-11-17 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-39180
MISC |
| college_management_system_project — college_management_system |
College Management System v1.0 – Authenticated remote code execution. An admin user (the authentication can be bypassed using SQL Injection that mentioned in my other report) can upload .php file that contains malicious code via student.php file. |
2022-11-17 |
7.2 |
CVE-2022-39179
MISC |
| concretecms — concrete_cms |
Concrete CMS is vulnerable to CSRF due to the lack of “State” parameter for external Concrete authentication service for users of Concrete who use the “out of the box” core OAuth. |
2022-11-14 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-43693
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| constantcontact — creative_mail |
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) vulnerability in Creative Mail plugin <= 1.5.4 on WordPress. |
2022-11-18 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-40686
CONFIRM |
| constantcontact — creative_mail |
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) vulnerability in Creative Mail plugin <= 1.5.4 on WordPress. |
2022-11-18 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-40687
CONFIRM |
| contec — solarview_compact_firmware |
SolarView Compact 6.00 was discovered to contain a command injection vulnerability via network_test.php |
2022-11-17 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-40881
MISC |
| crm42_project — crm42 |
A vulnerability was found in tholum crm42. It has been rated as critical. This issue affects some unknown processing of the file crm42classclass.user.php of the component Login. The manipulation of the argument user_name leads to sql injection. The attack may be initiated remotely. The exploit has been disclosed to the public and may be used. The identifier VDB-213461 was assigned to this vulnerability. |
2022-11-11 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-3955
N/A
N/A |
| deltaww — diaenergie |
SQL Injection in Handler_CFG.ashx in Delta Electronics DIAEnergie versions prior to v1.9.02.001 allows an attacker to inject SQL queries via Network |
2022-11-17 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-41775
MISC |
| deltaww — diaenergie |
SQL Injection in AM_EBillAnalysis.aspx in Delta Electronics DIAEnergie versions prior to v1.9.02.001 allows an attacker to inject SQL queries via Network |
2022-11-17 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-43447
MISC |
| deltaww — diaenergie |
SQL Injection in FtyInfoSetting.aspx in Delta Electronics DIAEnergie versions prior to v1.9.02.001 allows an attacker to inject SQL queries via Network |
2022-11-17 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-43452
MISC |
| deltaww — diaenergie |
SQL Injection in HandlerPage_KID.ashx in Delta Electronics DIAEnergie versions prior to v1.9.02.001 allows an attacker to inject SQL queries via Network |
2022-11-17 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-43457
MISC |
| deltaww — diaenergie |
SQL Injection in HandlerTag_KID.ashx in Delta Electronics DIAEnergie versions prior to v1.9.02.001 allows an attacker to inject SQL queries via Network |
2022-11-17 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-43506
MISC |
| diffie-hellman_key_exchange_project — diffie-hellman_key_exchange |
Using long exponents in the Diffie-Hellman Key Agreement Protocol allows remote attackers (from the client side) to trigger unnecessarily expensive server-side DHE modular-exponentiation calculations. An attacker may cause asymmetric resource consumption with any common client application which uses a DHE implementation that applies short exponents. The attack may be more disruptive in cases where a client sends arbitrary numbers that are actually not DH public keys (aka the D(HE)ater attack) or can require a server to select its largest supported key size. The basic attack scenario is that the client must claim that it can only communicate with DHE, and the server must be configured to allow DHE. This can affect TLS, SSH, and IKE. |
2022-11-14 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-40735
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| dolibarr — dolibarr_erp/crm |
Dolibarr Open Source ERP & CRM for Business before v14.0.1 allows attackers to escalate privileges via a crafted API. |
2022-11-17 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-43138
MISC |
| dreamer_cms_project — dreamer_cms |
Dreamer CMS 4.0.01 is vulnerable to SQL Injection. |
2022-11-17 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-42245
MISC |
| duofoxtechnologies — duofox_cms |
Doufox 0.0.4 contains a CSRF vulnerability that can add system administrator account. |
2022-11-17 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-42246
MISC |
| eolink — goku_lite |
A vulnerability classified as critical has been found in eolinker goku_lite. This affects an unknown part of the file /balance/service/list. The manipulation of the argument route/keyword leads to sql injection. It is possible to initiate the attack remotely. The exploit has been disclosed to the public and may be used. The identifier VDB-213453 was assigned to this vulnerability. |
2022-11-11 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-3947
N/A
N/A
N/A |
| eolink — goku_lite |
A vulnerability classified as critical was found in eolinker goku_lite. This vulnerability affects unknown code of the file /plugin/getList. The manipulation of the argument route/keyword leads to sql injection. The attack can be initiated remotely. The exploit has been disclosed to the public and may be used. VDB-213454 is the identifier assigned to this vulnerability. |
2022-11-11 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-3948
N/A
N/A
N/A |
| erp_project — erp |
A vulnerability was found in jerryhanjj ERP. It has been declared as critical. Affected by this vulnerability is the function uploadImages of the file application/controllers/basedata/inventory.php of the component Commodity Management. The manipulation leads to unrestricted upload. The attack can be launched remotely. The exploit has been disclosed to the public and may be used. The associated identifier of this vulnerability is VDB-213451. |
2022-11-11 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-3944
N/A
N/A |
| export_users_with_meta_project — export_users_with_meta |
Auth. CSV Injection vulnerability in Export Users With Meta plugin <= 0.6.8 on WordPress. |
2022-11-17 |
8 |
CVE-2022-44577
CONFIRM |
| eyoucms — eyoucms |
EyouCMS V1.5.9-UTF8-SP1 was discovered to contain a Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) via the Top Up Balance component under the Edit Member module. |
2022-11-14 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-43323
MISC |
| eyoucms — eyoucms |
EyouCMS V1.5.9-UTF8-SP1 was discovered to contain a Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) via the Basic Information component under the Edit Member module. |
2022-11-14 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-44387
MISC |
| facebook — redex |
DexLoader function get_stringidx_fromdex() in Redex prior to commit 3b44c64 can load an out of bound address when loading the string index table, potentially allowing remote code execution during processing of a 3rd party Android APK file. |
2022-11-11 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-36938
MISC |
| ferry_project — ferry |
A vulnerability, which was classified as critical, has been found in lanyulei ferry. Affected by this issue is some unknown functionality of the file apis/public/file.go of the component API. The manipulation of the argument file leads to path traversal. The attack may be launched remotely. VDB-213446 is the identifier assigned to this vulnerability. |
2022-11-11 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-3939
N/A |
| ferry_project — ferry |
A vulnerability, which was classified as problematic, was found in lanyulei ferry. This affects an unknown part of the file apis/process/task.go. The manipulation of the argument file_name leads to path traversal. The associated identifier of this vulnerability is VDB-213447. |
2022-11-11 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-3940
N/A |
