This article is contributed. See the original author and article here.
There are a variety of scenarios including but not limited to, installations of Office using Content Delivery Network (CDN), lean 2nd installs (removing the Office source files from the install packages), right-sized first install (only include most used language packs), and default behavior where Office stays up to date using CDN. Microsoft recommends optimizing these network operations because a device can get portions of the content from other devices on its local network instead of having to download the update completely from Microsoft CDN. The goal of this article is to provide solutions for challenges collected from customers in the field.
Typical challenges we’ve heard from our customers
- Office updates are too large.
- Too many egress points within on-premises network when obtaining content.
- In a remote work world, we need a solution to address on-premises and remote users.
- Are there additional costs for this optimization? (Spoiler…NO!)
- Fear of increased complexity for office installs and updates.
- Can my compliance deadlines still be met?
Solution: Use Windows Delivery Optimization (DO) or if available, Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager Connected Cache
All of these above concerns can be addressed with this proposed solution. You can use Delivery Optimization (DO) to reduce bandwidth consumption by sharing the work of downloading Office content among multiple Windows 10 devices in your deployment. DO can accomplish this because it is a self-organizing distributed cache that allows clients to download content from alternate sources (such as other peers on the network). Delivery Optimization is a cloud-managed solution. Access to the Delivery Optimization cloud services is a requirement. This means that to use the peer-to-peer functionality of DO, devices must have access to the DO cloud service end points.
Optionally, customers who use Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager can take advantage of a feature called Configuration Manager Connected Cache which delivers a powerful combination of DO plus Connected Cache leading to high hit rates for content searches. If the cache doesn’t contain necessary files, Configuration Manager Site Server will download content to Distribution Point to populate cache, based on the client needs. In this way, customers have far more flexibility in terms of supporting different architectures and languages as manual downloads are no longer required as they’ve been replaced by a dynamic workflow as well as making use of existing capital investments.
Prerequisites for solution
- At least Office Version 1808 for background updates
- At least Office Version 1908 for installing or user-initiated updates
- Windows 10 Delivery Optimization
-
For communication between clients and the Delivery Optimization cloud service:
*.do.dsp.mp.microsoft.com.
*.dl.delivery.mp.microsoft.com
*.emdl.ws.microsoft.comDelivery Optimization listens on port 7680 for requests from other peers by using TCP/IP. The service will register and open this port on the device, but you might need to set this port to accept inbound traffic through your firewall yourself. If you don’t allow inbound traffic over port 7680, you can’t use the peer-to-peer functionality of Delivery Optimization. However, devices can still successfully download by using HTTP or HTTPS traffic over port 80 (such as for default Windows Update data).
-
If you set up Delivery Optimization to create peer groups that include devices across NATs (or any form of internal subnet that uses gateways or firewalls between subnets), it will use Teredo. For this to work, you must allow inbound TCP/IP traffic over port 3544. Look for a “NAT traversal” setting in your firewall to set this up.
Delivery Optimization also communicates with its cloud service by using HTTP/HTTPS over port 80.
-
Recommended (if existing Configuration Manager customer, use Microsoft Connected Cache combined with Delivery Optimization)
-
Implementation steps.
1. Operationally, stop any future software updates for Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise using Configuration Manager
Group Policy or Configuration Manager Client Settings require setting “Management of Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise” (formerly known as Office 365 Client Management) to Disabled in order to restore default functionality where software update workflow for Office updates uses CDN not Configuration Manager. When available, Connected Cache feature will be enabled but software updates workflow for Office using Configuration Manager will no longer be used.
2. Configure Group Policy for Microsoft Office 2016 (Machine)/Updates
| Enable Automatic Updates | Enabled |
| Hide option to enable or disable updates | Enabled |
| Management of Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise | Disabled |
| Update Deadline | 3 (Deadline count starts once content download has completed on client) |
3. Configure Group Policy for Microsoft Office 2016 (Machine)/Updates
| Allow uploads while the device is on battery while under set Battery level (Percentage) | Enabled (60) |
| Delay background download from http (in secs) | Enabled *Higher time will increase likelihood of finding peer but slow background update. Example (240) |
| Delay foreground download from http (in secs) | Enabled (60) |
| Download Mode | Enabled (Group 2) |
| Enable Peer Caching while the device connects via VPN | Disabled |
| Minimum Peer Caching Content File Size (in MB) | Enabled (1) |
| Select a method to restrict Peer Selection | Enabled (subnet) |
| Set Business Hours to Limit Background Download Bandwidth | Enabled |
4. (optionally) Configure Connected Cache for Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager
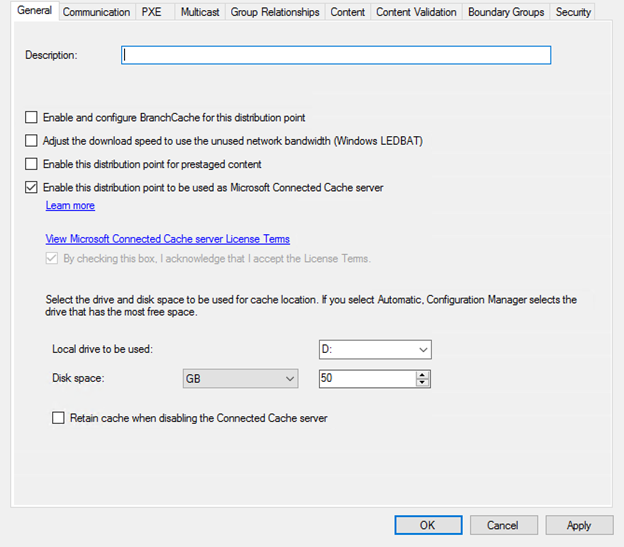
Navigate using Configuration Manger Console to AdministrationOverviewDistribution Points and select properties of Distribution Point. Enable Connected Cache by checking box and designate LUN to host cached content.