| ffmpeg — ffmpeg |
A vulnerability classified as problematic has been found in ffmpeg. This affects an unknown part of the file libavcodec/rpzaenc.c of the component QuickTime RPZA Video Encoder. The manipulation of the argument y_size leads to out-of-bounds read. It is possible to initiate the attack remotely. The name of the patch is 92f9b28ed84a77138105475beba16c146bdaf984. It is recommended to apply a patch to fix this issue. The associated identifier of this vulnerability is VDB-213543. |
2022-11-13 |
8.1 |
CVE-2022-3964
N/A
N/A |
| ffmpeg — ffmpeg |
A vulnerability classified as problematic was found in ffmpeg. This vulnerability affects the function smc_encode_stream of the file libavcodec/smcenc.c of the component QuickTime Graphics Video Encoder. The manipulation of the argument y_size leads to out-of-bounds read. The attack can be initiated remotely. The name of the patch is 13c13109759090b7f7182480d075e13b36ed8edd. It is recommended to apply a patch to fix this issue. The identifier of this vulnerability is VDB-213544. |
2022-11-13 |
8.1 |
CVE-2022-3965
N/A
N/A |
| follow_me_plugin_project — follow_me_plugin |
The “Follow Me Plugin” plugin for WordPress is vulnerable to Cross-Site Request Forgery in versions up to, and including, 3.1.1. This is due to missing nonce validation on the FollowMeIgniteSocialMedia_options_page() function. This makes it possible for unauthenticated attackers to modify the plugin’s settings and inject malicious JavaScript via a forged request granted they can trick a site administrator into performing an action such as clicking on a link. |
2022-11-15 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-3240
MISC
MISC |
| freerdp — freerdp |
FreeRDP is a free remote desktop protocol library and clients. Affected versions of FreeRDP are missing input length validation in the `urbdrc` channel. A malicious server can trick a FreeRDP based client to read out of bound data and send it back to the server. This issue has been addressed in version 2.9.0 and all users are advised to upgrade. Users unable to upgrade should not use the `/usb` redirection switch. |
2022-11-16 |
9.1 |
CVE-2022-39319
CONFIRM
MISC |
| freerdp — freerdp |
FreeRDP is a free remote desktop protocol library and clients. Affected versions of FreeRDP are missing input length validation in `drive` channel. A malicious server can trick a FreeRDP based client to read out of bound data and send it back to the server. This issue has been addressed in version 2.9.0 and all users are advised to upgrade. Users unable to upgrade should not use the drive redirection channel – command line options `/drive`, `+drives` or `+home-drive`. |
2022-11-16 |
9.1 |
CVE-2022-41877
CONFIRM
MISC |
| freerdp — freerdp |
FreeRDP is a free remote desktop protocol library and clients. In affected versions there is an out of bound read in ZGFX decoder component of FreeRDP. A malicious server can trick a FreeRDP based client to read out of bound data and try to decode it likely resulting in a crash. This issue has been addressed in the 2.9.0 release. Users are advised to upgrade. |
2022-11-16 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-39316
MISC
CONFIRM |
| freerdp — freerdp |
FreeRDP is a free remote desktop protocol library and clients. Affected versions of FreeRDP are missing input validation in `urbdrc` channel. A malicious server can trick a FreeRDP based client to crash with division by zero. This issue has been addressed in version 2.9.0. All users are advised to upgrade. Users unable to upgrade should not use the `/usb` redirection switch. |
2022-11-16 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-39318
CONFIRM
MISC |
| freerdp — freerdp |
FreeRDP is a free remote desktop protocol library and clients. Affected versions of FreeRDP are missing path canonicalization and base path check for `drive` channel. A malicious server can trick a FreeRDP based client to read files outside the shared directory. This issue has been addressed in version 2.9.0 and all users are advised to upgrade. Users unable to upgrade should not use the `/drive`, `/drives` or `+home-drive` redirection switch. |
2022-11-16 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-39347
CONFIRM
MISC |
| guitar-pro — guitar_pro |
Arobas Music Guitar Pro for iPad and iPhone before v1.10.2 allows attackers to perform directory traversal and download arbitrary files via a crafted web request. |
2022-11-16 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-43264
MISC |
| hashicorp — consul |
HashiCorp Consul and Consul Enterprise 1.13.0 up to 1.13.3 do not filter cluster filtering’s imported nodes and services for HTTP or RPC endpoints used by the UI. Fixed in 1.14.0. |
2022-11-16 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-3920
MISC |
| heimdal_project — heimdal |
Heimdal is an implementation of ASN.1/DER, PKIX, and Kerberos. Versions prior to 7.7.1 are vulnerable to a denial of service vulnerability in Heimdal’s PKI certificate validation library, affecting the KDC (via PKINIT) and kinit (via PKINIT), as well as any third-party applications using Heimdal’s libhx509. Users should upgrade to Heimdal 7.7.1 or 7.8. There are no known workarounds for this issue. |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-41916
CONFIRM |
| hhims_project — hhims |
A vulnerability classified as critical has been found in tsruban HHIMS 2.1. Affected is an unknown function of the component Patient Portrait Handler. The manipulation of the argument PID leads to sql injection. It is possible to launch the attack remotely. It is recommended to apply a patch to fix this issue. VDB-213462 is the identifier assigned to this vulnerability. |
2022-11-11 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-3956
N/A
N/A |
| hms-php_project — hms-php |
A vulnerability was found in Pingkon HMS-PHP. It has been rated as critical. This issue affects some unknown processing of the file admin/adminlogin.php. The manipulation of the argument uname/pass leads to sql injection. The attack may be initiated remotely. The exploit has been disclosed to the public and may be used. The associated identifier of this vulnerability is VDB-213551. |
2022-11-13 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-3972
N/A
N/A |
| hms-php_project — hms-php |
A vulnerability classified as critical has been found in Pingkon HMS-PHP. Affected is an unknown function of the file /admin/admin.php of the component Data Pump Metadata. The manipulation of the argument uname/pass leads to sql injection. It is possible to launch the attack remotely. The exploit has been disclosed to the public and may be used. The identifier of this vulnerability is VDB-213552. |
2022-11-13 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-3973
N/A
N/A |
| hoosk — hoosk |
An arbitrary file upload vulnerability in the /attachments component of Hoosk v1.8 allows attackers to execute arbitrary code via a crafted PHP file. |
2022-11-16 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-43234
MISC |
| hospital_management_center_project — hospital_management_center |
A vulnerability classified as critical has been found in Hospital Management Center. Affected is an unknown function of the file patient-info.php. The manipulation of the argument pt_id leads to sql injection. It is possible to launch the attack remotely. The exploit has been disclosed to the public and may be used. VDB-213786 is the identifier assigned to this vulnerability. |
2022-11-16 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-4012
N/A
N/A |
| hospital_management_center_project — hospital_management_center |
A vulnerability classified as problematic was found in Hospital Management Center. Affected by this vulnerability is an unknown functionality of the file appointment.php. The manipulation leads to cross-site request forgery. The attack can be launched remotely. The exploit has been disclosed to the public and may be used. The associated identifier of this vulnerability is VDB-213787. |
2022-11-16 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-4013
N/A
N/A |
| human_resource_management_system_project — human_resource_management_system |
Human Resource Management System v1.0 was discovered to contain a SQL injection vulnerability via the password parameter at /hrm/controller/login.php. |
2022-11-16 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-43262
MISC |
| hyperledger — fabric |
Hyperledger Fabric 2.3 allows attackers to cause a denial of service (orderer crash) by repeatedly sending a crafted channel tx with the same Channel name. NOTE: the official Fabric with Raft prevents exploitation via a locking mechanism and a check for names that already exist. |
2022-11-12 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-45196
MISC
MISC |
| ibm — cics_tx |
IBM CICS TX 11.7 uses weaker than expected cryptographic algorithms that could allow an attacker to decrypt highly sensitive information. IBM X-Force ID: 229463. |
2022-11-14 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-34319
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| ibm — cics_tx |
IBM CICS TX 11.1 uses weaker than expected cryptographic algorithms that could allow an attacker to decrypt highly sensitive information. IBM X-Force ID: 229464. |
2022-11-14 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-34320
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| ibm — cloud_pak_for_security |
IBM Cloud Pak for Security (CP4S) 1.10.0.0 through 1.10.2.0 could allow a remote authenticated attacker to execute arbitrary commands on the system by sending a specially crafted request. IBM X-Force ID: 233786. |
2022-11-11 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-38387
MISC
MISC |
| ibm — cloud_pak_for_security |
IBM Cloud Pak for Security (CP4S) 1.10.0.0 through 1.10.2.0 could allow an authenticated user to obtain highly sensitive information or perform unauthorized actions due to improper input validation. IBM X-Force ID: 233777. |
2022-11-15 |
8.1 |
CVE-2022-38385
MISC
MISC |
| ibm — infosphere_information_server |
IBM InfoSphere DataStage 11.7 is vulnerable to a command injection vulnerability due to improper neutralization of special elements. IBM X-Force ID: 236687. |
2022-11-16 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-40752
MISC
MISC |
| ibm — powervm_hypervisor |
After performing a sequence of Power FW950, FW1010 maintenance operations a SRIOV network adapter can be improperly configured leading to desired VEPA configuration being disabled. IBM X-Force ID: 229695. |
2022-11-11 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-34331
MISC
MISC |
| ikus-soft — rdiffweb |
Insufficient Session Expiration in GitHub repository ikus060/rdiffweb prior to 2.5.0. |
2022-11-14 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-3362
CONFIRM
MISC |
| insyde — insydeh2o |
DMA transactions which are targeted at input buffers used for the StorageSecurityCommandDxe software SMI handler could cause SMRAM corruption through a TOCTOU attack. DMA transactions which are targeted at input buffers used for the software SMI handler used by the StorageSecurityCommandDxe driver could cause SMRAM corruption. This issue was discovered by Insyde engineering based on the general description provided by |
2022-11-14 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-34325
MISC
MISC |
| insyde — kernel |
DMA transactions which are targeted at input buffers used for the AhciBusDxe software SMI handler could cause SMRAM corruption (a TOCTOU attack). DMA transactions which are targeted at input buffers used for the software SMI handler used by the AhciBusDxe driver could cause SMRAM corruption through a TOCTOU attack. This issue was discovered by Insyde engineering based on the general description provided by Intel’s iSTARE group, Fixed in kernel 5.2: 05.27.23, kernel 5.3: 05.36.23, kernel 5.4: 05.44.23, kernel 5.5: 05.52.23 https://www.insyde.com/security-pledge/SA-2022047 |
2022-11-15 |
7 |
CVE-2022-33905
MISC
MISC |
| insyde — kernel |
DMA transactions which are targeted at input buffers used for the SdHostDriver software SMI handler could cause SMRAM corruption through a TOCTOU attack. DMA transactions which are targeted at input buffers used for the software SMI handler used by the SdHostDriver driver could cause SMRAM corruption through a TOCTOU attack. This issue was discovered by Insyde engineering based on the general description provided by Intel’s iSTARE group. Fixed in kernel 5.2: 05.27.25, kernel 5.3: 05.36.25, kernel 5.4: 05.44.25, kernel 5.5: 05.52.25 https://www.insyde.com/security-pledge/SA-2022050 |
2022-11-15 |
7 |
CVE-2022-33908
MISC
MISC |
| insyde — kernel |
DMA transactions which are targeted at input buffers used for the HddPassword software SMI handler could cause SMRAM corruption through a TOCTOU attack. DMA transactions which are targeted at input buffers used for the software SMI handler used by the HddPassword driver could cause SMRAM corruption through a TOCTOU attack..This issue was discovered by Insyde engineering based on the general description provided by Intel’s iSTARE group. Fixed in kernel Kernel 5.2: 05.27.23, Kernel 5.3: 05.36.23, Kernel 5.4: 05.44.23, Kernel 5.5: 05.52.23 https://www.insyde.com/security-pledge/SA-2022051 |
2022-11-15 |
7 |
CVE-2022-33909
MISC
MISC |
| insyde — kernel |
DMA transactions which are targeted at input buffers used for the NvmExpressLegacy software SMI handler could cause SMRAM corruption through a TOCTOU attack. DMA transactions which are targeted at input buffers used for the software SMI handler used by the NvmExpressLegacy driver could cause SMRAM corruption through a TOCTOU attack. This issue was discovered by Insyde engineering based on the general description provided by Intel’s iSTARE group. This issue was fixed in kernel 5.2: 05.27.25, kernel 5.3: 05.36.25, kernel 5.4: 05.44.25, kernel 5.5: 05.52.25 https://www.insyde.com/security-pledge/SA-2022053 |
2022-11-15 |
7 |
CVE-2022-33983
MISC
MISC |
| insyde — kernel |
DMA transactions which are targeted at input buffers used for the SdMmcDevice software SMI handler could cause SMRAM corruption through a TOCTOU attack. DMA transactions which are targeted at input buffers used for the software SMI handler used by the SdMmcDevice driver could cause SMRAM corruption through a TOCTOU attack. This issue was discovered by Insyde engineering based on the general description provided by Intel’s iSTARE group. This was fixed in kernel 5.2: 05.27.25, kernel 5.3: 05.36.25, kernel 5.4: 05.44.25, kernel 5.5: 05.52.25 https://www.insyde.com/security-pledge/SA-2022054 |
2022-11-15 |
7 |
CVE-2022-33984
MISC
MISC |
| insyde — kernel |
DMA transactions which are targeted at input buffers used for the NvmExpressDxe software SMI handler could cause SMRAM corruption through a TOCTOU attack. DMA transactions which are targeted at input buffers used for the software SMI handler used by the NvmExpressDxe driver could cause SMRAM corruption through a TOCTOU attack. This issue was discovered by Insyde engineering based on the general description provided by Intel’s iSTARE group. This issue was fixed in kernel 5.2: 05.27.25, kernel 5.3: 05.36.25, kernel 5.4: 05.44.25, kernel 5.5: 05.52.25 https://www.insyde.com/security-pledge/SA-2022055 |
2022-11-15 |
7 |
CVE-2022-33985
MISC
MISC |
| intel — active_management_technology |
Improper authentication in firmware for Intel(R) AMT before versions 11.8.93, 11.22.93, 11.12.93, 12.0.92, 14.1.67, 15.0.42, 16.1.25 may allow an unauthenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via network access. |
2022-11-11 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-26845
MISC |
| intel — active_management_technology |
Improper authentication in firmware for Intel(R) AMT before versions 11.8.93, 11.22.93, 11.12.93, 12.0.92, 14.1.67, 15.0.42, 16.1.25 may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via network access. |
2022-11-11 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-29893
MISC |
| intel — active_management_technology |
Null pointer dereference in firmware for Intel(R) AMT before version 11.8.93, 11.22.93, 11.12.93, 12.0.92, 14.1.67, 15.0.42, 16.1.25 may allow an unauthenticated user to potentially enable denial of service via network access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-27497
MISC |
| intel — advanced_link_analyzer |