Navigate using Configuration Manger Console to panel AdministrationOverviewHierarchy ConfigurationBoundary Groups. Select each on-premises boundary group and enable selection highlighted below. (toggle on other selections based on your environment preferences)
Finally, using Configuration Manger Console Navigate to AdministrationOverviewClient Settings, enable options below.
How to verify DO and Connected Cache are working?
1. Deploy Office to validation machine where per Update history for Microsoft 365 Apps (listed by date) build is N-2.
For example, at the time of this writing, today is “Patch Tuesday” so August 2020 Monthly Enterprise Channel is Version 2006 (Build 13001.20520). The reference machine should have June 2020 Version 2004 (Build 12730.20430) installed. This should result in Office moving to N-1 or N (depending on CDN throttle).
2. Allow up for 24 hours for scheduled task Office Automatic Updates 2.0 to detect and perform Office update.
For accelerated lab testing consider moving system clock forward by one day prior to running scheduled task.
3. [Client] Use PowerShell on Windows client to verify Office content used DO and Conncted Cache.
-
PS C:Windowssystem32> Get-DeliveryOptimizationStatus
- Search for field FileID from the list which contains string STREAM_X64_X_NONE or STREAM_X86_X_NONE for details which contains the build. (this is largest file containing Office). For the test, your looking for FileId is 95D2EE60-C9D3-45E4-876D-BAE16D758A87_16_0_13001_20520_STREAM_X64_X_NONE.
- Search for fields under FileID such as FileSize, TotalBytesDownloaded, BytesFromPeers, BytesFromHttp and BytesFromCacheServer. In my lab, the FileSize was 1863339050 bytes or 1.86 GB. Referencing TotalBytesDownloaded, the Office client using DO only downloaded 516967466 bytes or 517 MB because only the necessary pieces were downloaded not the entire Office build. Further, using BytesFromCacheServer I can confirm the 517 MB was downloaded from Configuration Manager connected cache, not egress to internet.
*In the example the client was N-2 plus Office was a new version which contributed to larger download.
4. [Server] Check the Configuration Manager Connected Cache disk for build.
- Browse the Connect Cache disk and explore content under officecdn.microsoft.com.edgesuite.net to find dynamically populated content for latest Monthly Enterprise Channel 16.0.13001.20520
Conclusion:
Delivery Optimization and Microsoft Connected Cache provide a powerful and low cost of ownership method for Office installations and updates using peer to peer sharing technologies.
FAQ
Are there some additional references for Delivery Optimization and its capabilities?
- Delivery Optimization reference
- Delivery Optimization: Scenarios and configuration options
- Delivery Optimization deep dive: How to reduce internet bandwidth impact on your network (Ignite 2018 presentation)
- Delivery Optimization – a deep dive (Ignite 2017 presentation)
- Delivery Optimization and Office 365 ProPlus
- Monitor Updates with Update Compliance
Are there some additional references for Configuration Manager and Connected Cache?
- Microsoft Connected Cache in Configuration Manager
- Introducing Microsoft Connected Cache: Microsoft’s cloud-managed cache solution
Where can I obtain more information about VPN and remote configuration options?
Can we use a third-party Configuration Manager alternate content provider with this solution?
No, alternate content providers typically depend on Configuration Manager software update workflow which won’t be used in scenario above.
For the UpdateDeadline GPO, how does that impact the end user experience?
Please see section “User Experience when updating from CDN” from blog posting Understanding Office 365 ProPlus Updates for IT Pros (CDN vs SCCM)
The Authors
This blog post is brought to you by @Dave Guenthner and @Martin Nothnagel, two Office Rangers at Microsoft. We’re looking forward to your questions and feedback in the comments below.
Brought to you by Dr. Ware, Microsoft Office 365 Silver Partner, Charleston SC.


Recent Comments