Uncontrolled search path element in the Intel(R) Advanced Link Analyzer Pro before version 22.2 and Standard edition software before version 22.1.1 STD may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-27638
MISC |
| intel — data_center_manager |
Protection mechanism failure in the Intel(R) DCM software before version 5.0 may allow an unauthenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via adjacent access. |
2022-11-11 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-33942
MISC |
| intel — endpoint_management_assistant |
Cross-site scripting in the Intel(R) EMA software before version 1.8.0 may allow a privileged user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-30297
MISC |
| intel — gametechdev_presentmon |
Uncontrolled search path element in the PresentMon software maintained by Intel(R) before version 1.7.1 may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.3 |
CVE-2022-26086
MISC |
| intel — glorp |
Uncontrolled search path element in the Intel(R) Glorp software may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-30548
MISC |
| intel — hyperscan |
Improper buffer restrictions in the Hyperscan library maintained by Intel(R) all versions downloaded before 04/29/2022 may allow an unauthenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via network access. |
2022-11-11 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-29486
MISC |
| intel — manageability_commander |
Insufficiently protected credentials in software in Intel(R) AMT SDK before version 16.0.4.1, Intel(R) EMA before version 1.7.1 and Intel(R) MC before version 2.3.2 may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via network access. |
2022-11-11 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-26341
MISC |
| intel — nuc7i3dnbe_firmware |
Improper access control in the Intel(R) NUC HDMI Firmware Update Tool for NUC7i3DN, NUC7i5DN and NUC7i7DN before version 1.78.2.0.7 may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-26024
MISC |
| intel — nuc_10_performance_kit_nuc10i7fnhn_firmware |
Improper access control in BIOS firmware for some Intel(R) NUC 10 Performance Kits and Intel(R) NUC 10 Performance Mini PCs before version FNCML357.0053 may allow a privileged user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-36789
MISC |
| intel — nuc_11_compute_element_cm11ebi38w_firmware |
Improper input validation in BIOS firmware for some Intel(R) NUC 11 Compute Elements before version EBTGL357.0065 may allow a privileged user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-38099
MISC |
| intel — nuc_11_pro_kit_nuc11tnhi70z_firmware |
Improper initialization in BIOS firmware for some Intel(R) NUC 11 Pro Kits and Intel(R) NUC 11 Pro Boards before version TNTGL357.0064 may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-37334
MISC |
| intel — nuc_8_rugged_kit_nuc8cchkrn_firmware |
Improper buffer restrictions in BIOS firmware for some Intel(R) NUC Boards, Intel(R) NUC 8 Boards, Intel(R) NUC 8 Rugged Boards and Intel(R) NUC 8 Rugged Kits before version CHAPLCEL.0059 may allow a privileged user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-26124
MISC |
| intel — nuc_kit_nuc5i3myhe_firmware |
Improper authentication in BIOS firmware for some Intel(R) NUC Boards and Intel(R) NUC Kits before version MYi30060 may allow a privileged user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-36370
MISC |
| intel — nuc_kit_nuc5i3ryh_firmware |
Improper authentication in BIOS firmware[A1] for some Intel(R) NUC Kits before version RY0386 may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-37345
MISC |
| intel — nuc_kit_wireless_adapter_driver_installer |
Incorrect default permissions in the installer software for some Intel(r) NUC Kit Wireless Adapter drivers for Windows 10 before version 22.40 may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-36377
MISC |
| intel — nuc_kit_wireless_adapter_driver_installer |
Path traversal in the installer software for some Intel(r) NUC Kit Wireless Adapter drivers for Windows 10 before version 22.40 may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-36400
MISC |
| intel — nuc_kit_wireless_adapter_driver_installer |
Uncontrolled search path in the installer software for some Intel(r) NUC Kit Wireless Adapter drivers for Windows 10 before version 22.40 may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.3 |
CVE-2022-36380
MISC |
| intel — nuc_kit_wireless_adapter_driver_installer |
Unquoted search path in the installer software for some Intel(r) NUC Kit Wireless Adapter drivers for Windows 10 before version 22.40 may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.3 |
CVE-2022-36384
MISC |
| intel — quartus_prime |
Uncontrolled search path element in the Intel(R) Quartus Prime Standard edition software before version 21.1 Patch 0.02std may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-27187
MISC |
| intel — quartus_prime |
XML injection in the Intel(R) Quartus Prime Pro and Standard edition software may allow an unauthenticated user to potentially enable information disclosure via network access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-27233
MISC |
| intel — server_debug_and_provisioning_tool |
Improper authentication in the Intel(R) SDP Tool before version 3.0.0 may allow an unauthenticated user to potentially enable information disclosure via network access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-26508
MISC |
| intel — system_studio |
Uncontrolled search path in the software installer for Intel(R) System Studio for all versions, may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.8 |
CVE-2021-33064
MISC |
| intel — vtune_profiler |
Uncontrolled search path in the Intel(R) VTune(TM) Profiler software before version 2022.2.0 may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.3 |
CVE-2022-26028
MISC |
| intel — xmm_7560_firmware |
Out-of-bounds write in some Intel(R) XMM(TM) 7560 Modem software before version M2_7560_R_01.2146.00 may allow an unauthenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via adjacent access. |
2022-11-11 |
9.6 |
CVE-2022-26513
MISC |
| intel — xmm_7560_firmware |
Incomplete cleanup in some Intel(R) XMM(TM) 7560 Modem software before version M2_7560_R_01.2146.00 may allow a privileged user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via adjacent access. |
2022-11-11 |
8.4 |
CVE-2022-27639
MISC |
| intel — xmm_7560_firmware |
Improper conditions check in some Intel(R) XMM(TM) 7560 Modem software before version M2_7560_R_01.2146.00 may allow a privileged user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2022-11-11 |
8.2 |
CVE-2022-26079
MISC |
| intel — xmm_7560_firmware |
Improper buffer restrictions in some Intel(R) XMM(TM) 7560 Modem software before version M2_7560_R_01.2146.00 may allow a privileged user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2022-11-11 |
8.2 |
CVE-2022-26367
MISC |
| intel — xmm_7560_firmware |
Improper input validation in some Intel(R) XMM(TM) 7560 Modem software before version M2_7560_R_01.2146.00 may allow a privileged user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. |
2022-11-11 |
8.2 |
CVE-2022-28126
MISC |
| intel — xmm_7560_firmware |
Out-of-bounds read in some Intel(R) XMM(TM) 7560 Modem software before version M2_7560_R_01.2146.00 may allow a privileged user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via adjacent access. |
2022-11-11 |
8.1 |
CVE-2022-26369
MISC |
| intel — xmm_7560_firmware |
Improper buffer restrictions in some Intel(R) XMM(TM) 7560 Modem software before version M2_7560_R_01.2146.00 may allow a privileged user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via physical access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.2 |
CVE-2022-26045
MISC |
| intel — xmm_7560_firmware |
Improper authentication in some Intel(R) XMM(TM) 7560 Modem software before version M2_7560_R_01.2146.00 may allow a privileged user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via physical access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.2 |
CVE-2022-27874
MISC |
| intel — xmm_7560_firmware |
Improper input validation in some Intel(R) XMM(TM) 7560 Modem software before version M2_7560_R_01.2146.00 may allow a privileged user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via physical access. |
2022-11-11 |
7.2 |
CVE-2022-28611
MISC |
| ironmansoftware — powershell_universal |
Escalation of privileges in the Web Server in Ironman Software PowerShell Universal 2.x and 3.x allows an attacker with a valid app token to retrieve other app tokens by ID via an HTTP web request. Patched Versions are 3.5.3, 3.4.7, and 2.12.6. |
2022-11-14 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-45183
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
| ironmansoftware — powershell_universal |
The Web Server in Ironman Software PowerShell Universal v3.x and v2.x allows for directory traversal outside of the configuration directory, which allows a remote attacker with administrator privilege to create, delete, update, and display files outside of the configuration directory via a crafted HTTP request to particular endpoints in the web server. Patched Versions are 3.5.3 and 3.4.7. |
2022-11-14 |
7.2 |
CVE-2022-45184
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC |
| jenkins — cccc |
Jenkins CCCC Plugin 0.6 and earlier does not configure its XML parser to prevent XML external entity (XXE) attacks. |
2022-11-15 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-45395
CONFIRM |
| jenkins — cloudbees_docker_hub/registry_notification |
A missing permission check in Jenkins CloudBees Docker Hub/Registry Notification Plugin 2.6.2 and earlier allows unauthenticated attackers to trigger builds of jobs corresponding to the attacker-specified repository. |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-45385
CONFIRM |
| jenkins — config_rotator |
Jenkins Config Rotator Plugin 2.0.1 and earlier does not restrict a file name query parameter in an HTTP endpoint, allowing unauthenticated attackers to read arbitrary files with ‘.xml’ extension on the Jenkins controller file system. |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-45388
CONFIRM |
| jenkins — japex |
Jenkins JAPEX Plugin 1.7 and earlier does not configure its XML parser to prevent XML external entity (XXE) attacks. |
2022-11-15 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-45400
CONFIRM |
| jenkins — ns-nd_integration_performance_publisher |
Jenkins NS-ND Integration Performance Publisher Plugin 4.8.0.146 and earlier unconditionally disables SSL/TLS certificate and hostname validation for several features. |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-38666
CONFIRM |
| jenkins — ns-nd_integration_performance_publisher |
Jenkins NS-ND Integration Performance Publisher Plugin 4.8.0.143 and earlier globally and unconditionally disables SSL/TLS certificate and hostname validation for the entire Jenkins controller JVM. |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-45391
CONFIRM |
| jenkins — osf_builder_suite_ |
Jenkins OSF Builder Suite : : XML Linter Plugin 1.0.2 and earlier does not configure its XML parser to prevent XML external entity (XXE) attacks. |
2022-11-15 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-45397
CONFIRM |
| jenkins — pipeline_utility_steps |
Jenkins Pipeline Utility Steps Plugin 2.13.1 and earlier does not restrict the set of enabled prefix interpolators and bundles versions of Apache Commons Configuration library that enable the ‘file:’ prefix interpolator by default, allowing attackers able to configure Pipelines to read arbitrary files from the Jenkins controller file system. |
2022-11-15 |
9.1 |
CVE-2022-45381
CONFIRM |
| jenkins — script_security |
Jenkins Script Security Plugin 1189.vb_a_b_7c8fd5fde and earlier stores whole-script approvals as the SHA-1 hash of the script, making it vulnerable to collision attacks. |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-45379
CONFIRM |
| jenkins — sourcemonitor |
Jenkins SourceMonitor Plugin 0.2 and earlier does not configure its XML parser to prevent XML external entity (XXE) attacks. |
2022-11-15 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-45396
CONFIRM |
| joinmastodon — mastodon |
Improper Restriction of Excessive Authentication Attempts in GitHub repository mastodon/mastodon prior to 4.0.0. |
2022-11-16 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-2166
CONFIRM
MISC |
| kavitareader — kavita |
Authentication Bypass by Primary Weakness in GitHub repository kareadita/kavita prior to 0.6.0.3. |
2022-11-14 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-3993
CONFIRM
MISC |
| keking — kkfileview |
kkFileView v4.1.0 was discovered to contain a Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) via the component cn.keking.web.controller.OnlinePreviewController#getCorsFile. This vulnerability allows attackers to force the application to make arbitrary requests via injection of crafted URLs into the url parameter. |
2022-11-17 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-43140
MISC |
| konker — konker_platform |
Konker v2.3.9 was to discovered to contain a Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF). |
2022-11-15 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-35613
MISC |
| libtiff — libtiff |
A vulnerability was found in LibTIFF. It has been classified as critical. This affects the function TIFFReadRGBATileExt of the file libtiff/tif_getimage.c. The manipulation leads to integer overflow. It is possible to initiate the attack remotely. The exploit has been disclosed to the public and may be used. The name of the patch is 227500897dfb07fb7d27f7aa570050e62617e3be. It is recommended to apply a patch to fix this issue. The identifier VDB-213549 was assigned to this vulnerability. |
2022-11-13 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-3970
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A |
| liferay — digital_experience_platform |
A Zip slip vulnerability in the Elasticsearch Connector in Liferay Portal 7.3.3 through 7.4.3.18, and Liferay DXP 7.3 before update 6, and 7.4 before update 19 allows attackers to create or overwrite existing files on the filesystem via the installation of a malicious Elasticsearch Sidecar plugin. |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-42123
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| liferay — digital_experience_platform |
ReDoS vulnerability in LayoutPageTemplateEntryUpgradeProcess in Liferay Portal 7.3.2 through 7.4.3.4 and Liferay DXP 7.2 fix pack 9 through fix pack 18, 7.3 before update 4, and DXP 7.4 GA allows remote attackers to consume an excessive amount of server resources via a crafted payload injected into the ‘name’ field of a layout prototype. |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-42124
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| liferay — digital_experience_platform |
Zip slip vulnerability in FileUtil.unzip in Liferay Portal 7.4.3.5 through 7.4.3.35 and Liferay DXP 7.4 update 1 through update 34 allows attackers to create or overwrite existing files on the filesystem via the deployment of a malicious plugin/module. |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-42125
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| liferay — dxp |
A SQL injection vulnerability in the Fragment module in Liferay Portal 7.3.3 through 7.4.3.16, and Liferay DXP 7.3 before update 4, and 7.4 before update 17 allows attackers to execute arbitrary SQL commands via a PortletPreferences’ `namespace` attribute. |
2022-11-15 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-42120
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| liferay — liferay_portal |
A SQL injection vulnerability in the Friendly Url module in Liferay Portal 7.3.7, and Liferay DXP 7.3 fix pack 2 through update 4 allows attackers to execute arbitrary SQL commands via a crafted payload injected into the `title` field of a friendly URL. |
2022-11-15 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-42122
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| liferay — liferay_portal |
A SQL injection vulnerability in the Layout module in Liferay Portal 7.1.3 through 7.4.3.4, and Liferay DXP 7.1 before fix pack 27, 7.2 before fix pack 17, 7.3 before service pack 3, and 7.4 GA allows remote authenticated attackers to execute arbitrary SQL commands via a crafted payload injected into a page template’s ‘Name’ field. |
2022-11-15 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-42121
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| limesurvey — limesurvey |
LimeSurvey v5.4.4 was discovered to contain a SQL injection vulnerability via the component /application/views/themeOptions/update.php. |
2022-11-15 |
7.2 |
CVE-2022-43279
MISC |
| linux — linux_kernel |
A double-free flaw was found in the Linux kernel’s NTFS3 subsystem in how a user triggers remount and umount simultaneously. This flaw allows a local user to crash or potentially escalate their privileges on the system. |
2022-11-14 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-3238
MISC |
| linuxfoundation — software_for_open_networking_in_the_cloud |
There is a vulnerability in DHCPv6 packet parsing code that could be explored by remote attacker to craft a packet that could cause buffer overflow in a memcpy call, leading to out-of-bounds memory write that would cause dhcp6relay to crash. Dhcp6relay is a critical process and could cause dhcp relay docker to shutdown. Discovered by Eugene Lim of GovTech Singapore. |
2022-11-14 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-0324
MISC
MISC |
| manydesigns — portofino |
A vulnerability has been found in ManyDesigns Portofino 5.3.2 and classified as problematic. Affected by this vulnerability is the function createTempDir of the file WarFileLauncher.java. The manipulation leads to creation of temporary file in directory with insecure permissions. Upgrading to version 5.3.3 is able to address this issue. The name of the patch is 94653cb357806c9cf24d8d294e6afea33f8f0775. It is recommended to upgrade the affected component. The identifier VDB-213457 was assigned to this vulnerability. |
2022-11-11 |
7.1 |
CVE-2022-3952
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A |
| muffingroup — betheme |
Auth. (subscriber+) PHP Object Injection vulnerability in Betheme theme <= 26.5.1.4 on WordPress. |
2022-11-17 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-45077
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| mz-automation — libiec61850 |
A vulnerability has been found in MZ Automation libiec61850 up to 1.4 and classified as critical. This vulnerability affects unknown code of the file src/mms/iso_mms/client/mms_client_files.c of the component MMS File Services. The manipulation of the argument filename leads to path traversal. Upgrading to version 1.5 is able to address this issue. The name of the patch is 10622ba36bb3910c151348f1569f039ecdd8786f. It is recommended to upgrade the affected component. The identifier of this vulnerability is VDB-213556. |
2022-11-13 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-3976
N/A
N/A
N/A |
| nagvis — nagvis |
A vulnerability was found in NagVis up to 1.9.33 and classified as problematic. This issue affects the function checkAuthCookie of the file share/server/core/classes/CoreLogonMultisite.php. The manipulation of the argument hash leads to incorrect type conversion. The attack may be initiated remotely. Upgrading to version 1.9.34 is able to address this issue. The name of the patch is 7574fd8a2903282c2e0d1feef5c4876763db21d5. It is recommended to upgrade the affected component. The identifier VDB-213557 was assigned to this vulnerability. |
2022-11-13 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-3979
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| netatalk_project — netatalk |
Netatalk through 3.1.13 has an afp_getappl heap-based buffer overflow resulting in code execution via a crafted .appl file. This provides remote root access on some platforms such as FreeBSD (used for TrueNAS). |
2022-11-12 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-45188
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| nextcloud — desktop |
The Nextcloud Desktop Client is a tool to synchronize files from Nextcloud Server with your computer. In version 3.6.0, if a user received a malicious file share and has it synced locally or the virtual filesystem enabled and clicked a nc://open/ link it will open the default editor for the file type of the shared file, which on Windows can also sometimes mean that a file depending on the type, e.g. “vbs”, is being executed. It is recommended that the Nextcloud Desktop client is upgraded to version 3.6.1. As a workaround, users can block the Nextcloud Desktop client 3.6.0 by setting the `minimum.supported.desktop.version` system config to `3.6.1` on the server, so new files designed to use this attack vector are not downloaded anymore. Already existing files can still be used. Another workaround would be to enforce shares to be accepted by setting the `sharing.force_share_accept` system config to `true` on the server, so new files designed to use this attack vector are not downloaded anymore. Already existing shares can still be abused. |
2022-11-11 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-41882
MISC
CONFIRM
MISC
MISC |
| online_diagnostic_lab_management_system_project — online_diagnostic_lab_management_system |
Online Diagnostic Lab Management System v1.0 was discovered to contain a SQL injection vulnerability via the username parameter at /diagnostic/login.php. |
2022-11-16 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-43135
MISC |
| online_diagnostic_lab_management_system_project — online_diagnostic_lab_management_system |
Online Diagnostic Lab Management System v1.0 was discovered to contain a SQL injection vulnerability via the id parameter at /tests/view_test.php. |
2022-11-17 |
7.2 |
CVE-2022-43162
MISC |
| online_diagnostic_lab_management_system_project — online_diagnostic_lab_management_system |
Online Diagnostic Lab Management System v1.0 was discovered to contain a SQL injection vulnerability via the id parameter at /clients/view_client.php. |
2022-11-17 |
7.2 |
CVE-2022-43163
MISC |
| online_leave_management_system_project — online_leave_management_system |
Online Leave Management System v1.0 was discovered to contain a SQL injection vulnerability via the component /admin/?page=user/manage_user&id=. |
2022-11-17 |
7.2 |
CVE-2022-43179
MISC |
| palantir — foundry_build2 |
Information Exposure Through Log Files vulnerability discovered in Foundry when logs were captured using an underlying library known as Build2. This issue was present in versions earlier than 1.785.0. Upgrade to Build2 version 1.785.0 or greater. |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-27895
MISC |
| palantir — foundry_code-workbooks |
Information Exposure Through Log Files vulnerability discovered in Foundry Code-Workbooks where the endpoint backing that console was generating service log records of any Python code being run. These service logs included the Foundry token that represents the Code-Workbooks Python console. Upgrade to Code-Workbooks version 4.461.0. This issue affects Palantir Foundry Code-Workbooks version 4.144 to version 4.460.0 and is resolved in 4.461.0. |
2022-11-14 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-27896
MISC |
| phoenixcontact — automationworx_software_suite |
In PHOENIX CONTACT Automationworx Software Suite up to version 1.89 manipulated PC Worx or Config+ files could lead to a heap buffer overflow and a read access violation. Availability, integrity, or confidentiality of an application programming workstation might be compromised by attacks using these vulnerabilities. |
2022-11-15 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-3461
MISC |
| phoenixcontact — automationworx_software_suite |
In PHOENIX CONTACT Automationworx Software Suite up to version 1.89 memory can be read beyond the intended scope due to insufficient validation of input data. Availability, integrity, or confidentiality of an application programming workstation might be compromised by attacks using these vulnerabilities. |
2022-11-15 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-3737
MISC |
| phoenixcontact — fl_mguard_centerport_firmware |
A remote, unauthenticated attacker could cause a denial-of-service of PHOENIX CONTACT FL MGUARD and TC MGUARD devices below version 8.9.0 by sending a larger number of unauthenticated HTTPS connections originating from different source IP’s. Configuring firewall limits for incoming connections cannot prevent the issue. |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-3480
MISC |
| php — php |
In PHP versions prior to 7.4.33, 8.0.25 and 8.2.12, when using imageloadfont() function in gd extension, it is possible to supply a specially crafted font file, such as if the loaded font is used with imagechar() function, the read outside allocated buffer will be used. This can lead to crashes or disclosure of confidential information. |
2022-11-14 |
7.1 |
CVE-2022-31630
MISC |
| pistar — pi-star_digital_voice_dashboard |
Pi-Star_DV_Dash (for Pi-Star DV) before 5aa194d mishandles the module parameter. |
2022-11-11 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-45182
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| python — pillow |
Pillow before 9.2.0 performs Improper Handling of Highly Compressed GIF Data (Data Amplification). |
2022-11-14 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-45198
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| python — pillow |
Pillow before 9.3.0 allows denial of service via SAMPLESPERPIXEL. |
2022-11-14 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-45199
MISC
MISC
MISC
MISC |
| qualcomm — apq8009_firmware |
Memory corruption in graphics due to buffer overflow while validating the user address in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wearables |
2022-11-15 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-25724
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — apq8009_firmware |
Memory corruption in graphics due to use-after-free while importing graphics buffer in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wearables |
2022-11-15 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-25743
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — apq8009_firmware |
Denial of service due to null pointer dereference when GATT is disconnected in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-25710
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — apq8009_firmware |
Transient DOS due to loop with unreachable exit condition in WLAN firmware while parsing IPV6 extension header. in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer Electronics Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wearables, Snapdragon Wired Infrastructure and Networking |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-33239
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — aqt1000_firmware |
Memory corruption in video due to configuration weakness. in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Wearables |
2022-11-15 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-33234
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — aqt1000_firmware |
Denial of service in WLAN due to potential null pointer dereference while accessing the memory location in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Wearables |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-25741
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — aqt1000_firmware |
Transient DOS due to buffer over-read in WLAN firmware while processing PPE threshold. in Snapdragon Auto, Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer Electronics Connectivity, Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Voice & Music, Snapdragon Wearables, Snapdragon Wired Infrastructure and Networking |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-33237
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — ar8031_firmware |
Cryptographic issues in WLAN during the group key handshake of the WPA/WPA2 protocol in Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Voice & Music |
2022-11-15 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-25674
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — ar8031_firmware |
Memory Corruption in modem due to improper length check while copying into memory in Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Voice & Music |
2022-11-15 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-25727
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — ar8031_firmware |
Denial of service in modem due to infinite loop while parsing IGMPv2 packet from server in Snapdragon Consumer IOT, Snapdragon Industrial IOT, Snapdragon Voice & Music |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-25742
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — ar8035_firmware |
Denial of service in MODEM due to reachable assertion in Snapdragon Mobile |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-25671
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — ar8035_firmware |
Transient DOS due to buffer over-read in WLAN firmware while parsing cipher suite info attributes. in Snapdragon Compute, Snapdragon Connectivity, Snapdragon Mobile, Snapdragon Wired Infrastructure and Networking |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-33236
CONFIRM |
| qualcomm — ar9380_firmware |
Information disclosure in kernel due to improper handling of ICMP requests in Snapdragon Wired Infrastructure and Networking |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-25667
CONFIRM |
| rconfig — rconfig |
An arbitrary file upload vulnerability in rconfig v3.9.6 allows attackers to execute arbitrary code via a crafted PHP file. |
2022-11-17 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-44384
MISC |
| rukovoditel — rukovoditel |
Rukovoditel v3.2.1 was discovered to contain a SQL injection vulnerability via the order_by parameter at /rukovoditel/index.php?module=logs/view&type=php. |
2022-11-14 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-43288
MISC |
| seacms — seacms |
SeaCms before v12.6 was discovered to contain a SQL injection vulnerability via the component /js/player/dmplayer/dmku/index.php. |
2022-11-16 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-43256
MISC |
| silabs — emberznet |
Improper Restriction of Operations within the Bounds of a Memory Buffer vulnerability in Silicon Labs Ember ZNet allows Overflow Buffers. |
2022-11-14 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-24937
MISC
MISC |
| silabs — emberznet |
A malformed packet causes a stack overflow in the Ember ZNet stack. This causes an assert which leads to a reset, immediately clearing the error. |
2022-11-14 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-24938
MISC
MISC |
| simple_history_project — simple_history |
A vulnerability was found in Simple History Plugin. It has been rated as critical. This issue affects some unknown processing of the component Header Handler. The manipulation of the argument X-Forwarded-For leads to improper output neutralization for logs. The attack may be initiated remotely. The exploit has been disclosed to the public and may be used. The identifier VDB-213785 was assigned to this vulnerability. |
2022-11-16 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-4011
N/A
N/A
N/A |
| simple_image_gallery_web_app_project — simple_image_gallery_web_app |
A SQL injection vulnerability exits on the Simple Image Gallery System 1.0 application through “id” parameter on the album page. |
2022-11-17 |
8.8 |
CVE-2021-38819
MISC |
| siyucms — siyucms |
Siyucms v6.1.7 was discovered to contain a remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability in the background. SIYUCMS is a content management system based on ThinkPaP5 AdminLTE. SIYUCMS has a background command execution vulnerability, which can be used by attackers to gain server privileges |
2022-11-14 |
7.2 |
CVE-2022-43030
MISC
MISC |
| sophos — mobile |
An XML External Entity (XEE) vulnerability allows server-side request forgery (SSRF) and potential code execution in Sophos Mobile managed on-premises between versions 5.0.0 and 9.7.4. |
2022-11-16 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-3980
CONFIRM |
| sports_club_management_system_project — sports_club_management_system |
A vulnerability, which was classified as critical, was found in Sports Club Management System 119. This affects an unknown part of the file admin/make_payments.php. The manipulation of the argument m_id/plan leads to sql injection. It is possible to initiate the attack remotely. The exploit has been disclosed to the public and may be used. The identifier VDB-213789 was assigned to this vulnerability. |
2022-11-16 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-4015
N/A
N/A |
| student_attendance_management_system_project — student_attendance_management_system |
A vulnerability was found in Student Attendance Management System and classified as critical. This issue affects some unknown processing of the file /Admin/createClass.php. The manipulation of the argument Id leads to sql injection. The attack may be initiated remotely. The exploit has been disclosed to the public and may be used. The identifier VDB-213845 was assigned to this vulnerability. |
2022-11-17 |
7.2 |
CVE-2022-4052
MISC
MISC |
| tagdiv_composer_project — tagdiv_composer |
The tagDiv Composer WordPress plugin before 3.5, required by the Newspaper WordPress theme before 12.1 and Newsmag WordPress theme before 5.2.2, does not properly implement the Facebook login feature, allowing unauthenticated attackers to login as any user by just knowing their email address |
2022-11-14 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-3477
CONFIRM |
| tasmota_project — tasmota |
Tasmota before commit 066878da4d4762a9b6cb169fdf353e804d735cfd was discovered to contain a stack overflow via the ClientPortPtr parameter at lib/libesp32/rtsp/CRtspSession.cpp. |
2022-11-14 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-43294
MISC
MISC |
| tenda — ac1200_v-w15ev2_firmware |
Tenda AC1200 Router Model W15Ev2 V15.11.0.10(1576) was discovered to contain a stack overflow via the setRemoteWebManage function. This vulnerability allows attackers to cause a Denial of Service (DoS) via crafted overflow data. |
2022-11-15 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-42058
MISC |
| tenda — ac1200_v-w15ev2_firmware |
In Tenda AC1200 Router model W15Ev2 V15.11.0.10(1576), there exists a command injection vulnerability in the function formSetFixTools. This vulnerability allows attackers to run arbitrary commands on the server via the hostname parameter. |
2022-11-15 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-40847
MISC |
| tenda — ac1200_v-w15ev2_firmware |
Tenda AC1200 Router Model W15Ev2 V15.11.0.10(1576) was discovered to contain a command injection vulnerability via the dmzHost parameter in the setDMZ function. |
2022-11-15 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-41395
MISC |
| tenda — ac1200_v-w15ev2_firmware |
Tenda AC1200 Router Model W15Ev2 V15.11.0.10(1576) was discovered to contain multiple command injection vulnerabilities in the function setIPsecTunnelList via the IPsecLocalNet and IPsecRemoteNet parameters. |
2022-11-15 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-41396
MISC |
| tenda — ac1200_v-w15ev2_firmware |
Tenda AC1200 Router Model W15Ev2 V15.11.0.10(1576) was discovered to contain a command injection vulnerability via the PortMappingServer parameter in the setPortMapping function. |
2022-11-15 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-42053
MISC |
| tenda — ac1200_v-w15ev2_firmware |
Tenda AC1200 Router Model W15Ev2 V15.11.0.10(1576) was discovered to contain a stack overflow via the setWanPpoe function. This vulnerability allows attackers to cause a Denial of Service (DoS) via crafted overflow data. |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-42060
MISC |
| thriveweb — wooswipe_woocommerce_gallery |
Auth. (subscriber+) Broken Access Control vulnerability in WooSwipe WooCommerce Gallery plugin <= 2.0.1 on WordPress. |
2022-11-17 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-45066
CONFIRM |
| ultimatemember — ultimate_member |
A vulnerability, which was classified as critical, has been found in Ultimate Member Plugin up to 2.5.0. This issue affects the function load_template of the file includes/core/class-shortcodes.php of the component Template Handler. The manipulation of the argument tpl leads to pathname traversal. The attack may be initiated remotely. Upgrading to version 2.5.1 is able to address this issue. The name of the patch is e1bc94c1100f02a129721ba4be5fbc44c3d78ec4. It is recommended to upgrade the affected component. The identifier VDB-213545 was assigned to this vulnerability. |
2022-11-13 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-3966
N/A
N/A
N/A |
| vestacp — control_panel |
A vulnerability, which was classified as critical, was found in Vesta Control Panel. Affected is an unknown function of the file func/main.sh of the component sed Handler. The manipulation leads to argument injection. An attack has to be approached locally. The name of the patch is 39561c32c12cabe563de48cc96eccb9e2c655e25. It is recommended to apply a patch to fix this issue. VDB-213546 is the identifier assigned to this vulnerability. |
2022-11-13 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-3967
N/A
N/A |
| wbce — wbce_cms |
A vulnerability, which was classified as problematic, has been found in WBCE CMS. Affected by this issue is the function increase_attempts of the file wbce/framework/class.login.php of the component Header Handler. The manipulation of the argument X-Forwarded-For leads to improper restriction of excessive authentication attempts. The attack may be launched remotely. The name of the patch is d394ba39a7bfeb31eda797b6195fd90ef74b2e75. It is recommended to apply a patch to fix this issue. The identifier of this vulnerability is VDB-213716. |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-4006
MISC
MISC
MISC |
wiesemann_&_theis — multiple_products
|
Multiple W&T products of the ComServer Series are prone to an authentication bypass. An unathenticated remote attacker, can log in without knowledge of the password by crafting a modified HTTP GET Request. |
2022-11-15 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-42785
MISC |
| wordplus — better_messages |
Auth. (subscriber+) Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) vulnerability in Better Messages plugin 1.9.10.68 on WordPress. |
2022-11-19 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-41609
CONFIRM
CONFIRM |
| wowonder — wowonder |
WoWonder Social Network Platform 4.1.4 was discovered to contain a SQL injection vulnerability via the offset parameter at requests.php?f=search&s=recipients. |
2022-11-15 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-42984
MISC
MISC |
| wowonder — wowonder |
WoWonder Social Network Platform v4.1.2 was discovered to contain a SQL injection vulnerability via the offset parameter at requests.php?f=load-my-blogs. |
2022-11-15 |
7.5 |
CVE-2022-40405
MISC |
| wpforms — wpforms_pro |
The WPForms Pro WordPress plugin before 1.7.7 does not validate its form data when generating the exported CSV, which could lead to CSV injection. |
2022-11-14 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-3574
CONFIRM |
| xiongmaitech — xm-jpr2-lx_firmware |
Xiongmai Camera XM-JPR2-LX V4.02.R12.A6420987.10002.147502.00000 is vulnerable to account takeover. |
2022-11-14 |
7.5 |
CVE-2021-38827
MISC |
| xuxueli — xxl-job |
XXL-Job before v2.3.1 contains a Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) via the component /admin/controller/JobLogController.java. |
2022-11-17 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-43183
MISC |
| zohocorp — manageengine_access_manager_plus |
Zoho ManageEngine Password Manager Pro before 12122, PAM360 before 5711, and Access Manager Plus before 4306 allow SQL Injection. |
2022-11-12 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-43671
MISC |
| zohocorp — manageengine_access_manager_plus |
Zoho ManageEngine Password Manager Pro before 12122, PAM360 before 5711, and Access Manager Plus before 4306 allow SQL Injection (in a different software component relative to CVE-2022-43671. |
2022-11-12 |
9.8 |
CVE-2022-43672
MISC |
| zohocorp — manageengine_mobile_device_manager_plus |
In Zoho ManageEngine Mobile Device Manager Plus before 10.1.2207.5, the User Administration module allows privilege escalation. |
2022-11-12 |
7.8 |
CVE-2022-41339
MISC |
| zohocorp — manageengine_supportcenter_plus |
Zoho ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus MSP before 10609 and SupportCenter Plus before 11025 are vulnerable to privilege escalation. This allows users to obtain sensitive data during an exportMickeyList export of requests from the list view. |
2022-11-12 |
8.8 |
CVE-2022-40773
MISC
MISC |
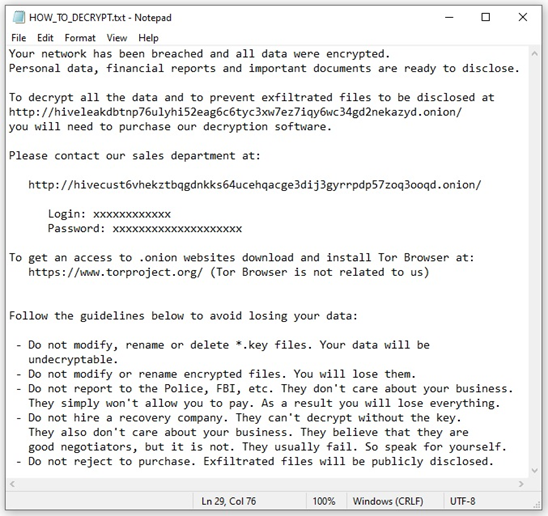

Recent Comments